
设计单位 密歇根大学陶布曼学院ADR实验室
项目地点 美国密歇根州
建成时间 2021年10月
建筑面积 43平方米
RFS(Robotically Fabricated Structure)是一个基于机械臂建造的木制展亭,它使用了定制算法进行设计,并运用先进的人机协作方式进行建造,力求以可靠及精准的方法,探索可持续低碳建筑的未来。
RFS is a robotically fabricated timber pavilion that explores responsible and precise methods contributing to sustainable and low-carbon construction outlooks. This structure is designed with the help of custom algorithms developed specifically for this project and built through state-of-the-art human-robot collaborative construction.
▲ 项目视频 ©ADR Laboratory
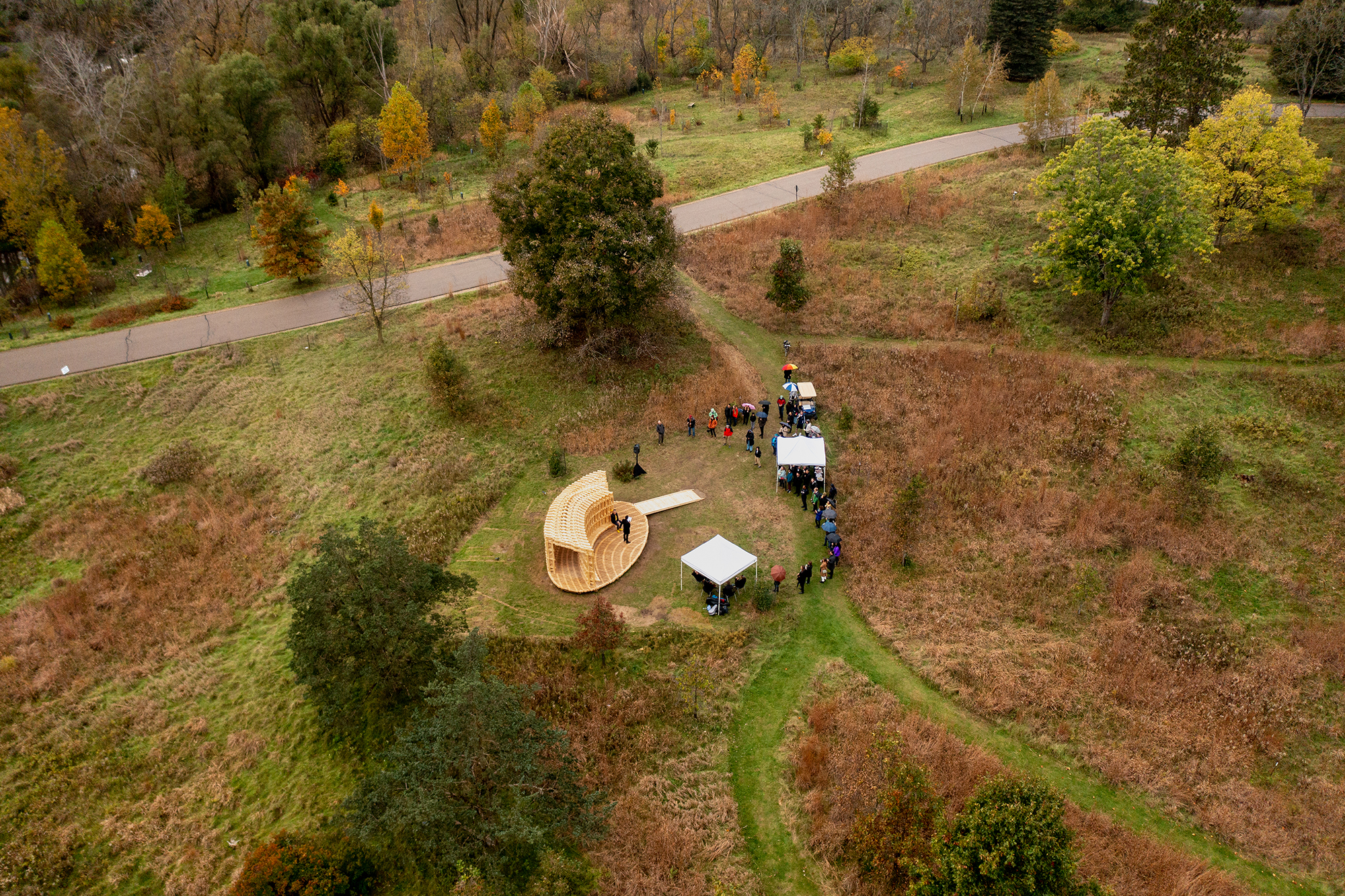
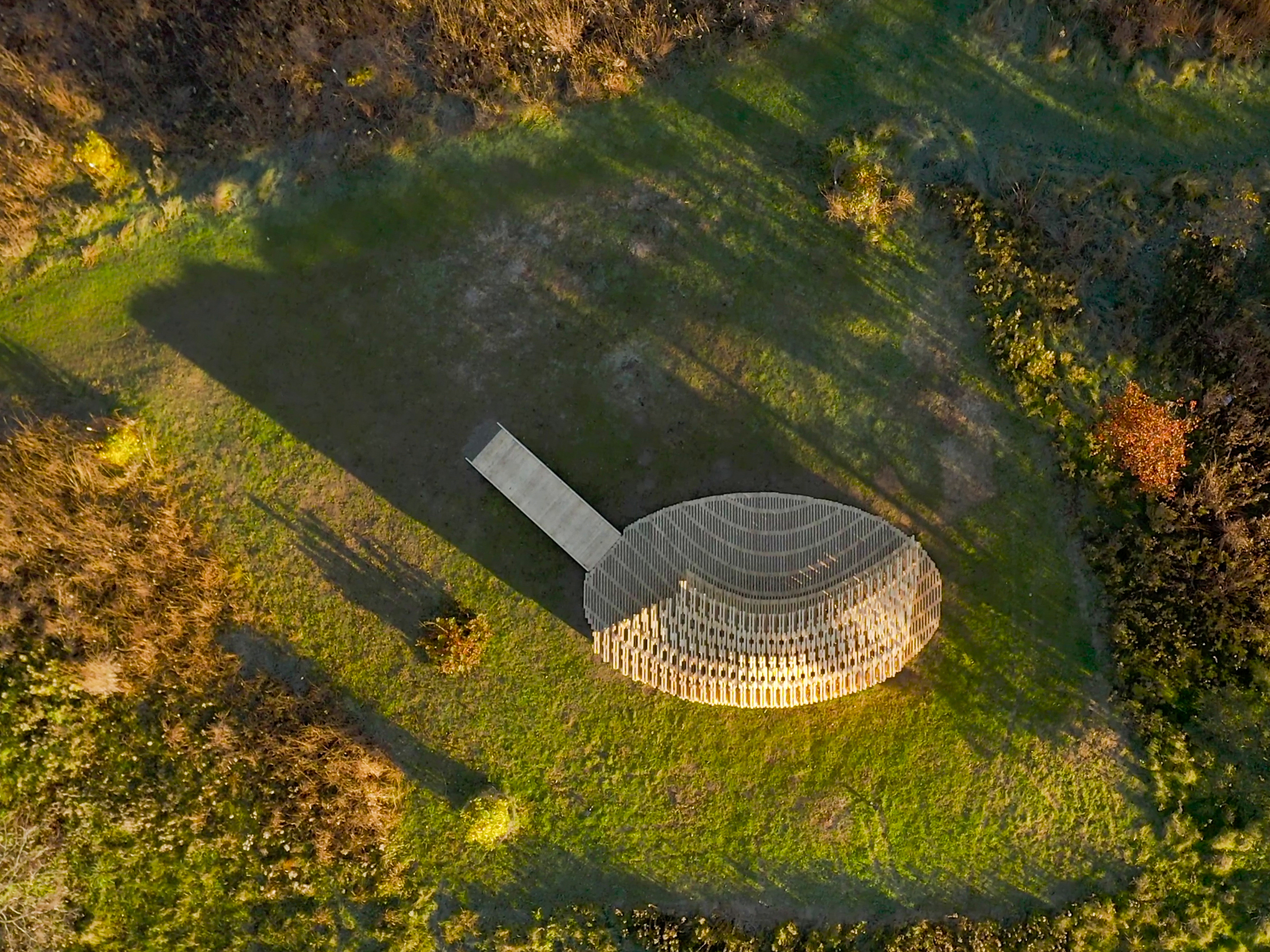


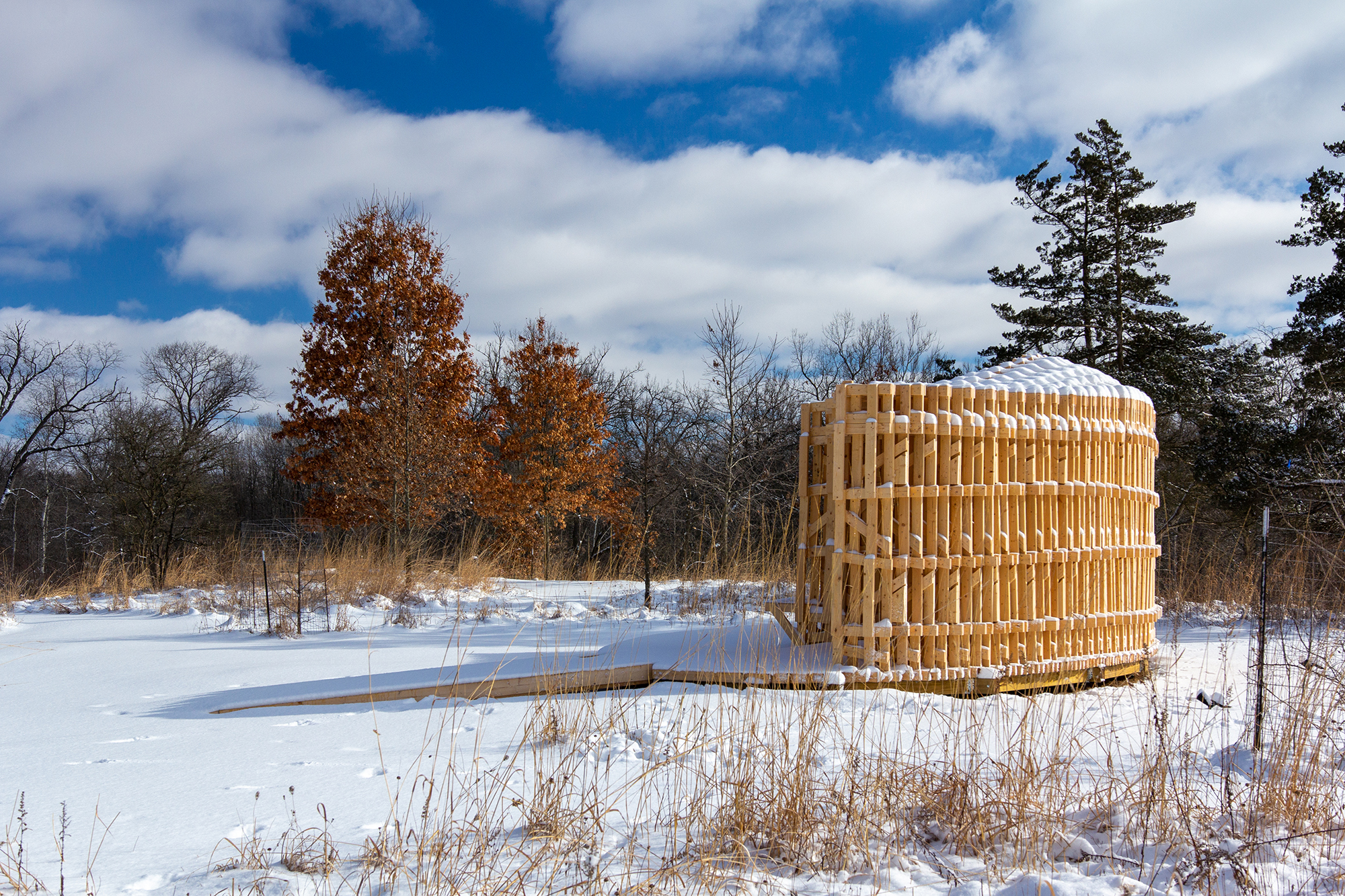
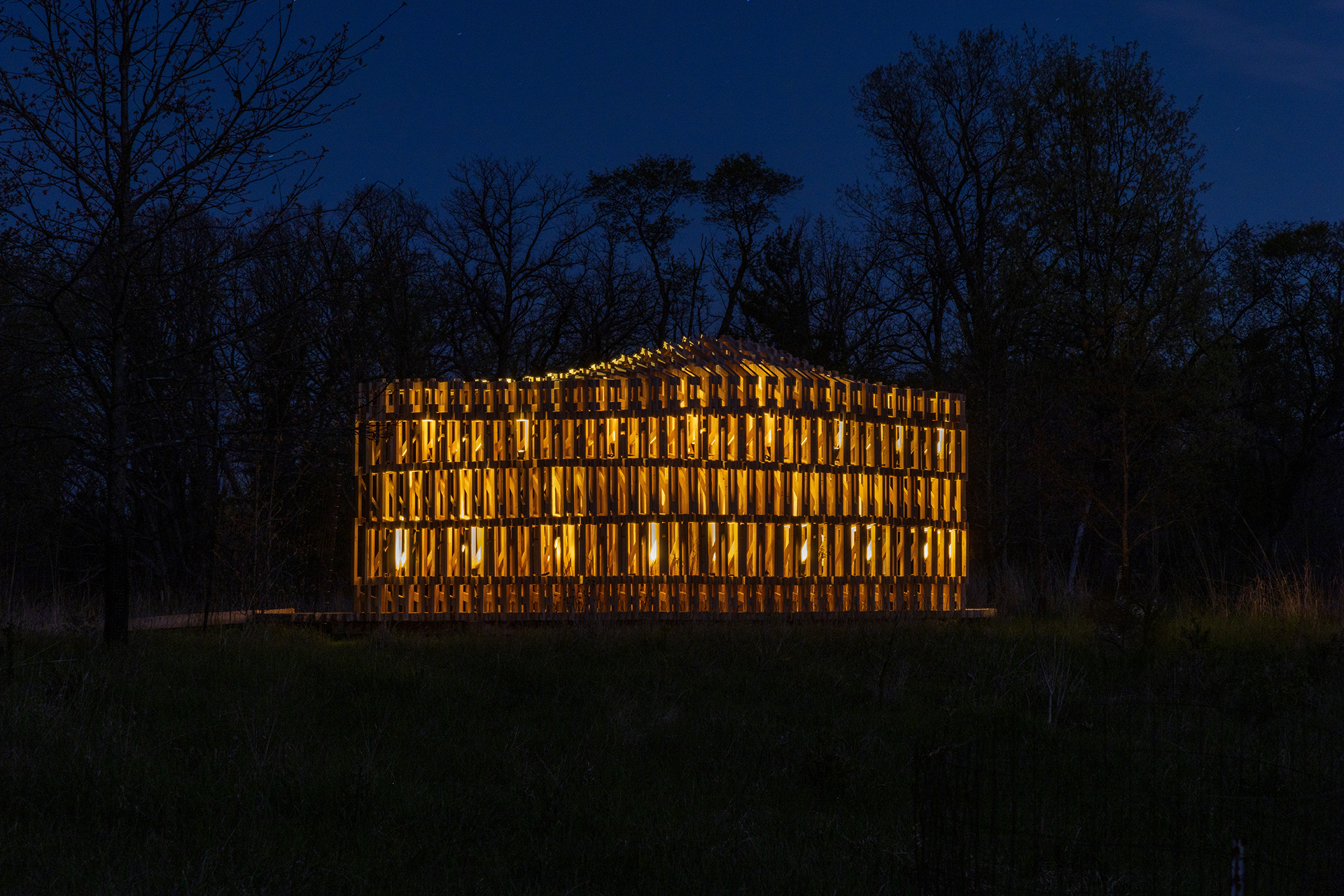
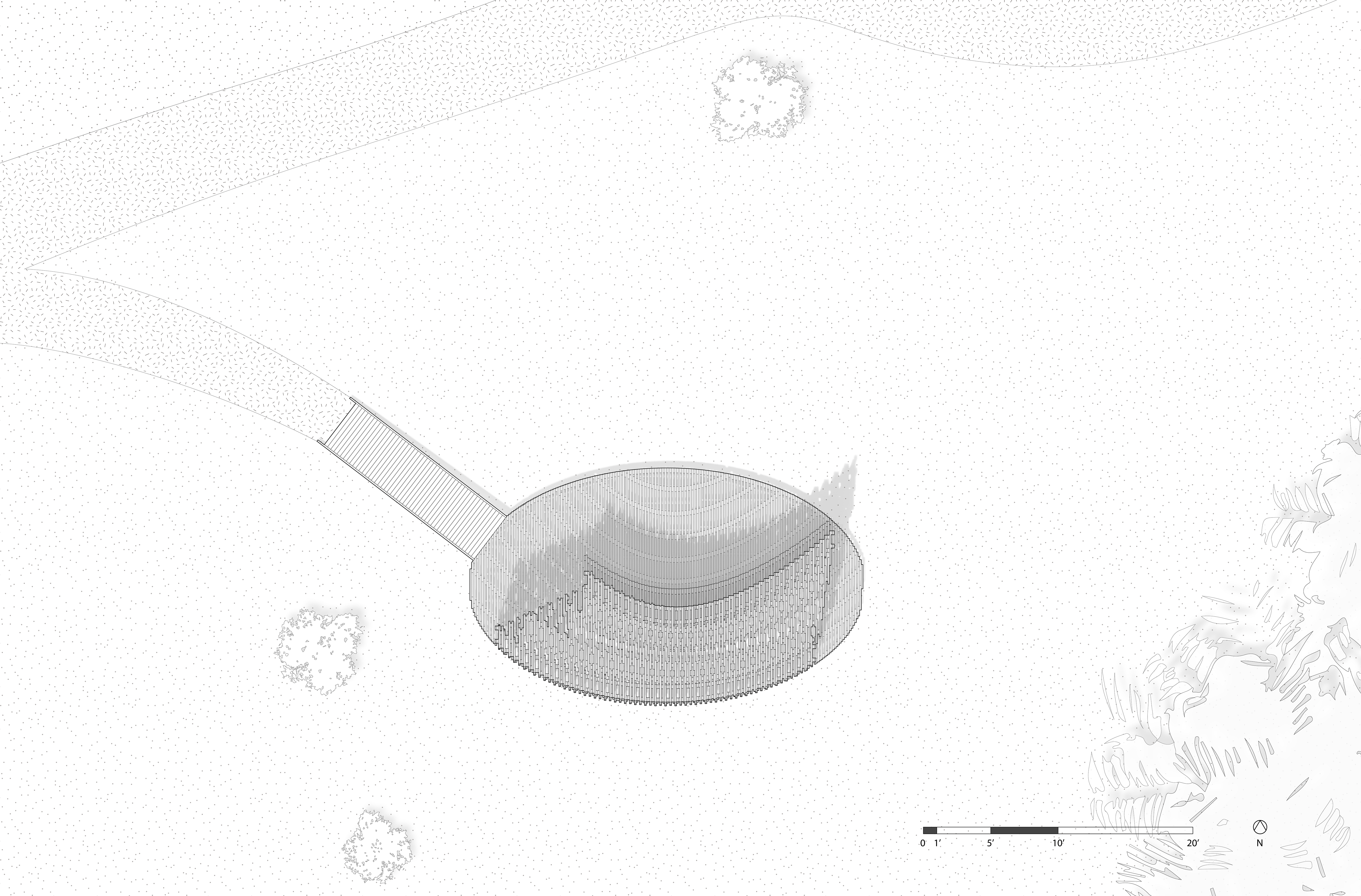
该展亭位于密歇根州安娜堡的马泰伊植物园,它是公共温室体系内为公众参与而设计的户外聚集点。展亭的形态设计受到周围景观、通道和交通人流的影响,形成了一个曲线形多孔结构,从公园道路上可见。
RFS is situated in the Matthaei Botanical Gardens in Ann Arbor, Michigan; it is designed for public engagement, acting as a defined gathering point located within the framework of a public conservatory while still maintaining an open-air condition. Formal configurations of the pavilion were influenced by views to and from the site, approach, and traffic flow, ultimately resulting in a curved, porous structure visible from the park road.



