
设计单位 蓝天组
项目地点 河北邢台
方案状态 中标方案
建筑面积 55.000平方米
科技馆的设计在于强调邢台作为河北省科技创新、科学发展、科技教育的新焦点,其以邢台固有的科学文化根源、天文学历史发展、工程学及其他本地科学家为基础,反映中国尖端经济、生态和建筑技术,并展示中国科学发展与技术的过去、现在和未来。
The aim of the project is to emphasise Xingtais role as a scientific and technological hotspot in the province of Hebei. Building up on Xingtais history of astronomers, engineers and other scientists, the project reflects past, current and future approaches of cutting edge economic, ecologic and building technologies.
建筑将采用全新的结构概念,实践最尖端的能源系统设计,反映丰富的中国传统文化,呈现邢台、河北省与中国从古至今以至于未来的科学历史成就,以及最新科技发展与动向。
The building will be designed with new structural concepts, hosting plus energy systems and will display the rich Chinese traditional culture, showcasing scientific and technological achievements the city, the province and china has offer.
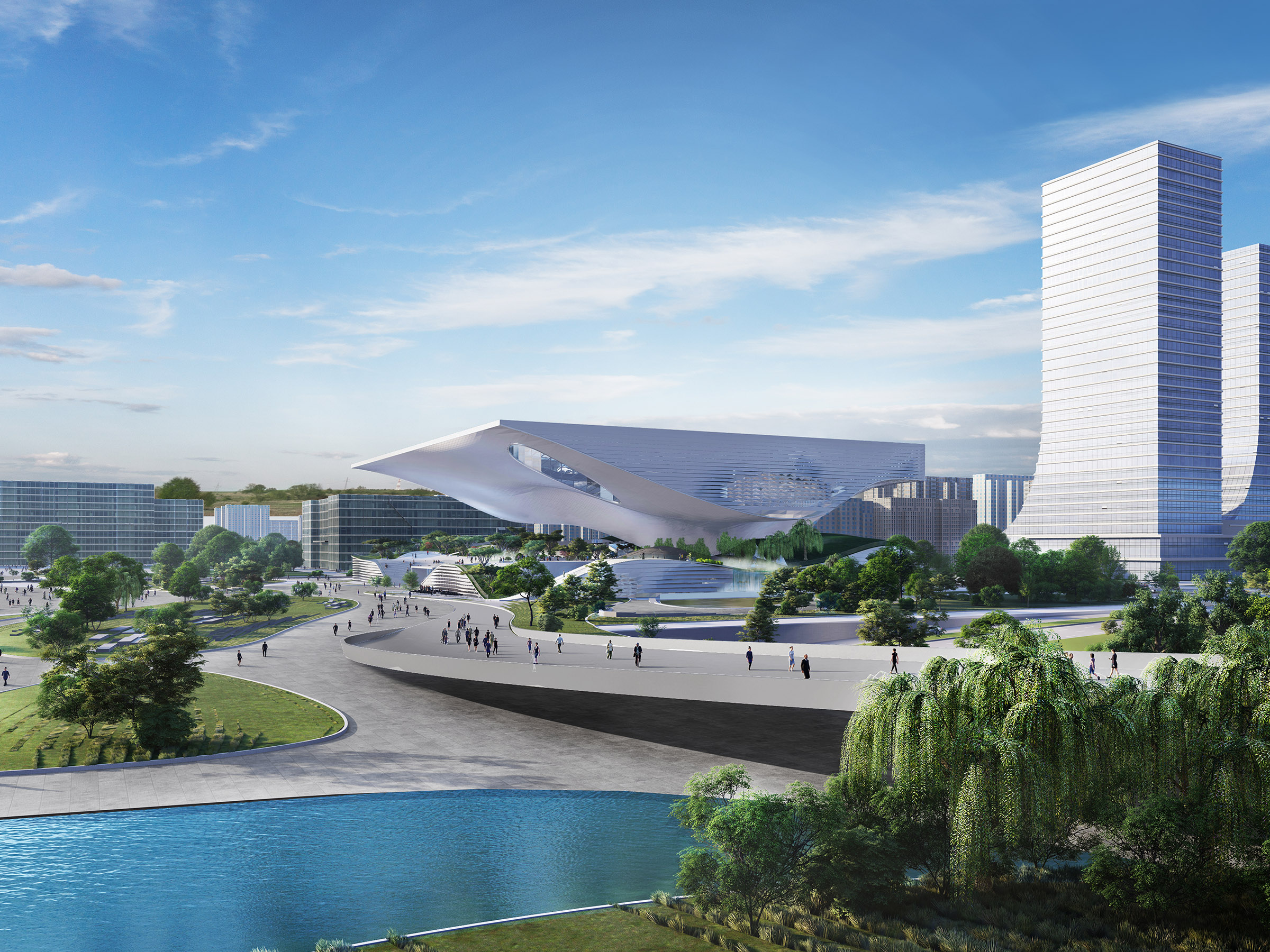

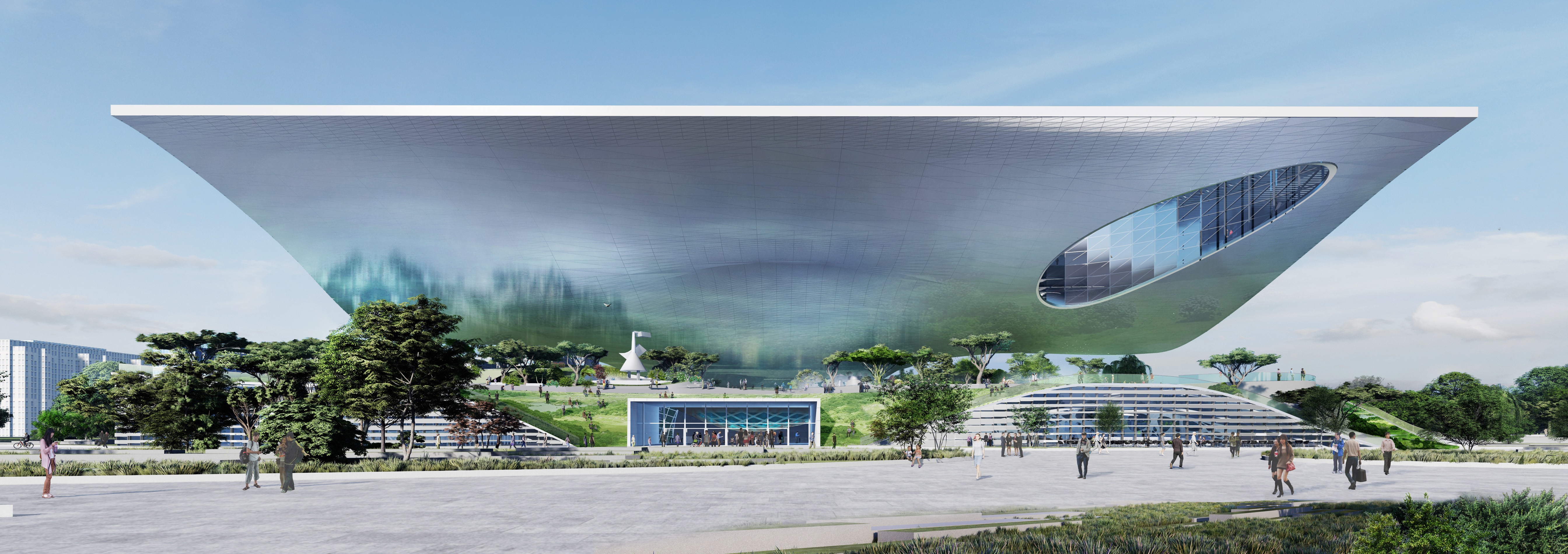
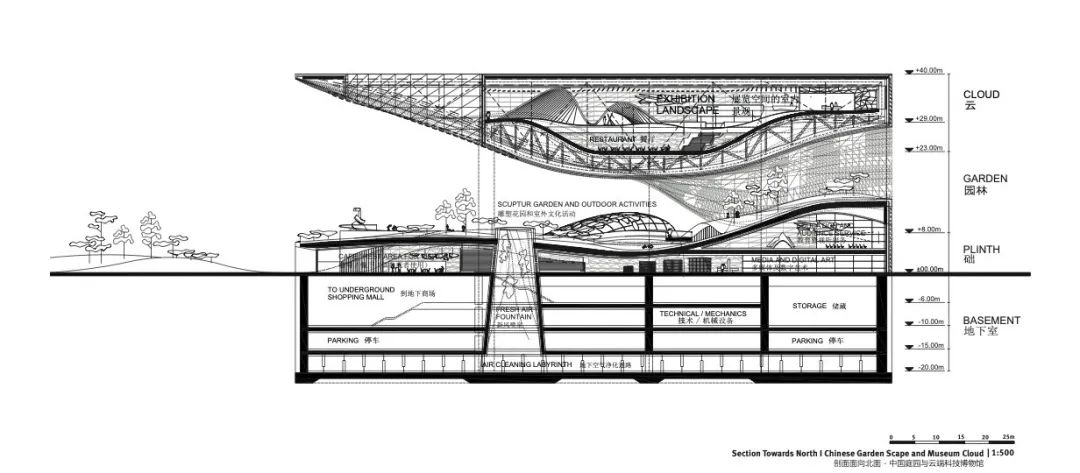
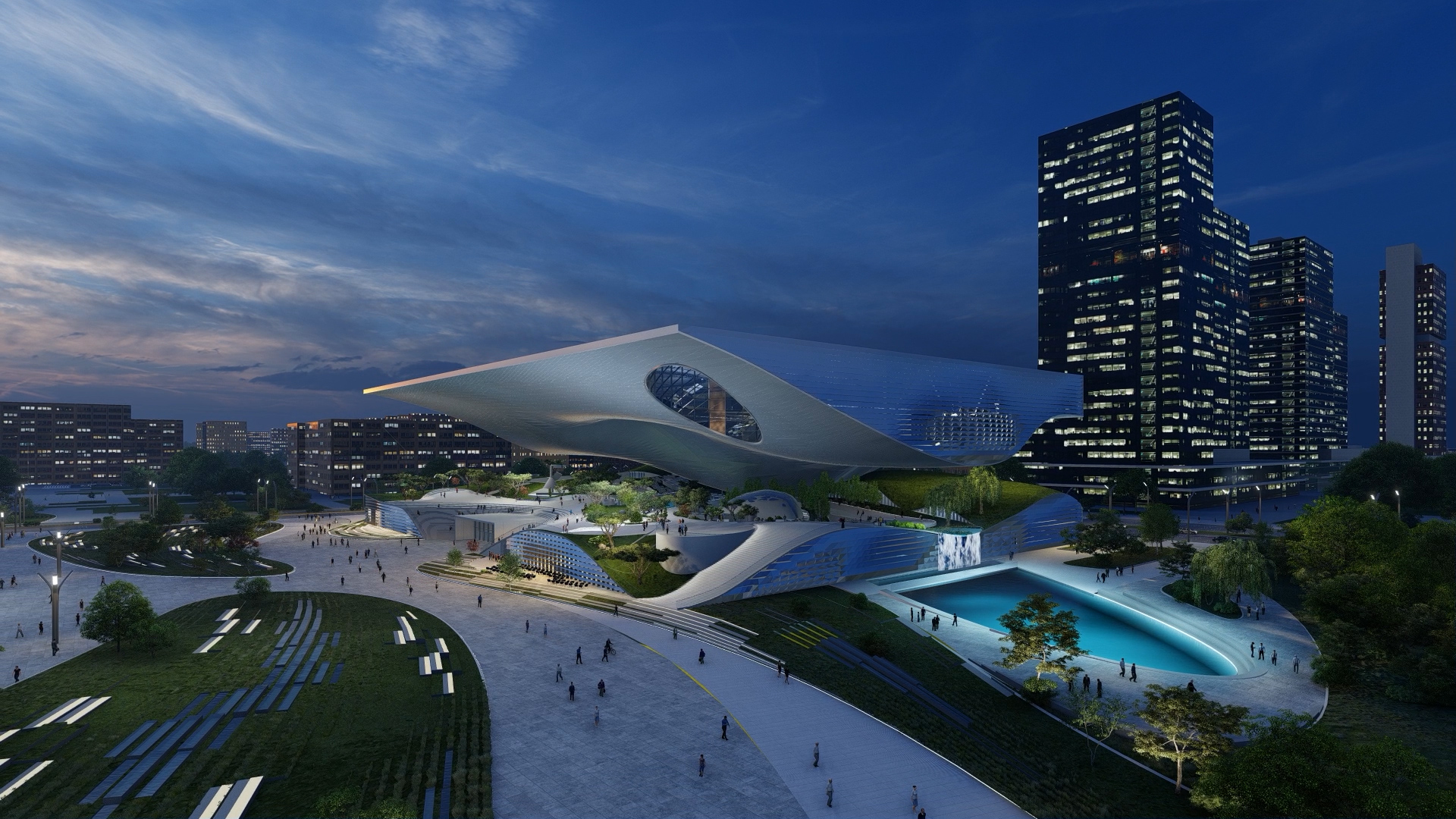
科技馆长120米,宽160米,高40米,建筑主体包括一个基座和一个呼之欲出的屋顶结构,主要展览空间就分布于屋顶内部。从不同层面来观赏,不管是结构、形式还是建筑自身的空间组织,皆如行云流水、挥洒自如,一切尽在无尽的变化之中。这座建筑自身蕴含着理性的设计方法,而其结构的复杂性则是对中国科技发展动态的思考和诠释。
