
设计单位 Bernard Tschumi urbanistes Architects、Groupe-6
项目地点 法国巴黎
建成时间 2022年
建筑面积 74,000平方米
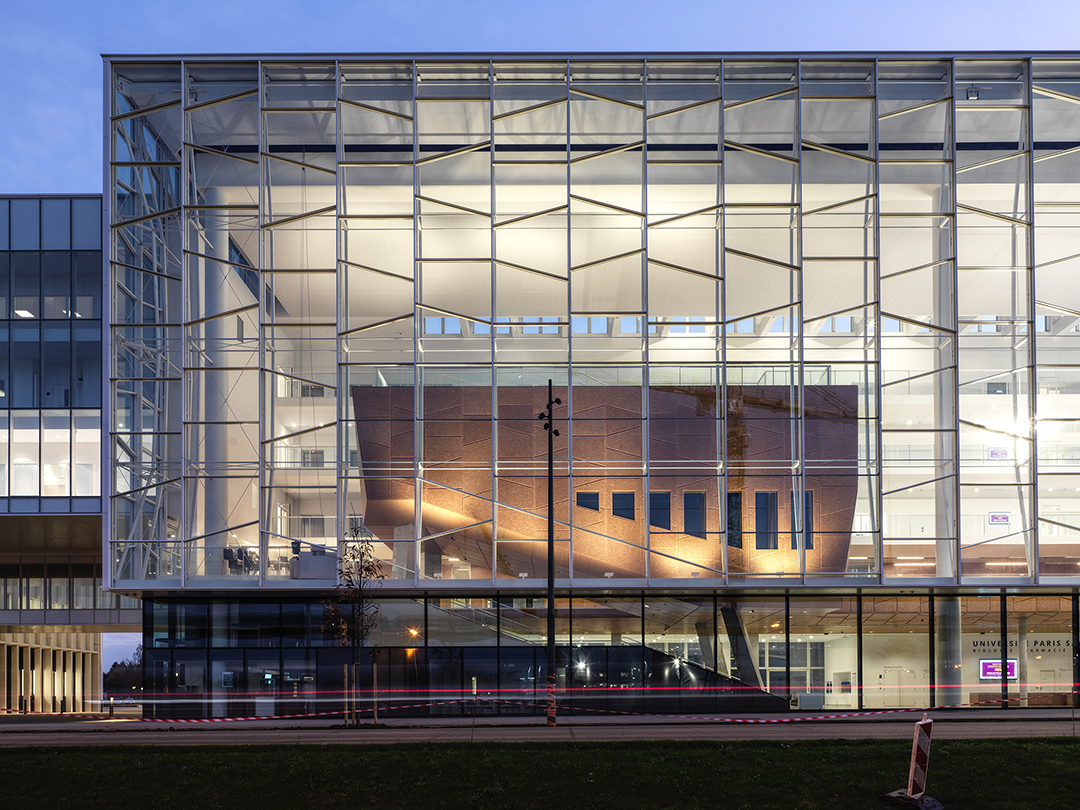
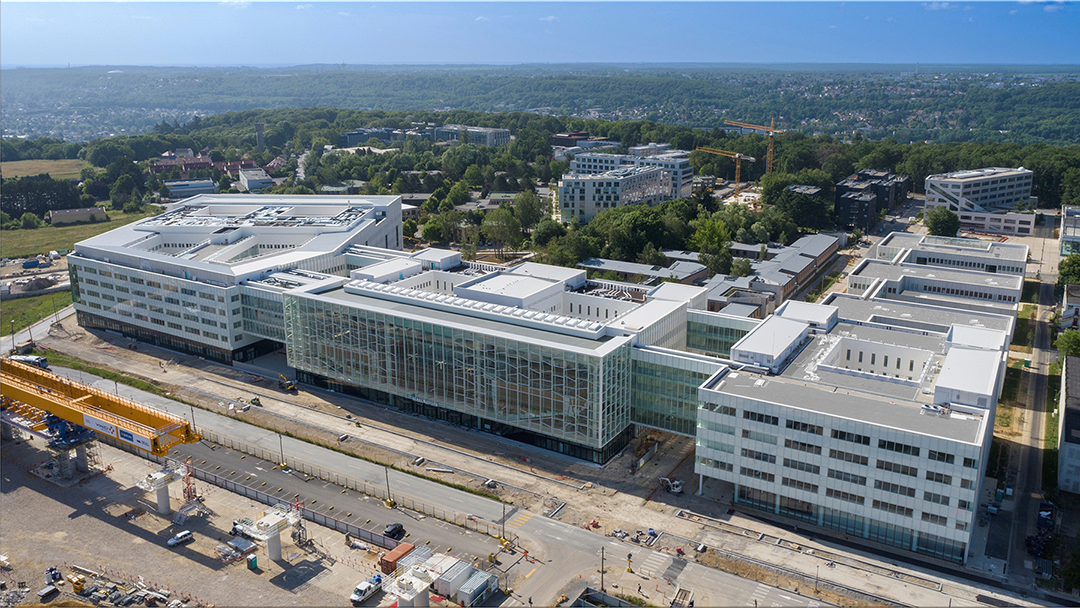
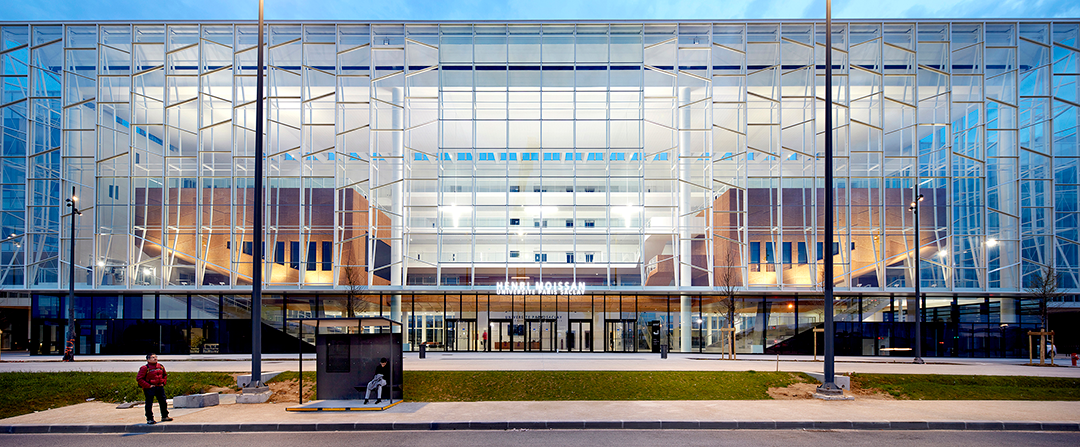
巴黎萨克雷大学新的生物-药物-化学教育研究综合体是法国最大的校园建筑之一,建筑面积7.4万平方米、耗资2.83亿欧元,将作为巴黎萨克雷大学重要的科学中心,容纳约3300名学生和1300名教师兼研究人员。项目位于新规划的“大巴黎快线”(the Grand Paris Express)的Orsay-Gif地铁站对面,将为该大学提供一个对外的校园门户,可通往其世界一流的科研设施。
Designed by Bernard Tschumi urbanistes Architects and Groupe-6, the new