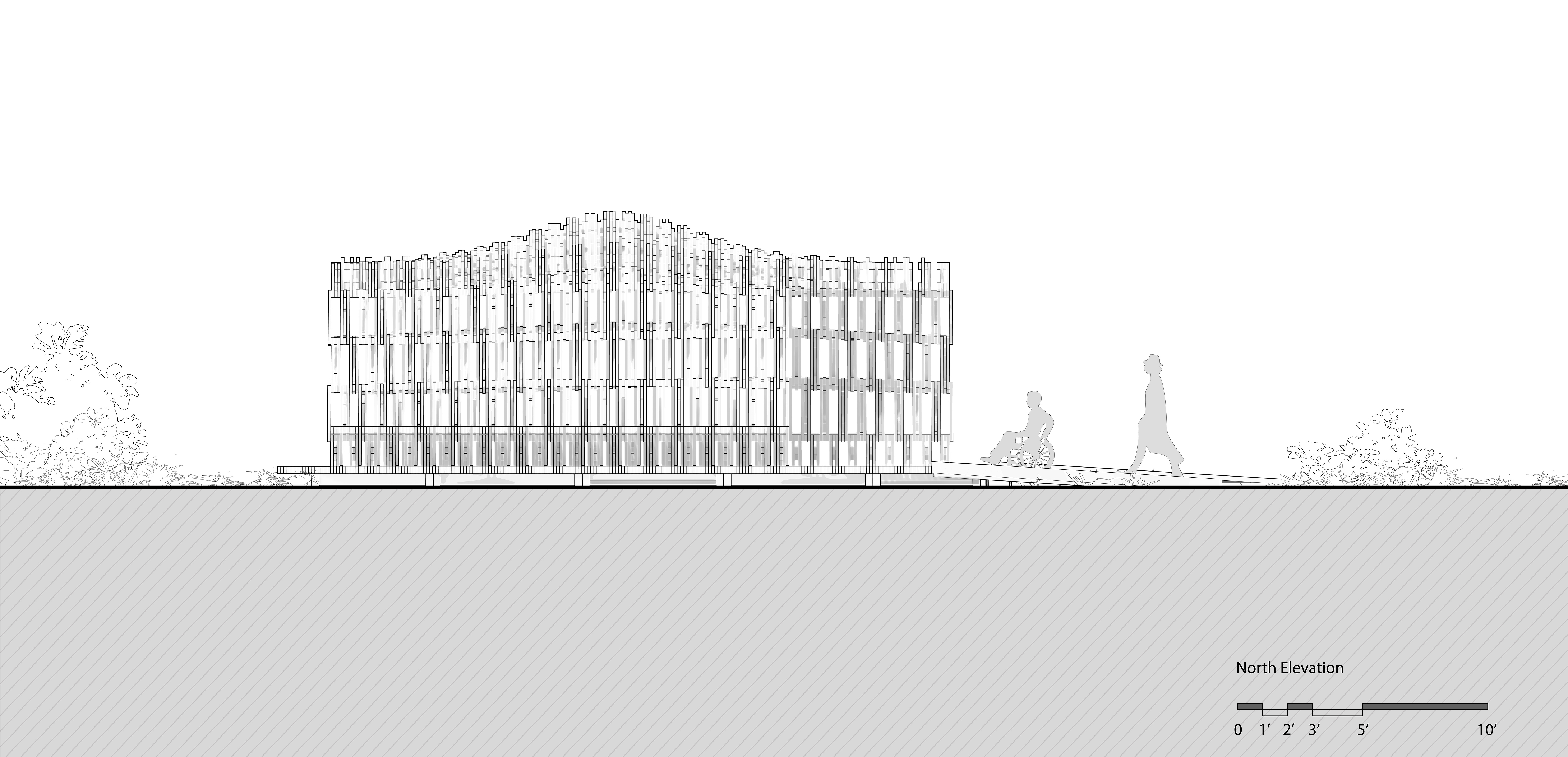
展亭的墙和天花板有着极具特点的复杂分层图案,从而创造了流动的气流和美丽、震撼的光影效果。
The walls and ceiling feature intricately layered patterns of timber that allow for airflow, striking shadows, and optical effects.
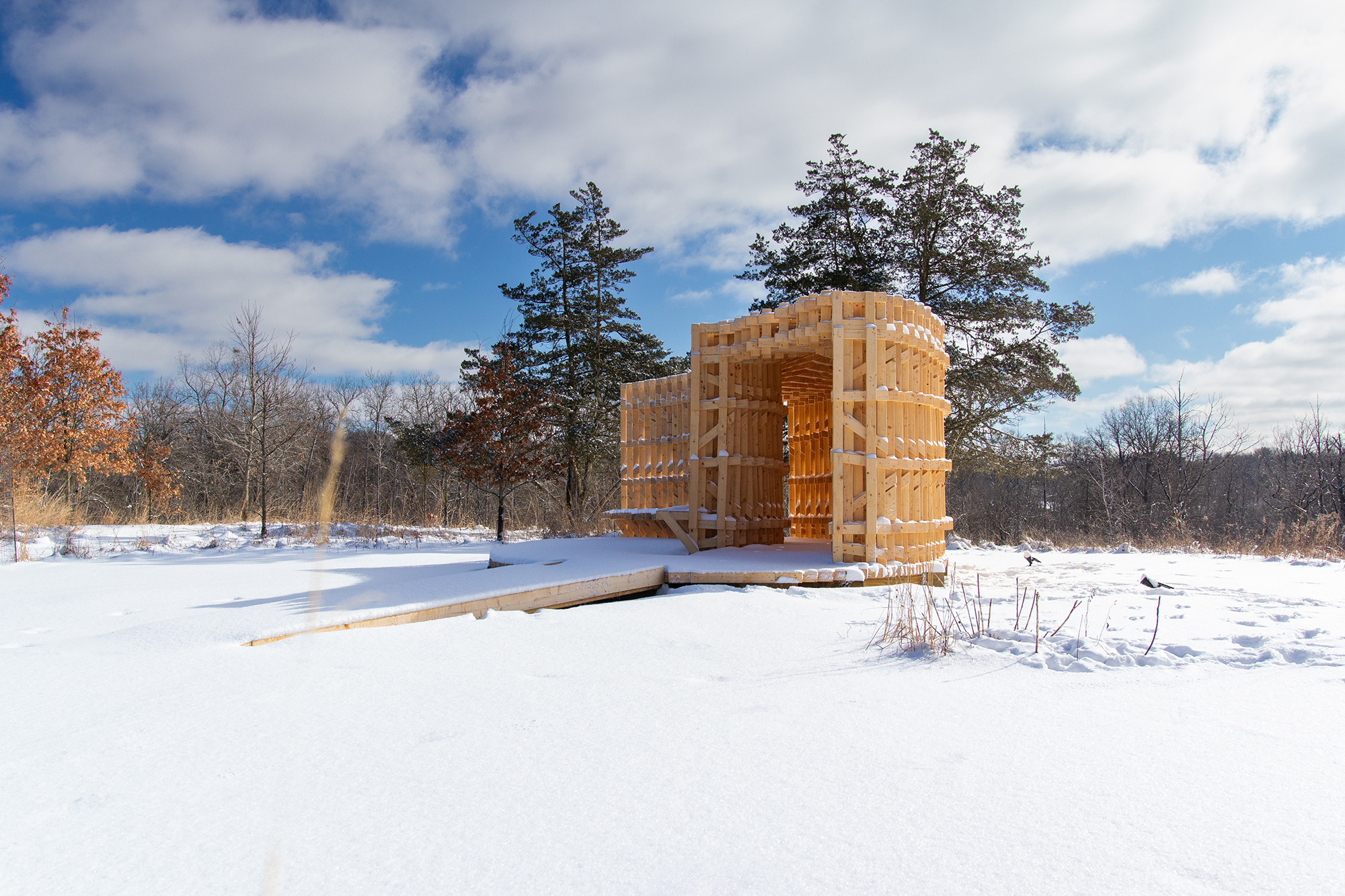


项目包括了一个可以进行展览和亲密会谈的封闭式步道、一个室外座位区,以及一个抬高的、为小型公共活动和表演创造机会的平台。
The pavilion includes an enclosed walkway that offers opportunities