The new Science and Technology Museum in Xingtai reaches a length of 120 m with a width of 160 m and a height of 40 m. It consists of a plinth building and a great flying roof which houses the main exhibition spaces. You can read it in every level, in the structure, in the way we organized it, everything is flowing - everything is moving so to say. I would like to explain the project on hand of sketches, not talking too much but illustrating the ideas by drawing it with hand. The building itself – is a scientific approach as well – because of its very complex structure, we need to show the dynamic of the scientific development in China.
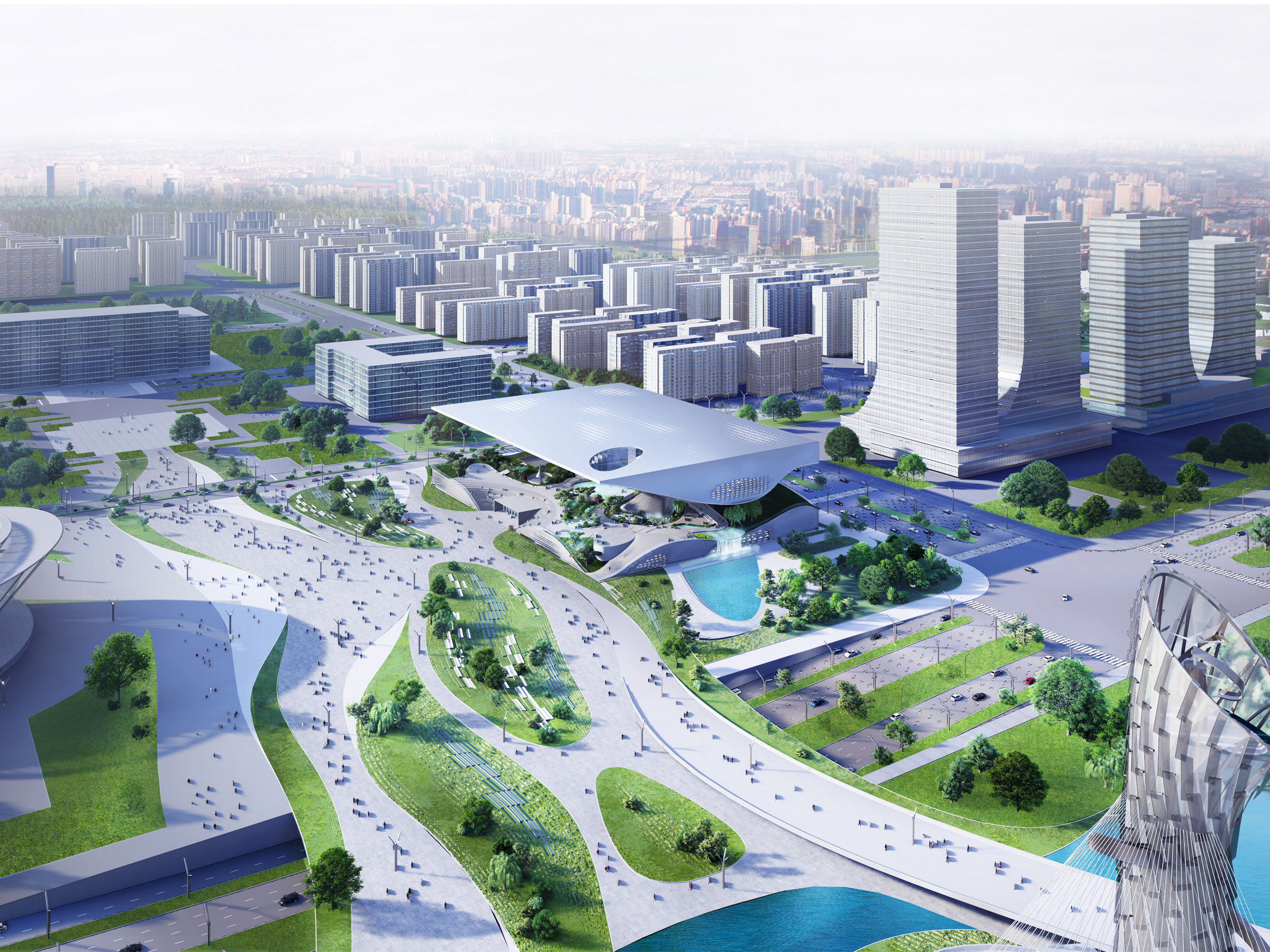


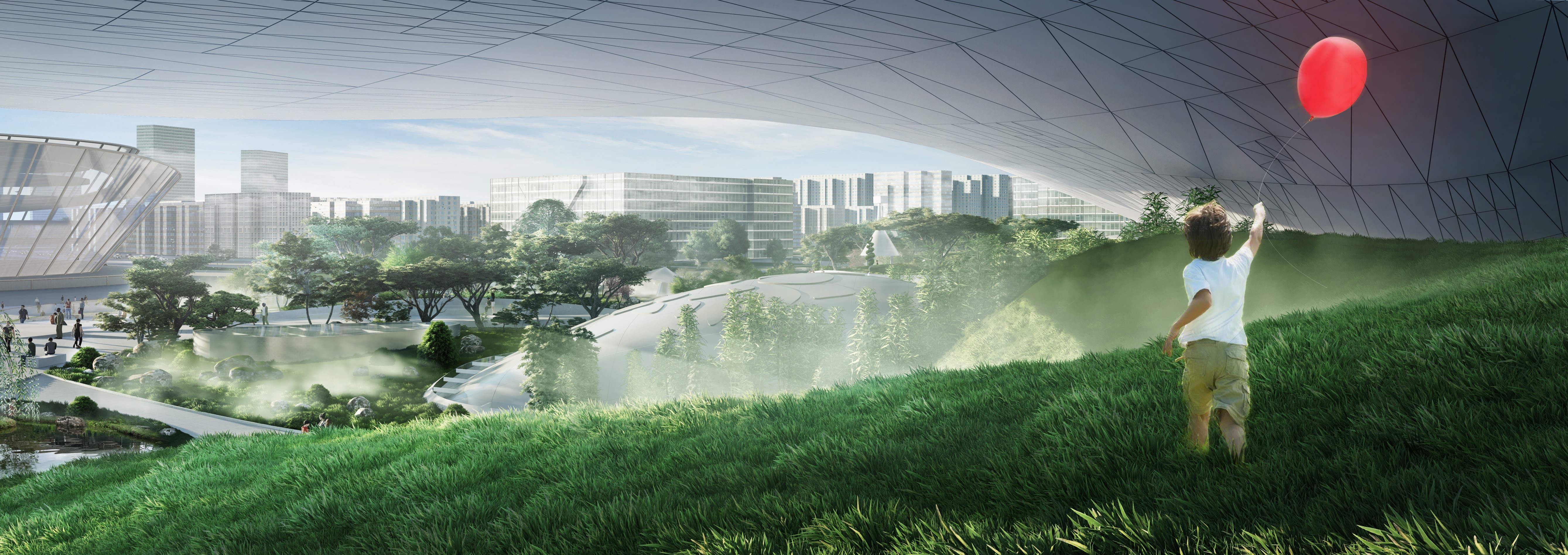
项目中有三处最为核心的构造设计:屋顶下方持续供给新鲜空气的绿色公共空间;屋顶结构的创新设计;以及与科技馆相毗邻、植入邢台市中央生态公园(园博园)的两座生态采风塔楼。塔楼将有助于雾霾的吸收与净化,新鲜的空气将在科技馆内的景观园林中释放,从而持续营造更为便捷、健康的公共空间。
The three major architectural interventions are: The green fresh air public space below the roof. The roof a an experiment in terms of construction and the third thing are two towers which are placed close to the building in the park, where the smog air is cleaned and the fresh air will come up through the landscape and create a very convenient and very healthy zone there.