Biology-Pharmacy-Chemistry Research and Education Complex for the Université Paris-Saclay is one of the largest educational projects in France. The 74,000 square-meter (800,000 square-foot), €283 million complex is a major scientific center for the university. Located opposite the future Orsay-Gif Metro station on the Grand Paris Express, the building offers an outward face of the new university and the gateway to its world-class science and research facilities.
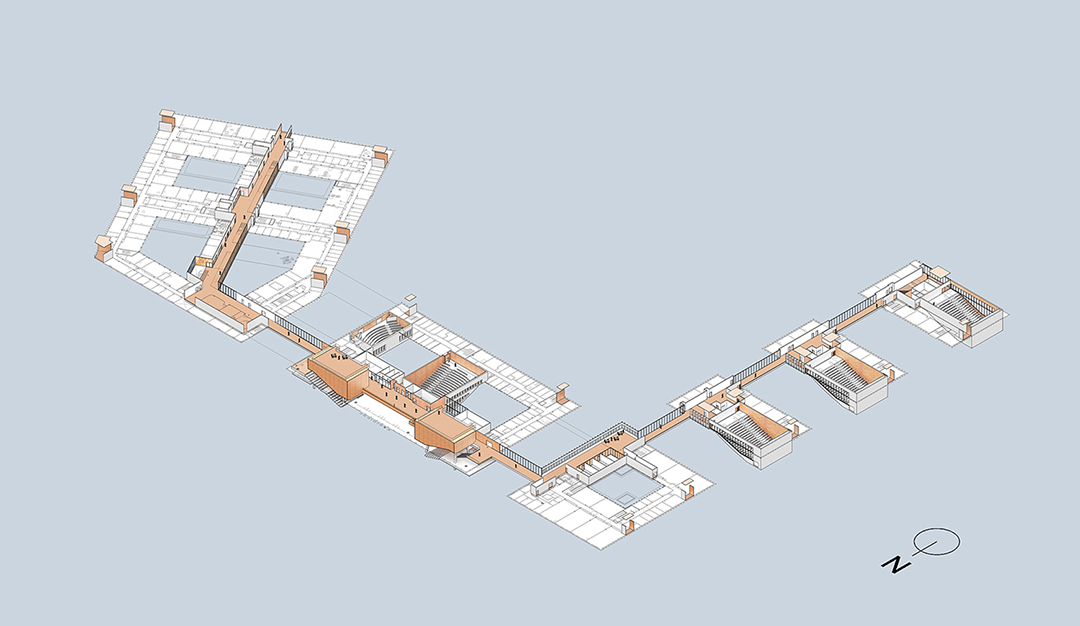