for exhibitions and intimate conversations, an exterior seating area, and a raised platform that creates an opportunity for small public events and performances.

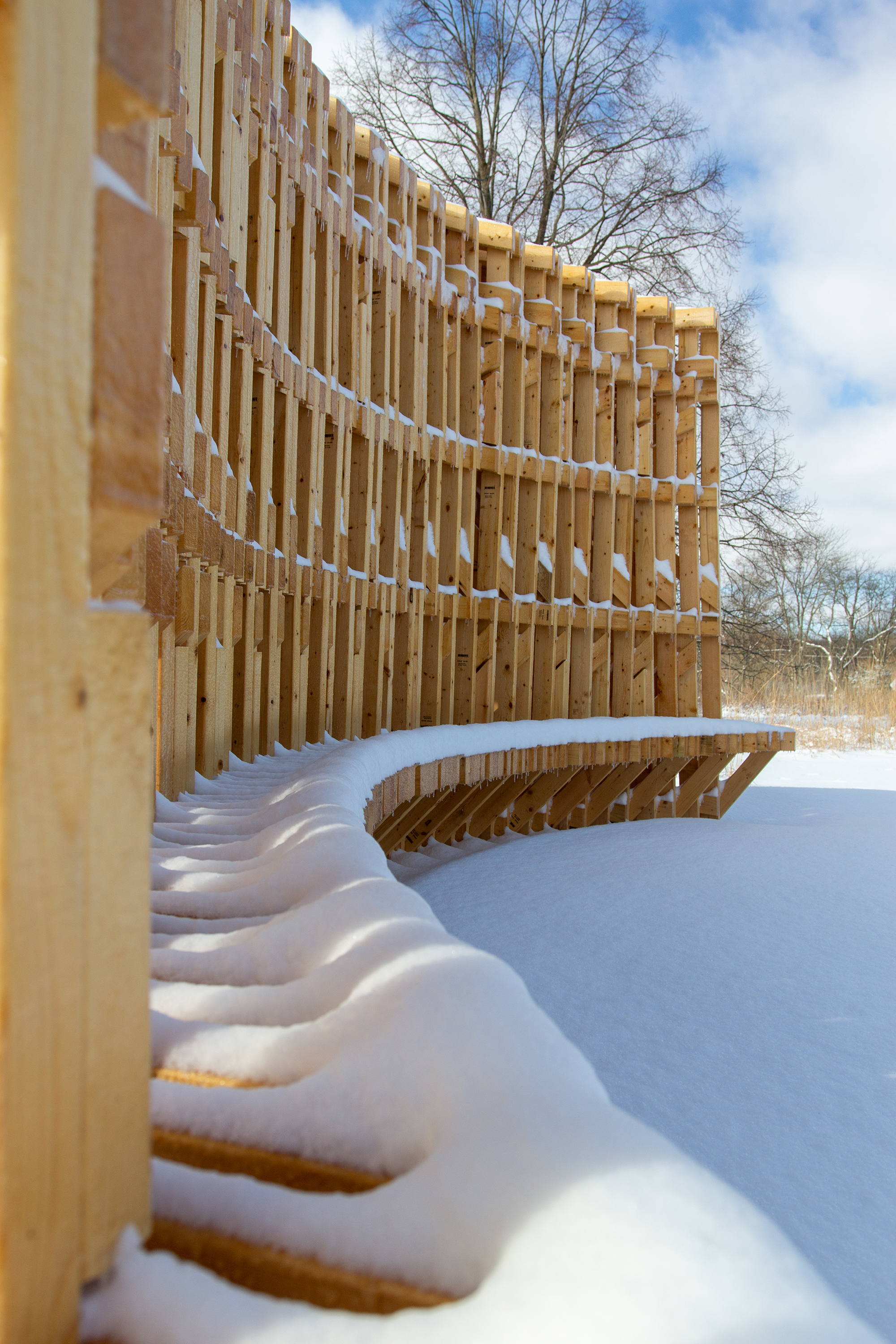
展亭木料经过最低限度的处理,以减少对周围地区的环境影响,并同时为人们提供一个耐用的临时性建筑。
RFS was left minimally treated to reduce the environmental impact on the surrounding area and produce a long-lasting but impermanent structure.