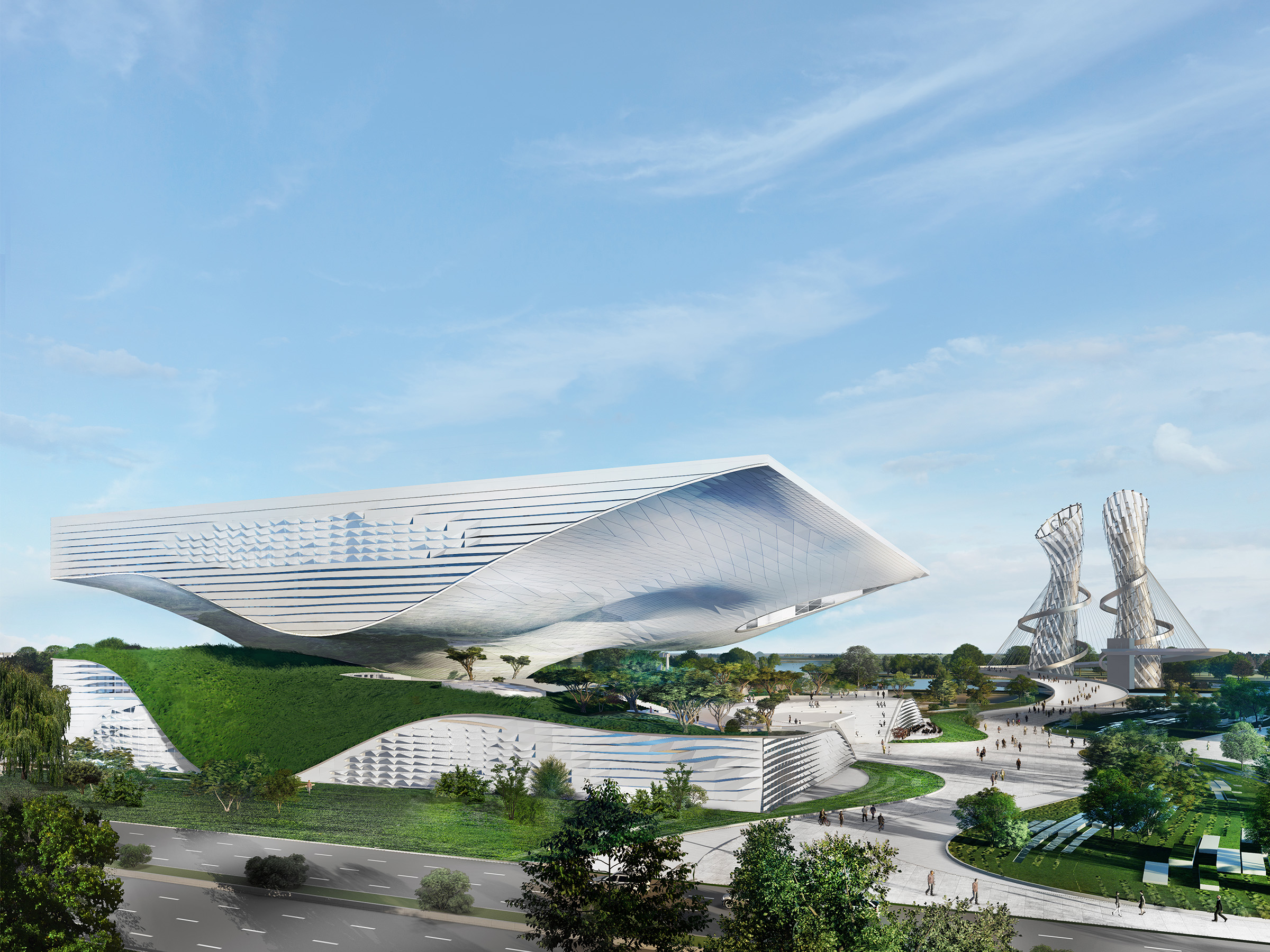

建筑顶部是一处由大屋檐覆盖的公共空间,这里设置了多种功能;而景观下方的下沉空间内,则分布了众多重要科学文教设施,以及影剧院、礼堂及视听空间等。基座由钢质的梁柱结构构成,覆盖轻质混凝土板,内设大礼堂、公共服务及必要的辅助空间,最大跨度约为12米。
By putting a lot of functions into the roof, creates a covered public space below the roof and in the pit of the landscape there some very important learning structures, cinemas and Auditorium Space.The space framework of the wide spanning roof follows the geometry of the outer hull. The base plinth structure is a steel column and beam construction with lightweight concrete slab covering which houses the auditorium, public service rooms and support spaces. The maximum span is approximately 12m.


顶部大空间的结构体系遵循其外部几何形体的形态。大跨度悬挑屋顶由24米见方的网格式桁架结构构成,并依据建筑成本估算进行了合理的优化。上部展览空间坐落于巨型桁架结构内部,由中、下部桁架结构共同支撑。垂直结构构件和对角线结构构件将中、上部桁架结构紧密相连,从而构筑了大型开放式展览空间。
The large cantilevering roof is composed of a mega truss structure with a 24 by 24m grid, which is optimized in regards to building costs and efficiency. The upper exhibition sits within the mega truss structure supported by the lower and intermediate truss structure. Vertical and diagonal members connect from the intermediate beams to the mega truss upper girder allowing for a large open exhibition space.