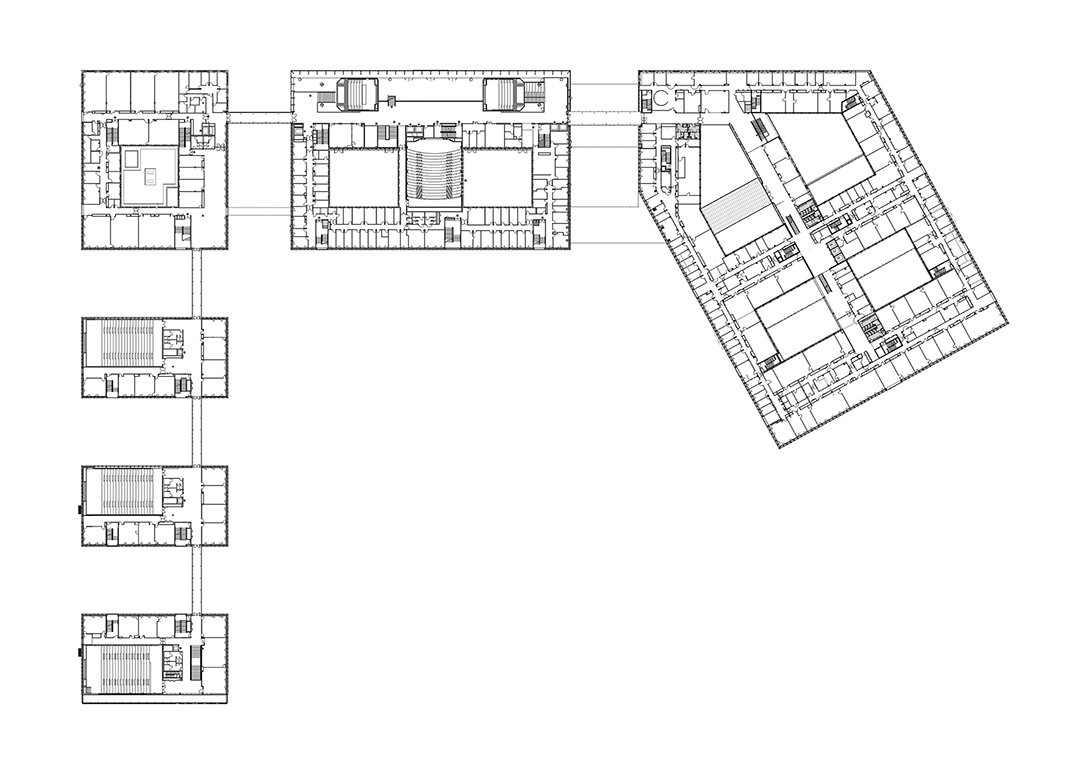
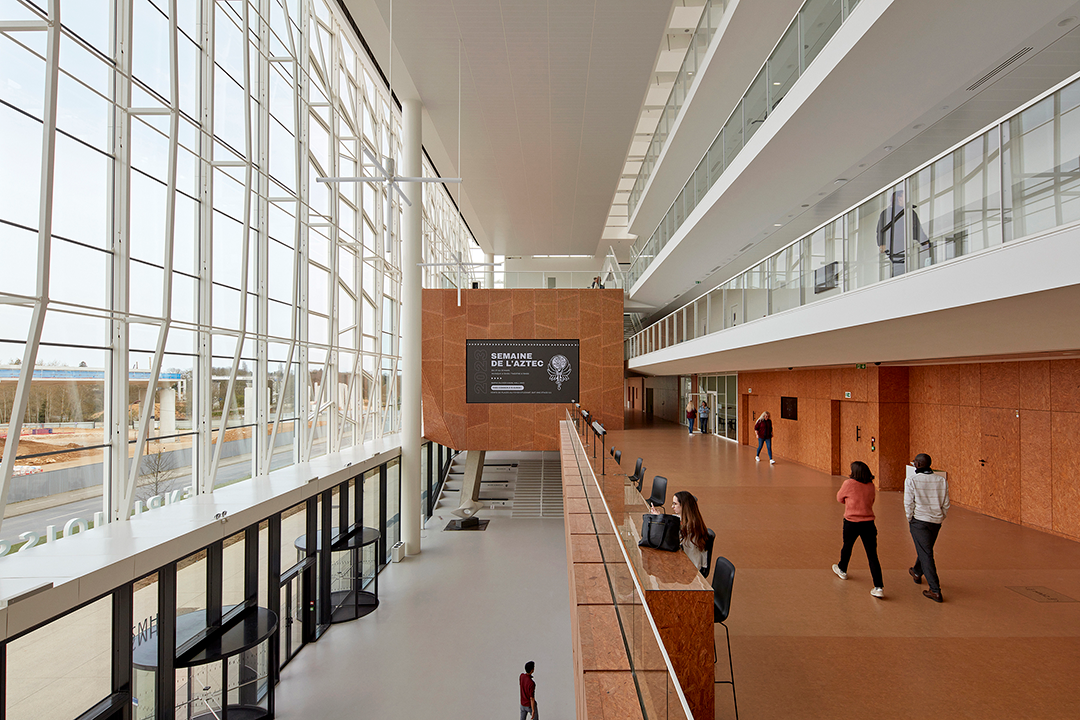
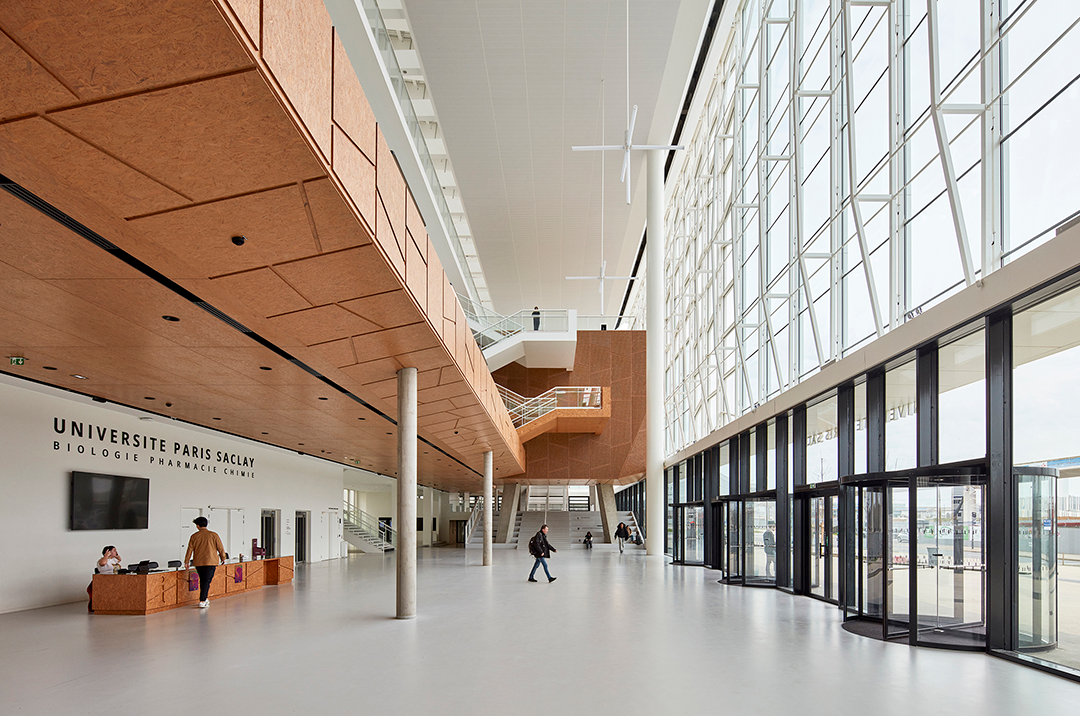
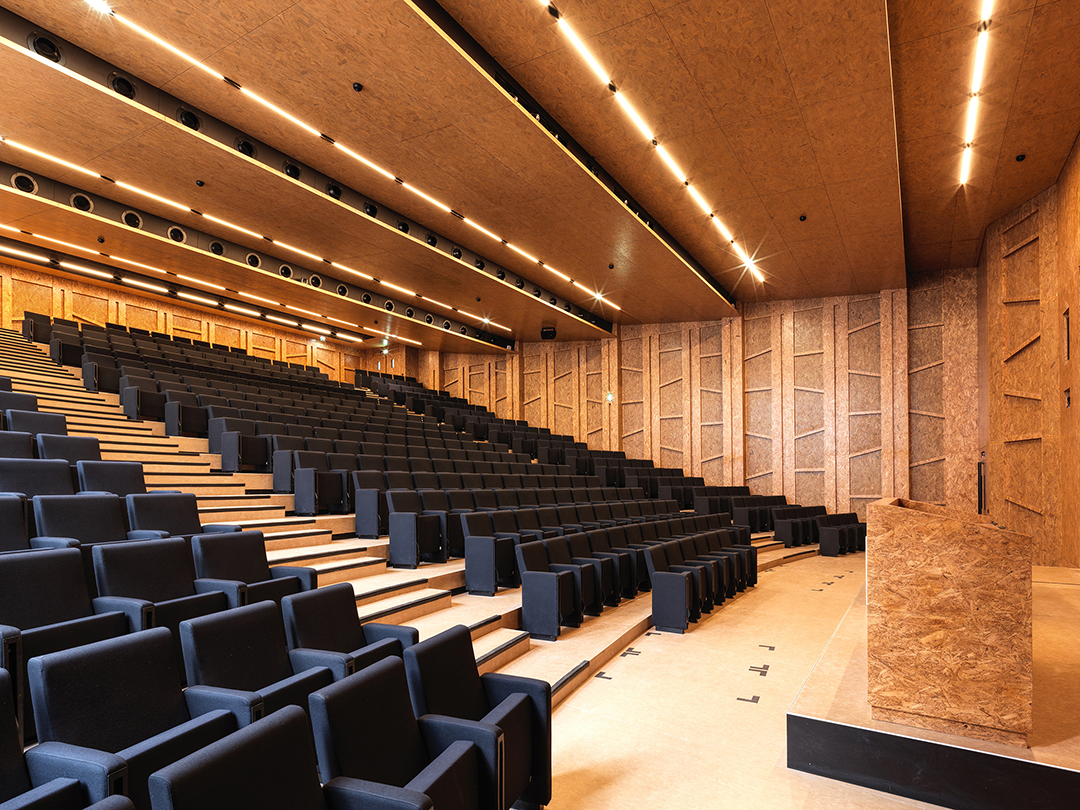
该综合体由三个主要部分组成——独立的教育、研究翼楼和将两部分连接起来的中央中庭“Cœur de Pôle”,包括研究实验室、教室及礼堂、社交空间、餐厅、办公室、后勤区和地下停车场。其中,伯纳德·屈米建筑事务所负责整个城市和建筑规划,以及中庭和教育空间设计;Groupe-6负责研究空间及其实验室和技术基础设施设计。
The complex is made up of three major components—independent educational and research wings linked by a central atrium, or “Cœur de Pôle”—and includes research laboratories, classrooms and auditoria, social spaces, restaurants, offices, logistical areas, and underground parking. Bernard Tschumi urbanistes Architectes oversaw the overall urban and architectural coordination as well as the Cœur de Pôle and teaching facilities, while Groupe-6 was responsible for the research units with their laboratories and technical infrastructure. The site will accommodate more than 4,500 people, with 3,300 students and 1,300 teacher-researchers.