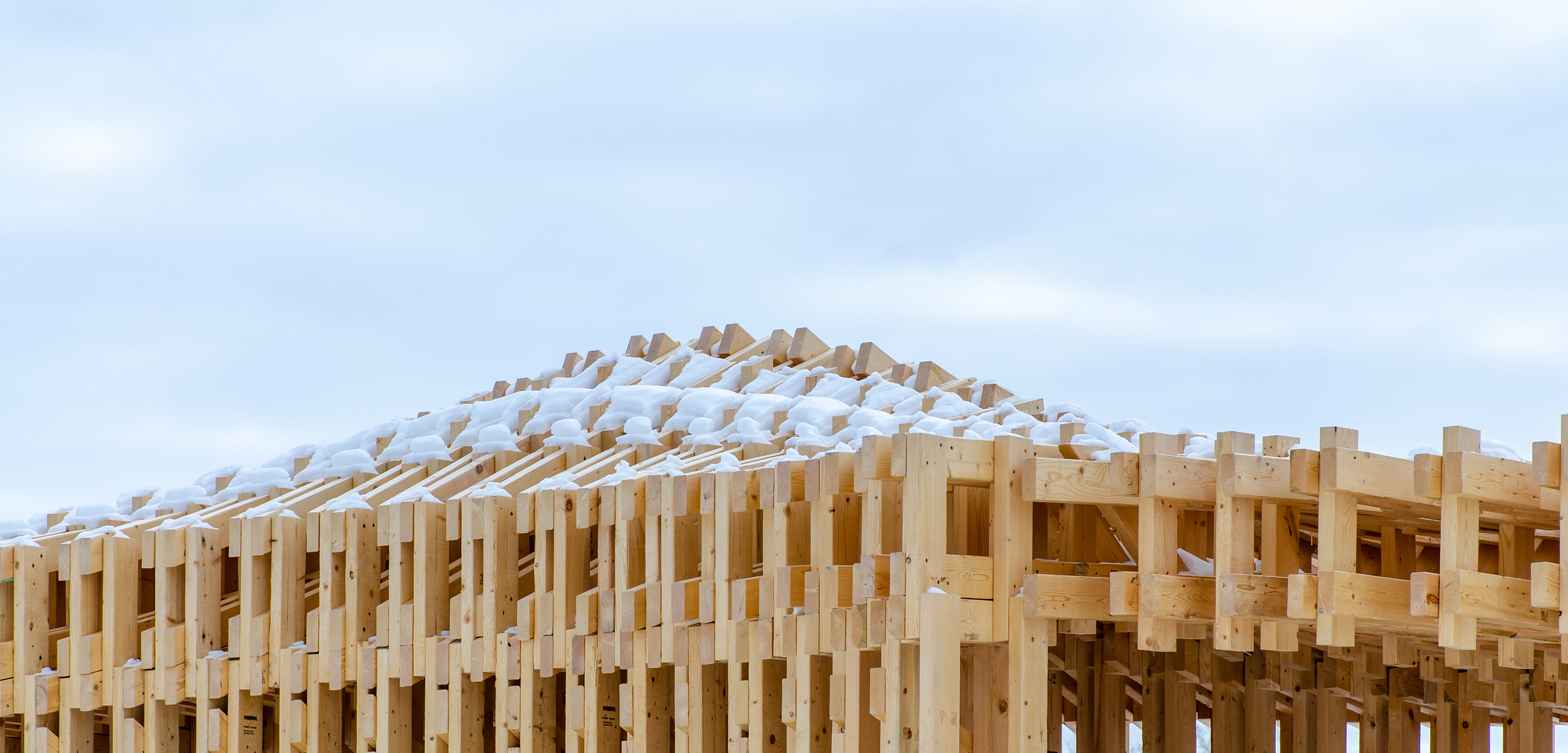


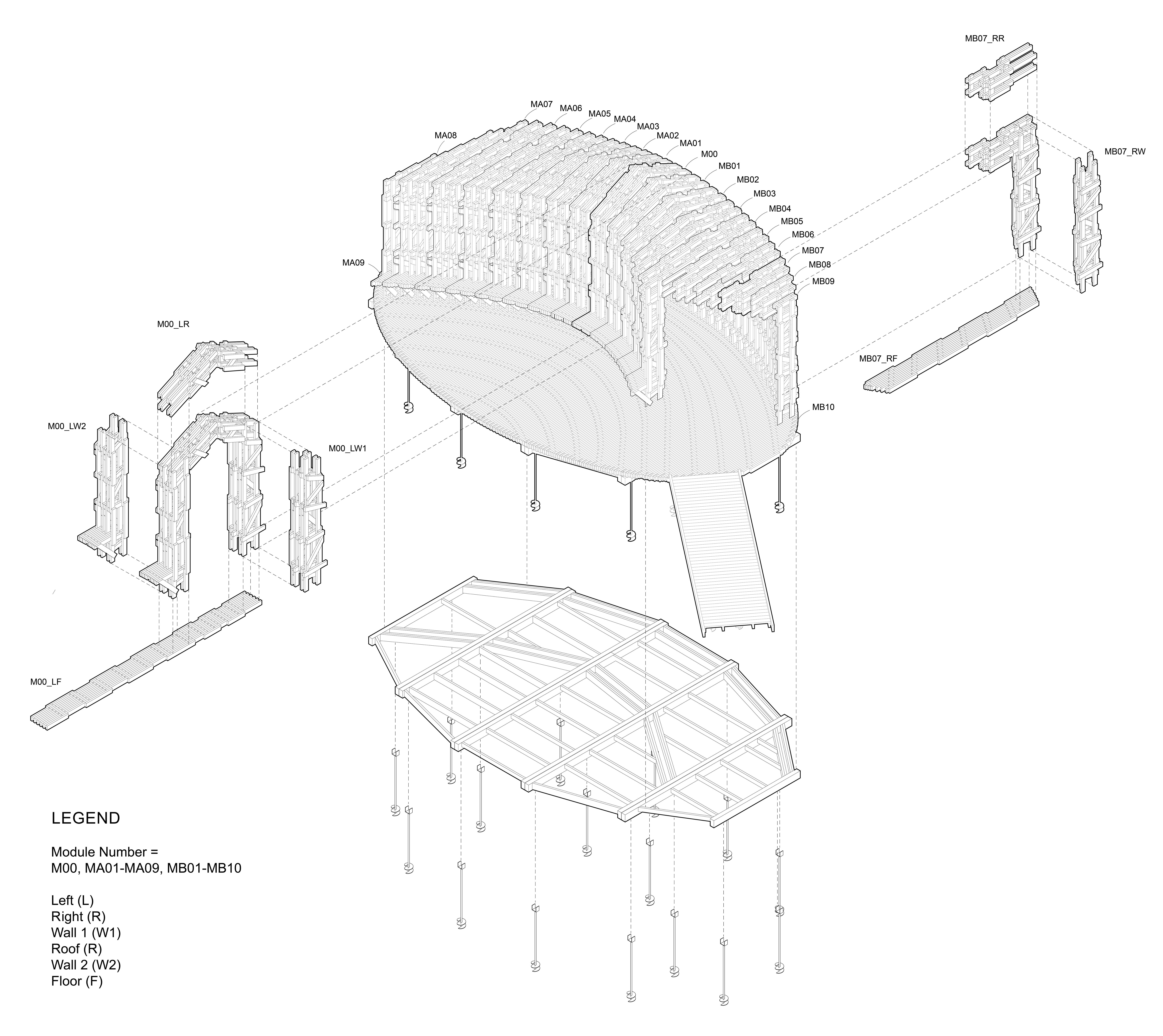
展亭采用了定制的装配式木材组件,并利用机械臂,将组件加工和组装成复杂的分层模块。组件为2×4 英寸(约50×100毫米)的短木材,从安娜堡地区采购。模块组装完成后被运到现场进行装配,工人将每个模块移到指定的位置拼接到一起,形成展亭。
RFS employs bespoke prefabricated timber sub-assemblies manufactured from regionally sourced short 2"×4" dimensional lumber and utilizes industrial robotic arms to process and assemble elements into intricately layered modules. After fabrication, modules are transported to the site, where human workers move each sub-assembly into place and attach them together to form the pavilion.