屋顶由位于建筑结构后部的钢筋混凝土核心筒支撑。核心筒将主要的垂直与水平荷载传递到地面之上。如有必要,可在结构中额外增加一至三个巨型立柱,立柱底部可使用剪力墙。这种方式可以减少屋顶结构的用钢量,从而对屋顶结构进行瘦身。两种结构设计概念皆充分考虑了垂直荷载及由风力和地震引起的水平荷载,以确保建筑的安全和舒适。
The roof is supported by the reinforced concrete core towards the back of the structure. The concrete core transfers the main vertical and horizontal loads towards the ground. There are additional variations to also include either one, two or three additional mega vertical columns with shear walls at their base. This allows for a reduction in the steel weight and profiles in the roof structure. Each version is designed for vertical and especially horizontal forces due to wind and earthquake to provide safety and comfort.

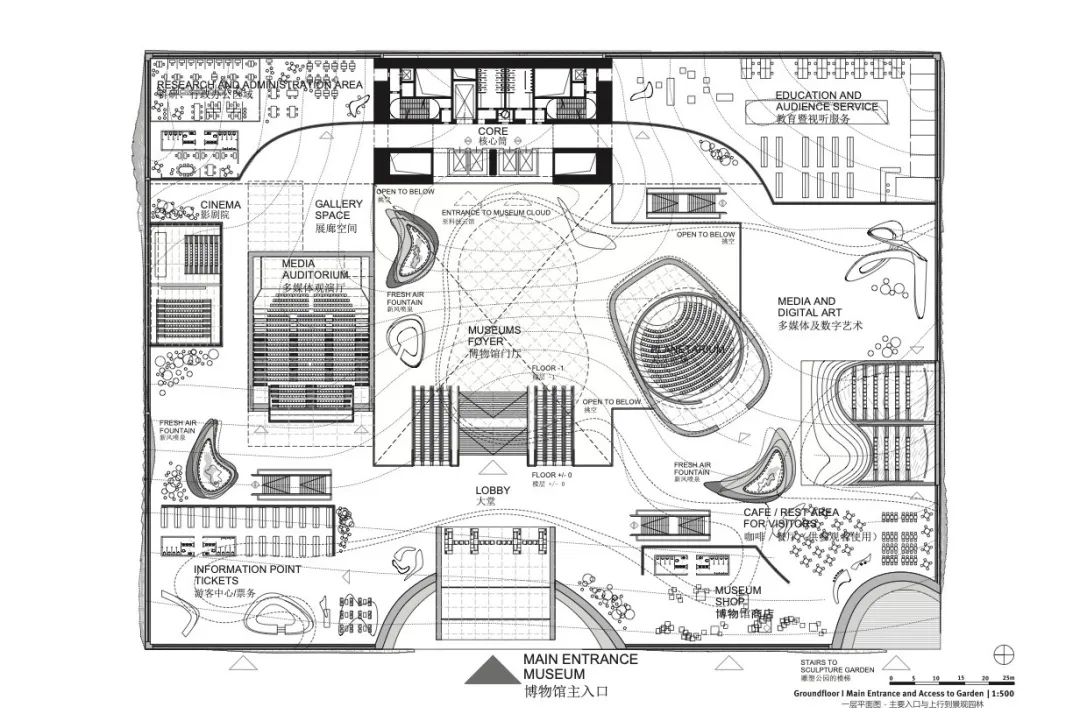
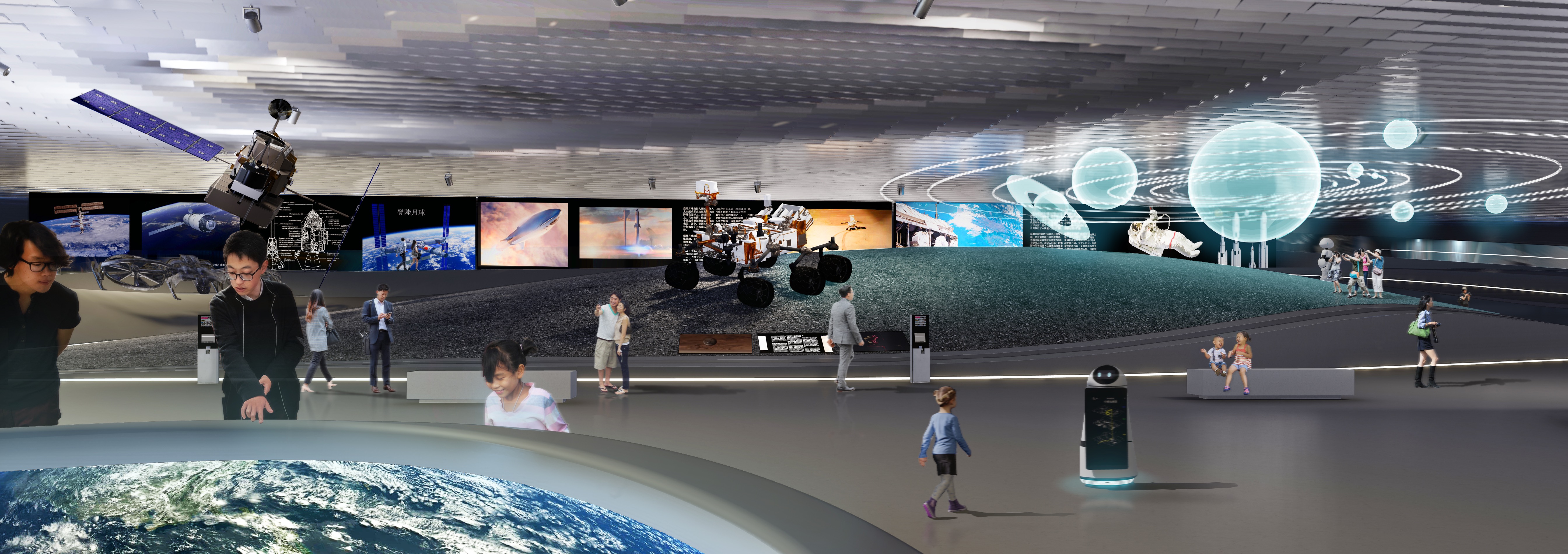
建筑的顶部是一个大尺度的展览空间,其景观师法自然,空间内部设置了一系列适用于各种互动性活动的展示空间。自公共景观处下行,会依次看到若干视听空间、影剧院和多功能厅,在这里,参观者可以根据自己的兴趣和时间进行选择,自由观看各种科学类影视短片;可以自己动手触摸、感受这里的模型;也可以借助虚拟现实装置,窥视科学发展的未来。
On top there is a big exhibition space, like a landscape where many interactive event spaces could take place. You coming to this landscape, going down and there will be a lot of Auditorium and cinemas, where people can see movies about the experiments.And on top there will be green. Green which produces a lot of good air.I would like to lift the secret of the inside of this building. You can see that roof here. So when people come up they can play around with all the models you can see. They can look through the glasses of virtual reality in to the next step of the development of science.