—
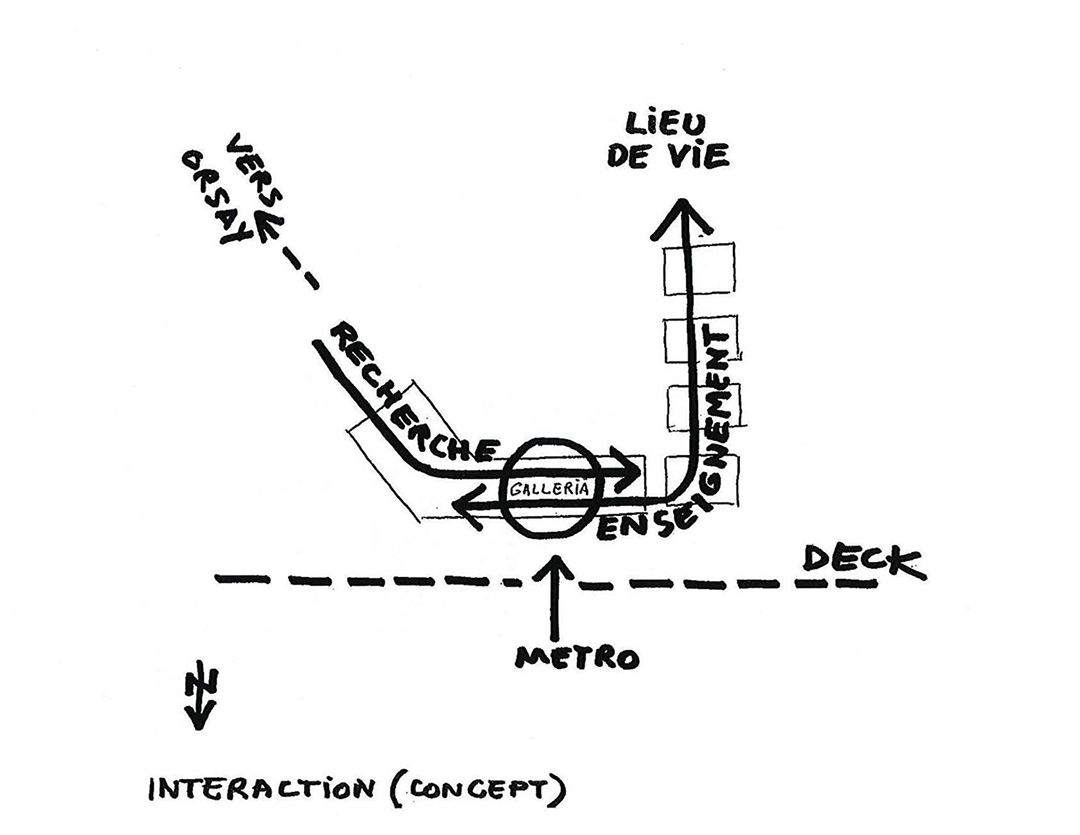
促进交流的生成器
“Cœur de Pôle”中庭是该综合体的主要入口,也是大学校园内不同人群的交汇之处。作为促进交流的场所,设计通过两条连续、清晰的内部“街道”来串联和布置空间,将研究和教育空间直接相连,鼓励科学合作,并促进生物、药学、化学等其他独立学科之间的跨学科交流。
The Cœur de Pôle is the main entry point as well as a crossroads for the different users of the university. This dynamic generator of exchange is extended through the clarity of circulation and the distribution of spaces along the two continuous internal “streets,” which encourages scientific collaboration by putting research and education in a direct relationship with each other and stimulating interdisciplinary overlaps among the otherwise separate disciplines of biology, chemistry, and pharmacy.
—
设计概念
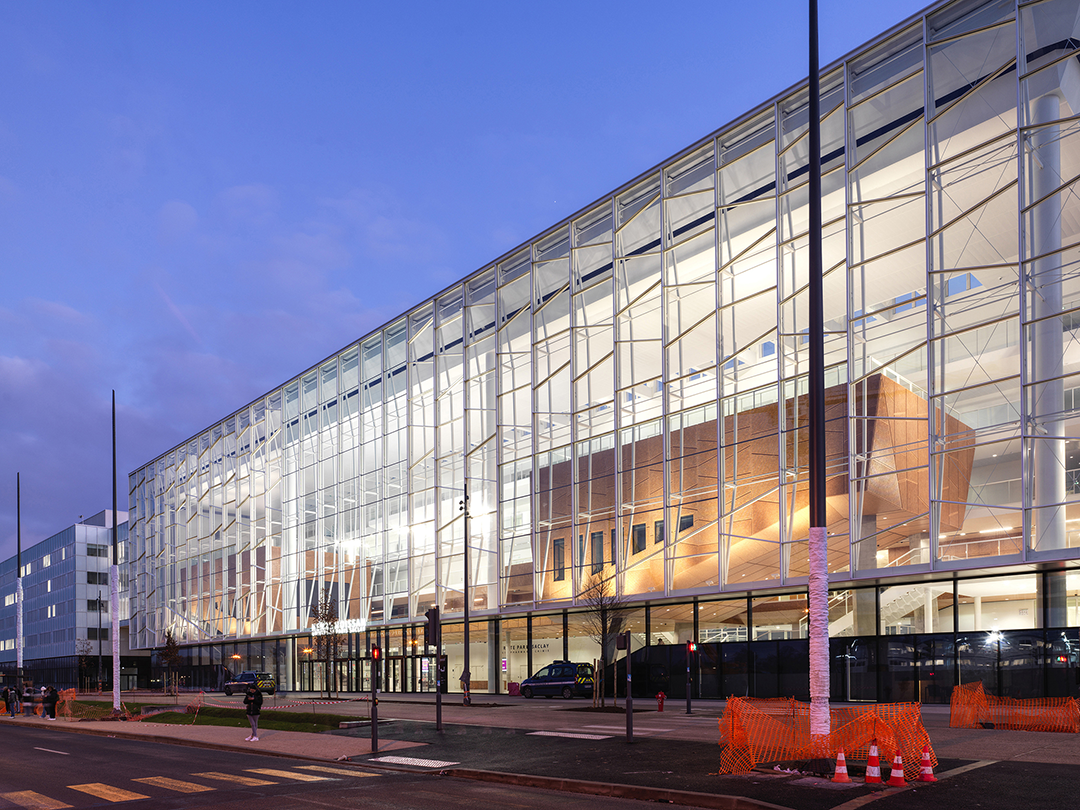
建筑和城市策略由伯纳德·屈米建筑事务所设计,该综合体由六个建筑体量组成,通过连续的“街道”和玻璃人行天桥相互连接。它横跨下方的车行道,同时形成一个近千米的主道,作为整体的统一特性。
The architectural and urban strategy, designed by Bernard Tschumi, consists of a chain of six buildings connected to each other by a continuous “street” and glazed pedestrian bridges. The complex spans the vehicular streets below while forming an elevated, nearly kilometer-long artery that serves as a common denominator for the whole.