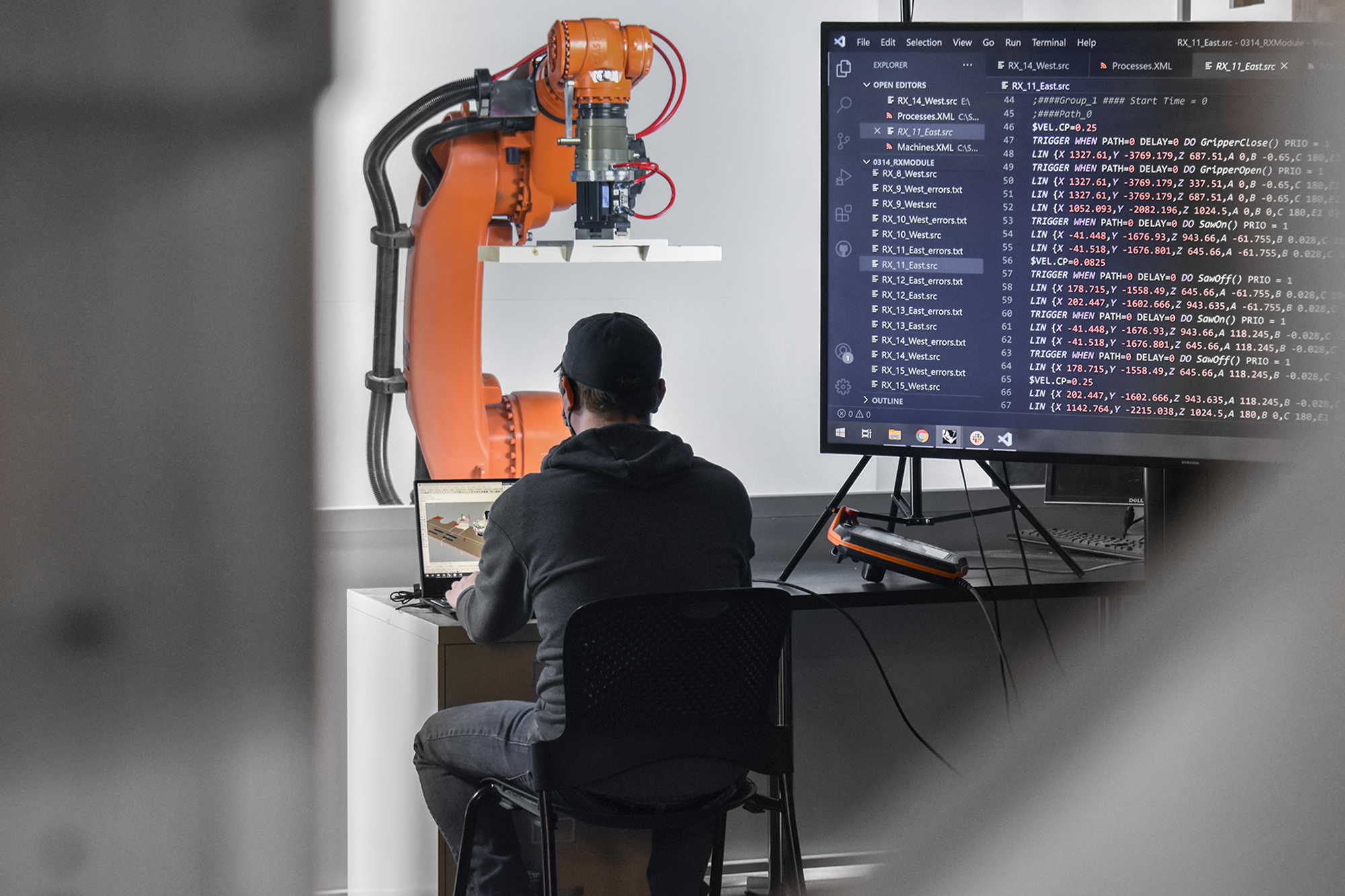
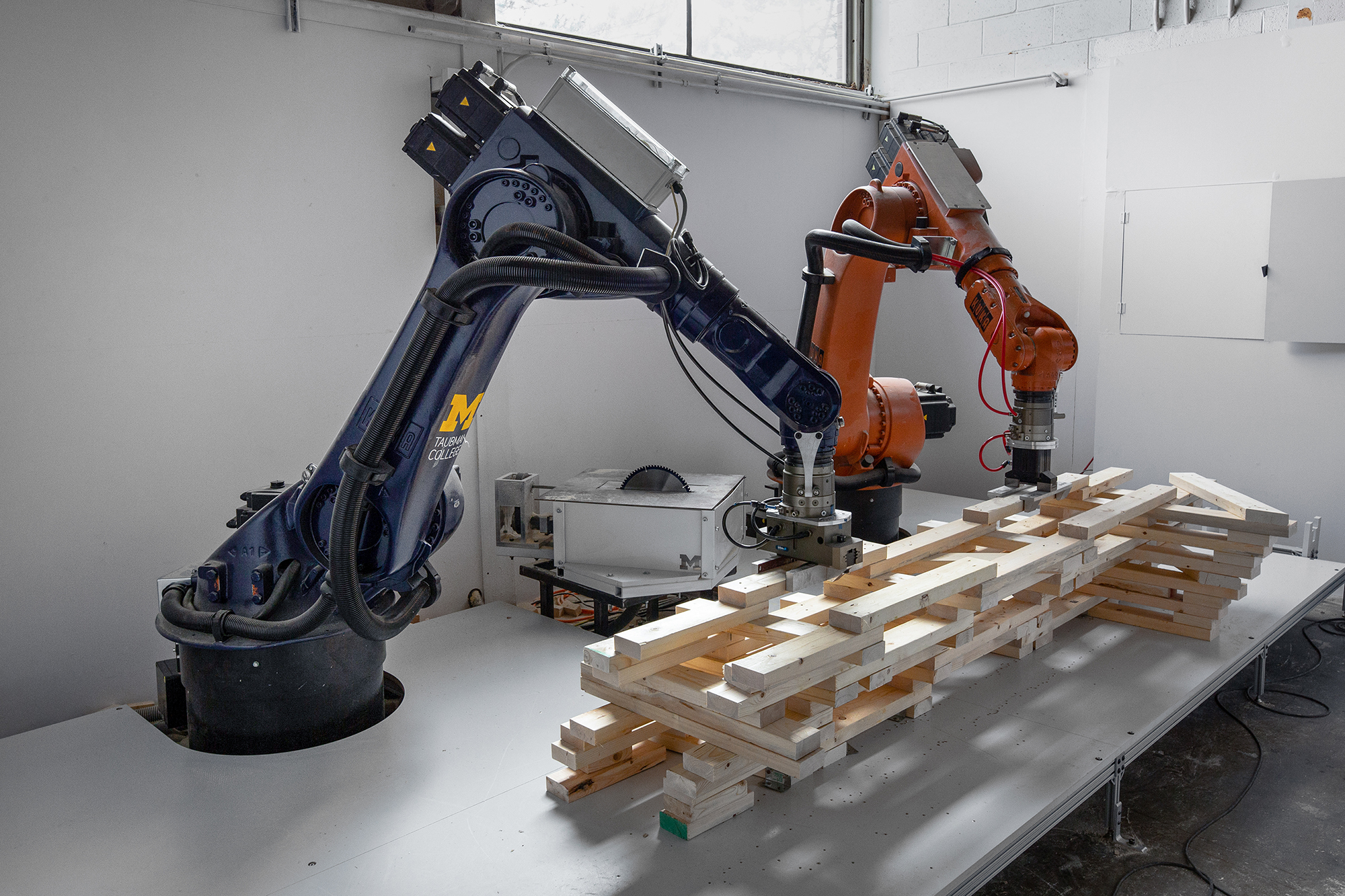



定制算法和机械臂建造的结合,验证了定制建筑构件的可行性,并将建筑浪费最小化。传统的建造手段和方法想要达到相同效果,大概率会因为技术上的困难或成本过高而难以实现。
The coupling of custom algorithms and robotic fabrication enables the feasible realization of bespoke building components that are otherwise difficult or costly to achieve through conventional means and methods, with minimal construction waste.
此外,使用短小组件意味着可以就地取材,充分利用当地标准规格(通常为8英尺)以下的木材,或者也可使用建筑建造中的余料和从拆除的建筑中回收的木料。因此,短小组件的利用有助于实现可持续建筑建造。
Moreover, short elements enable the use of indigenous trees that cannot easily produce full-length building elements (typically eight-foot dimensional lumber), construction and manufacturing off-cuts, and lumber elements reclaimed from the deconstruction of buildings, ultimately contributing to a more sustainable practice.

该项目过程整合了数字设计与建造,提供了一种重新思考材料使用、劳动力和环境问题的新方法论,从而创造出智能、应变且具有突出表现力的建筑。
The integrated digital design and construction process for RFS is a novel approach to reconsidering issues of material use, labor, and the environment to create intelligent and resourceful architecture with striking expressive qualities.

该项目的建成,将仍在发展中的人机协作建造研究,从实验室研究的层面提升为具有一定规模和复杂性的完整建筑系统。
Completing RFS elevated the ongoing research in human-robot collaborative construction beyond the laboratory to the scale and complexity of complete building systems.
这个研究性实践项目,旨在推动建筑中合理使用自动化,将建筑、工程和建造行业(AEC)的职责转变为寻找创造性解决方案,从而应对建造效率低下和气候变化威胁等方面的问题。
This case-study project is intended to provoke conversations about appropriate uses of automation in construction and the Architecture, Engineering, and Construction (AEC) community's shifting responsibility to find creative solutions to construction inefficiencies and the omnipresent threat of climate change.

RFS项目由密歇根大学陶布曼学院ADR实验室、数字和材料技术硕士课程的学生及研究助理设计和建造。工程的结构性能和建筑规范要求的评估工作,由ADR实验室与结构工程公司Silman合作完成。