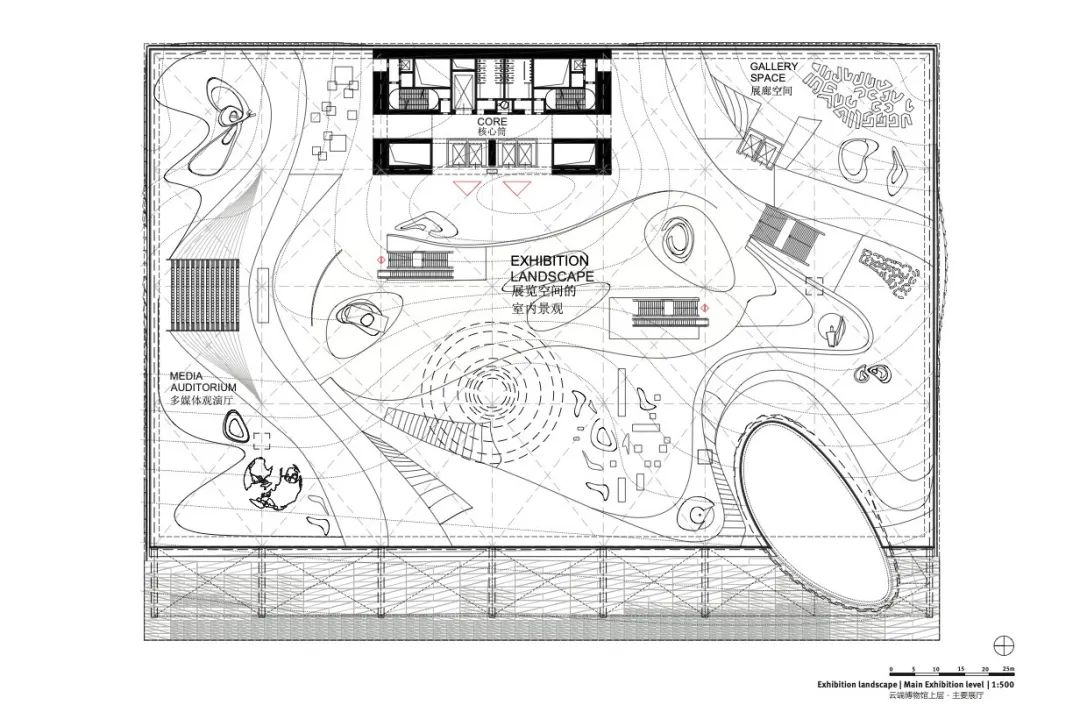
在这座建筑中行走的体验,如同穿越一座三维的中国园林,不同的区域分别由其具体功能所决定。这里的空间和区域主要用于各种科教活动,参观者可以在这里了解科学、学术前沿发展的最新动向;其上方设有更多的试验性活动空间,参观者可以与展示空间中的模型装置进行互动。
So the ways through the building is like a three-dimensional Chinese garden, where zones are differentiated by the content. Meaning that their spaces and zones - which are educational – where people can learn what is going on in science, and on top there a more the experimental event spaces, where people can interact with the models they can see.

科技馆的设计旨在为参观者及员工提供最优的空间气候环境。被动与主动式气候控制策略相结合的模式,最大限度地减少了科技馆对能源的需求。设计远不满足于传统的低能耗的节能设计,而是希望能够突破建筑自身边界的制约,改善建筑周边的城市空间气候小环境。
The new Science and Technology Museum in Xingtai is designed to provide optimal environmental conditions for visitors and staff while minimizing energy demand via a combination of passive and active climate control strategies. The buildings design is however far more ambitious than conventional low-energy design. The aim is to go beyond the boundaries of the building itself and improve the urban microclimate in the immediate surroundings.