在中心,“Cœur de Pôle”中庭连接两侧翼楼。中庭西侧、沿着Rue de l'enseignement的是教学设施和南部的场地入口,同样由伯纳德·屈米建筑事务所设计。
At its center, the atrium of the Cœur de Pôle links the two wings. To the west, along the Rue de l’Enseignement, are teaching facilities and the southern access to the site, also designed by Bernard Tschumi urbanistes Architects.
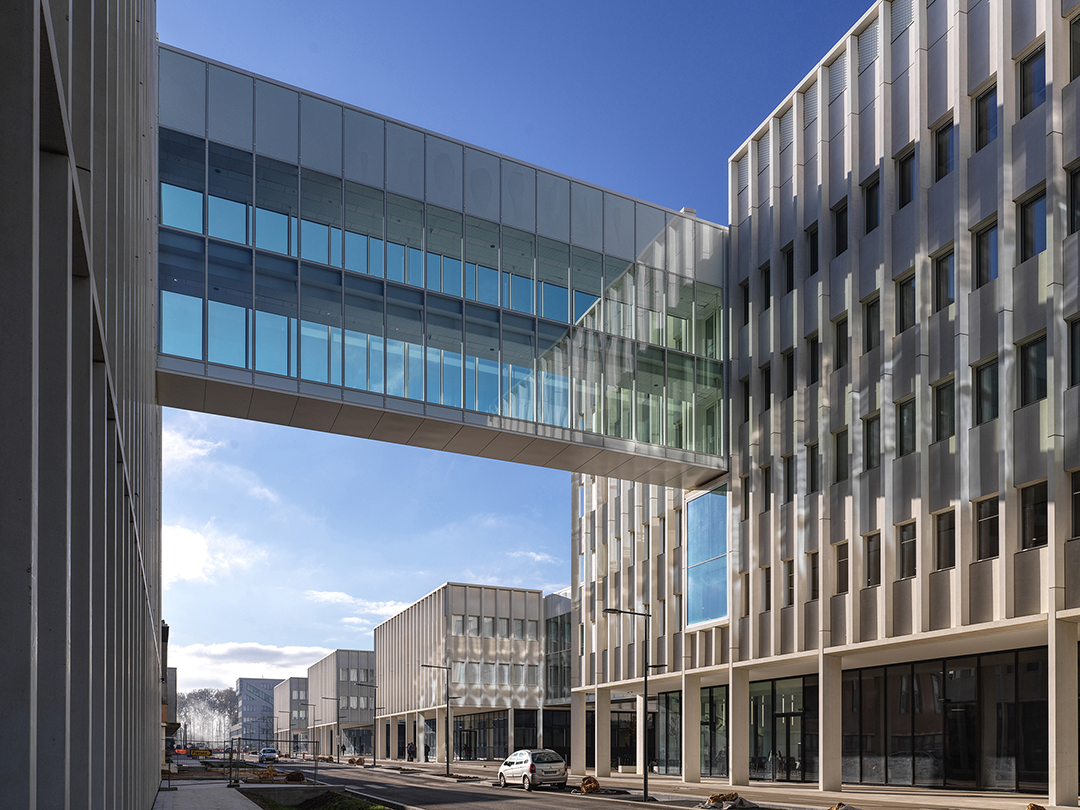


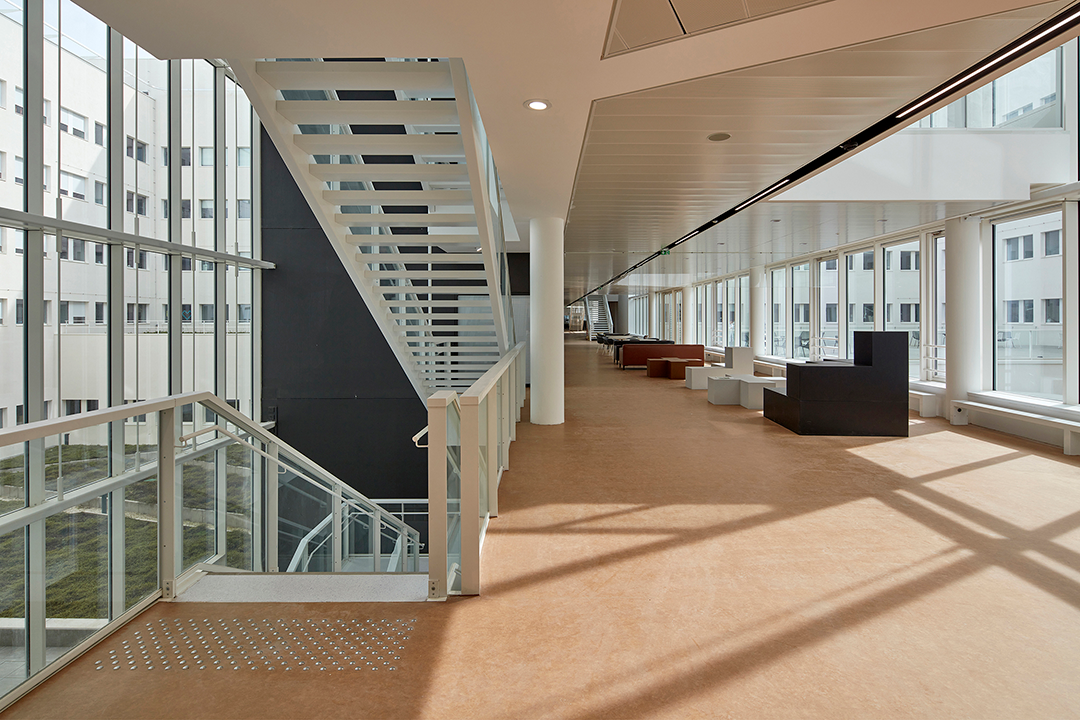
研究空间由Groupe-6设计,位于中庭东侧。它沿着Rue de la Recherche设有最先进的实验室、研究人员工作空间和会议场所。楼层之间的开口在视觉上连接了建筑体量和它的四个露台。Rue de la Recherche是24小时开放的,可以免费进入,不像实验室的入口受到严格控制。
The Research area, designed by Groupe-6, opens to the east of the atrium. The Rue de la Recherche hosts state-of-the-art laboratories, workspaces for researchers, and pleasant meeting places. The openings between floors visually connect thebuilding and its four patios. The research street is open 24 hours and free to access, unlike laboratories whose entry is strictly controlled.