RFS is designed and fabricated by ADR Laboratory, research assistants, and students of the University of Michigan’s Taubman College MS in Digital and Material Technologies program. The work is evaluated for structural performance and building code requirements in partnership with the structural engineering firm Silman.


设计图纸 ▽


完整项目信息
Project name: Robotically Fabricated Structure (RFS)
Location: Matthaei Botanical Gardens, Ann Arbor, MI, USA
Gross floor area: 43m²
Design: ADR Laboratory, Taubman College of Architecture and Urban Planning, University of Michigan
Completion: October, 2021
Chief Architect: Arash Adel
Principal Investigator and Project Lead: Prof. Arash Adel, ADR Laboratory
Research, Design, and Fabrication Assistants: Ben Lawson, Ryan Craney, Sarah Nail, Gabrielle Clune, Andrew Hoover, Juliette Zidek
Construction Assistants: Abdallah Kamhawi, Tharanesh Varadharajan, Ali Fahmy, Elliot Smithberger, Qian Li, Nadim Hajj Ahmad, Joshua Powell, Ivan Gort-Cabeza de Vaca
Students (MS in Digital and Material Technologies, Taubman College of Architecture and Urban Planning): Ruxin Xie, Daniel Ruan, Xinran Li, Jingwen Song, Mehdi Shirvani, Mackenzie Bruce, Chris Humphrey
Structural Engineers: Robert Silman Associates Structural Engineers (Nat Oppenheimer, Omid Oliyan, Justin Den Herder, Paul Evans)
Video Editors: Yunyan Li, Jacob Cofer
Videographers: Jacob Cofer, Bob Berg
Diagrams: Yunyan Li
Supported by the Herbert W. and Susan L. Johe Fund, Taubman College of Architecture and Urban Planning, University of Michigan
Special Thanks: Prof. Jonathan Massey, Prof. McLain Clutter, Prof. Catie Newell, Prof. Wes McGee, Cynthia Radecki, Earl Bell
Client: Matthaei Botanical Gardens
Photographer: Arash Adel, Bob Berg, Daniel Ruan, Matthew Weyhmiller, Mehdi Shirvani, Jacob Cofer
Photo copyright: ADR Laboratory
Translator: Jingwen Song
本文由密歇根大学陶布曼学院ADR实验室授权有方发布。欢迎转发,禁止以有方编辑版本转载。
上一篇:向山借风景:莫干山木子林夕云民宿 / 实在建筑设计工作室
下一篇:国家重型汽车工程技术研究中心 / 悉地国际21设计工作室