设计充分体现了这样的理念——一座单体建筑可以且必须成为其所在城市的有机组成部分。团队在设计中尝试了可以用于捕捉当地主导季风的“采风塔”。风能与低压轴流风机相结合,促使空气穿过由空气清新器和低压空气过滤体系构成的地下空气净化系统。空气经由地面蓄热供暖系统清洁、升温后,通过“气流喷泉”进入由科技馆主体建筑围合的露天公共区域,为该区域提供清新的空气和宜人的气候小环境。
In this way, the design demonstrates the contribution which individual buildings can and must make to the city as a whole. To this end, the design employs “Wind Towers”, which are used to capture the prevailing winds. These employ wind energy in combination with low pressure axial fans to cause the air to flow through an underground air-cleaning system, comprising air washers and a low-pressure air filtration system. After the air is cleaned and tempered by the thermal mass of the ground, it enters the open-air public space created within the building volume through the “Air Fountain”, providing the urban area with clean air and a pleasant microclimate.
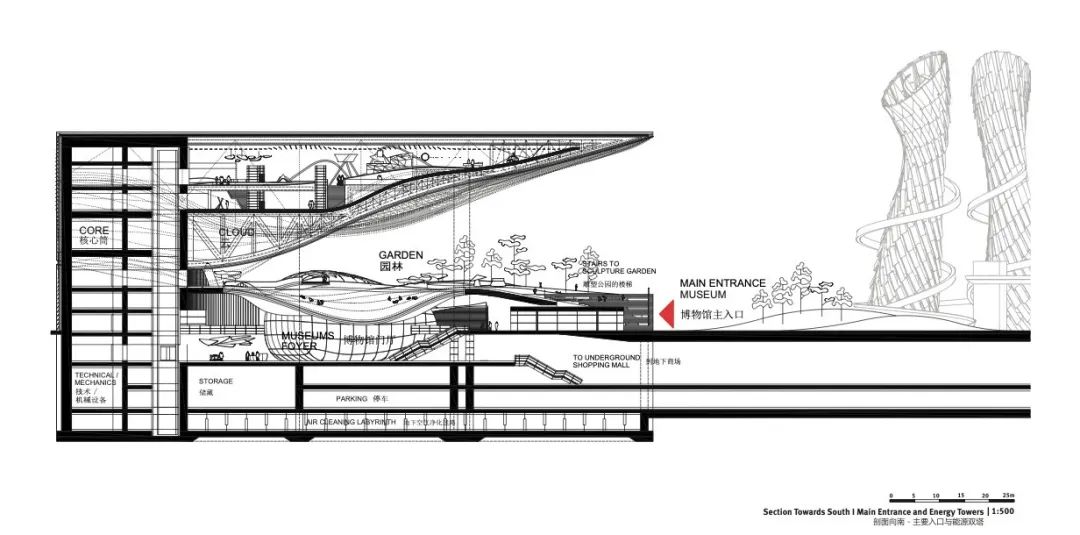
建筑顶面的雨水经收集后亦用于空气净化过程。空气净化系统所需的能量完全来源于再生能源,除了风能,还包括由集成在建筑顶面的光伏电池模块所产生的太阳能。上述节能体系是邢台科技馆展览概念的重要组成部分。而“生态采风塔”外表皮上整合的集成媒体系统,将实时向邢台市民通告空气净化过程的动态现状。
Rainwater from the roof is collected and used in the air-cleaning process. The energy required to power this air-cleaning system is provided entirely by renewable energy sources; alongside wind energy, solar electrical energy is generated by photovoltaic modules integrated into the buildings roof surface. These systems are an integral part of the exhibition concept of the new Science and Technology Museum. Integrated media systems in the external surfaces of the wind towers inform the public of the
current status of the air-cleaning process.
科技馆的内部空间完全由变风量空调系统(VAV)进行调控。制冷荷载取决于建筑内部的人流量,因此室内人员的活动量化地决定了需要提供的新风量,基于荷载的节能设计为建筑节能提供了巨大的潜力。
The museum spaces in the building itself are conditioned by all-air VAV (variable air volume) systems. People are a major contributor to the space cooling loads and also determine the amount of fresh air to be provided, so that the load dependent reductions in supply volume possible with a variable volume system provide a large energy saving potential.

完整项目信息
场地面积:69.400平方米
建筑面积:55.000平方米
建筑高度:40米
建筑尺度:120x60米
设计年份:2019年
规划:COOP HIMMELB(L)AU Wolf D. Prix & Partner ZT GmbH|蓝天组沃尔夫·狄·普瑞克斯及其合伙人有限责任公司
主创建筑师:Wolf dPrix|沃尔夫·狄·普瑞克斯
合伙人:Markus Prossnigg
项目团队负责人:Alexander Ott, Benjamin Schmidt
项目统筹:Lei Feng
设计团队:Yichen Lu, Shir Katz, Leonard Kern, Diana Kalimullina, Harry Varnavas, Daniel Bolojan, Paul Biernat
模型制作:Nam La Chi, Irem Coskun, Christos Grapas, Thanasis Farangas, Zarah-Fey La
3D 可视化:Constantin Papachrisotpoulos, Tudor Sabau
动画制作:Jan Rancke
平面制作:Johannes Qiu
结构工程师:B+G Ingenieure, Bollinger und Grohmann Gmbh Vienna, Austria
空气质量顾问:CMb.industries GmbH, Linz, Austria
ATMOS Aerosol Research
能源设计顾问:Energy Design Cody Consulting GmbH, Graz, Austria,
客户:邢台市政府
本文由蓝天组授权有方发布。欢迎转发,禁止以有方编辑版本转载。
上一篇:竞赛第一名方案 | 深圳八卦岭产业园城市更新:流转的立面曲线 / Aedas
下一篇:罗杰斯事务所,首尔综合体项目首秀:Parc.1