—
立面、环境和材料
该项目的位置决定了其立面设计的两个原则。在北面沿着主要的校园大道一侧,立面选择了全玻璃的幕墙作为“橱窗”,可展示内部的交流和活动,而且不需要专门的防晒措施。
The urban siting of the project determined two principles for the project’s facades. To the north and along the main campus avenue, the architects chose a fully glazed façade—a “vitrine” capable of showcasing activities of exchange and encounter without requiring significant protection from sunlight.
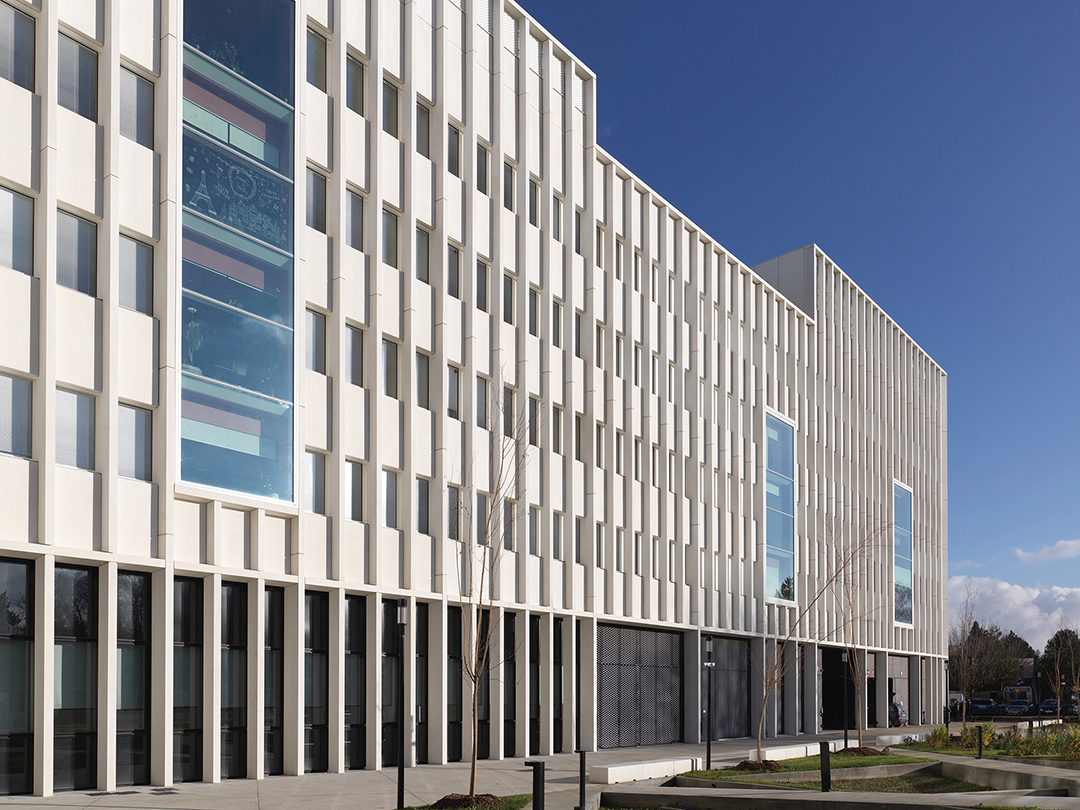
在南面、东面和西面,立面设计则选用白色预制混凝土肋将建筑的体量连接起来。结构混凝土的垂直性与大面积的玻璃表面相呼应,突出了白色立面,并反映出周边景观。
To the south, east, and west, the white precast concrete ribs articulate the building’s mass. The verticality of the structural concrete is echoed in the large glass surfaces of the windows punctuating the white facades and reflecting the surrounding landscape.

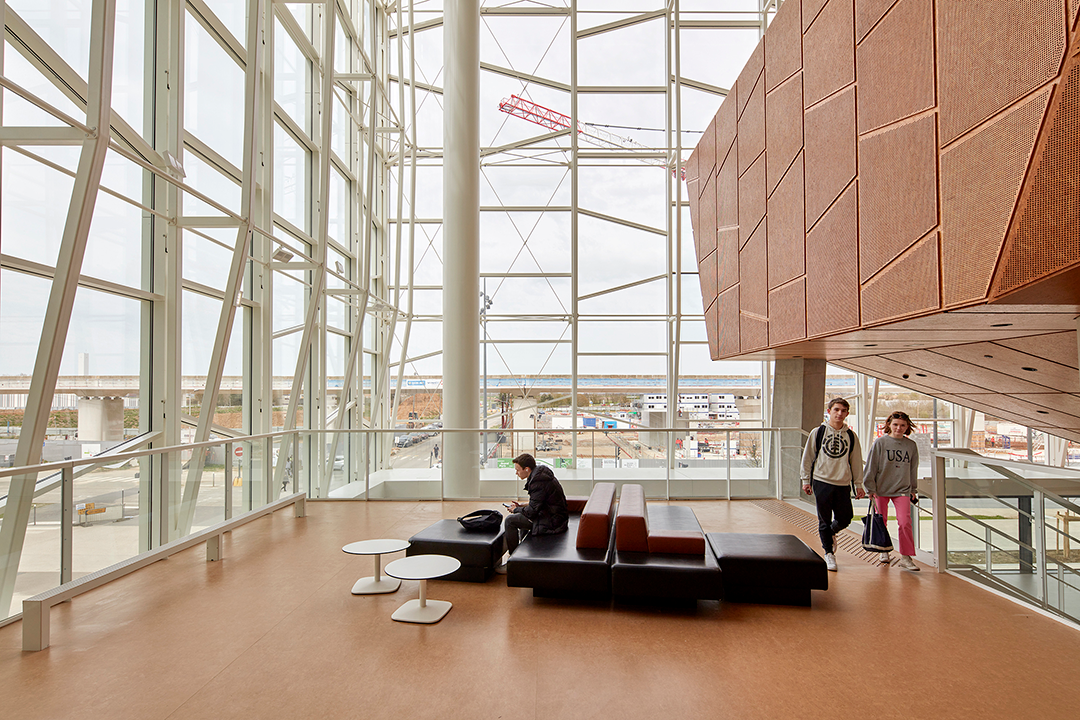
外部的玻璃、光线和白色表皮的冷静,与内部OSB穿孔隔音木板形成强烈对比。该木板应用于整个项目中,这种低成本、可持续的材料提供了内部视觉上的温暖感。
The intentionally sober expression of glass, light, and white surfaces is offset by perforated acoustic OSB wood panels that are used throughout the project to deliver visual warmth through a low-cost, sustainable material.



内部花园分散布置于整个建筑群地面层中,外部景观则包括种植药用植物的药剂师花园(Apothecary Gardens)。该综合体通过地热井与大学的能源网相连,并已被认证为符合法国绿色建筑的高质量环境标准,具有先进的能源效率水平。
Internal gardens are dispersed throughout the complex at ground level, and the external landscaping features Apothecary Gardens planted with medicinal herbs and grasses. The complex is linked to the University’s energy grid via geothermic wells and has been certified as conforming to France’s High Quality Environmental standard of green building, with an advanced level of energy efficiency.



巴黎萨克雷大学生物-药物-化学教育研究综合体
完整项目信息
SCHEDULE
Preliminary design: 2015
Competition Winner: 2018
Completion: 2022
LOCATION: Paris-Saclay, France
SIZE: 74,000m²
CLIENT AND CONTRACTING COMPANY: Paris-Saclay University / Bouygues-Construction
TEAM
Bernard Tschumi urbanistes Architectes
Architect: Bernard Tschumi
Project coordination and supervision: Véronique Descharrières, co-director and partner Bernard Tschumi urbanistes Architectes (BTuA), Paris
Competition and Schematic Design: Joel Rutten, co-director, Bernard Tschumi Architects, New York
(Cœur de Pôle and teaching spaces, Urban and architectural coordination)
Group-6
Associate architects: Alain Eyraud, Denis Bouvier
Project director: Nathalie Pierre
(Research spaces and laboratories)
PHOTOGRAPHERS: Christian Richters, Fred Delangle, Yves Chanoit
本文由伯纳德·屈米建筑事务所授权有方发布。欢迎转发,禁止以有方编辑版本转载。
上一篇:简朴舒适:巴塞罗那1737社会住宅区 / HARQUITECTES
下一篇:南方新住宅:深圳南山建工村公共住房设计公开竞赛