

建筑设计 Henning Larsen+Cobe
景观设计 SLA
项目地点 瑞典隆德
项目状态 部分在建
建筑面积 100,000平方米
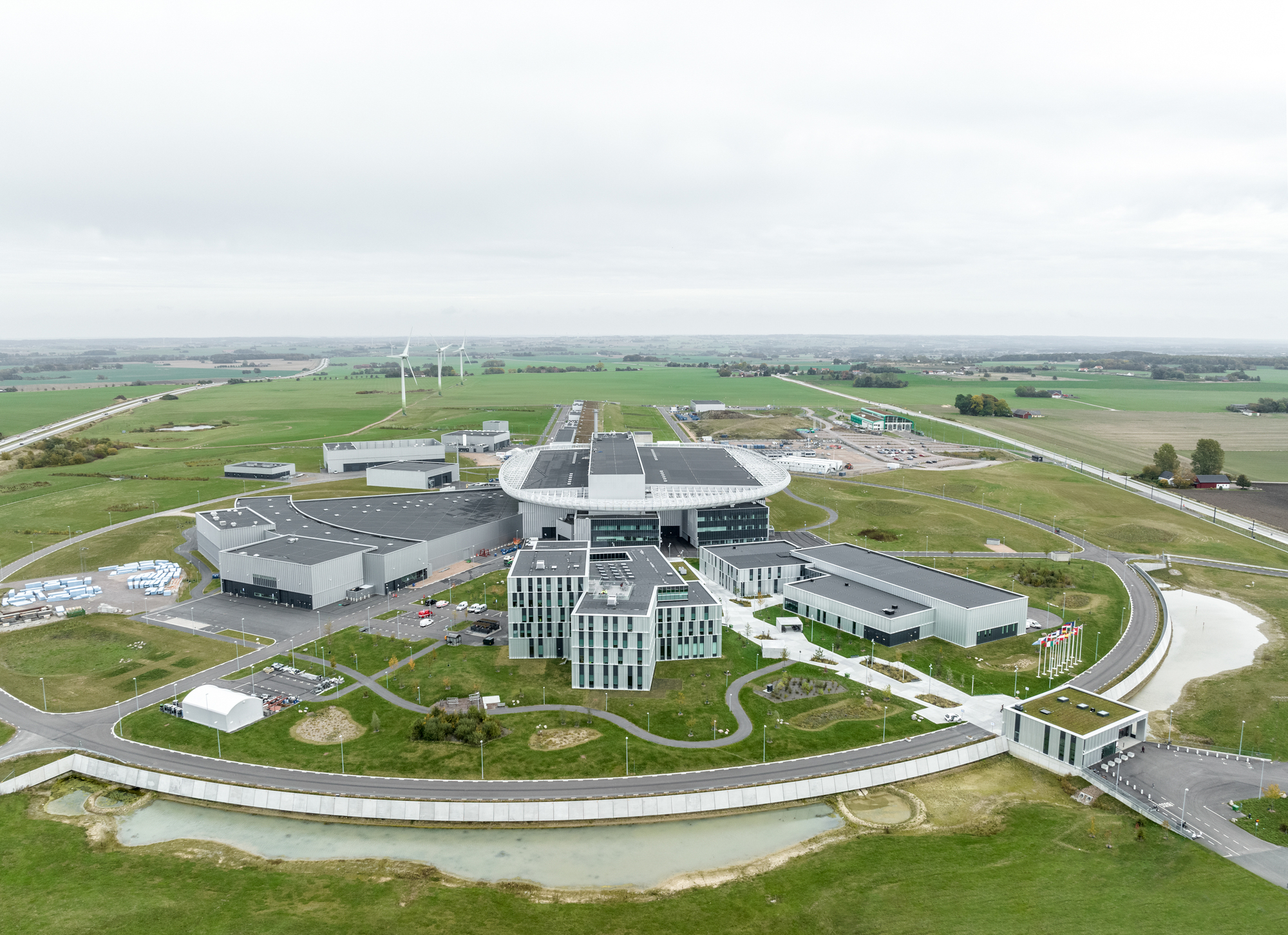
位于瑞典隆德的欧洲散裂中子源(ESS)是未来最强大的加速器中子源的所在地,将推动材料领域上的科研创新。作为容纳世界知名科学家的国际中心,ESS的设计将园区的“社区感”放在首位,创造了一个有着极高水准的合作与学习环境。
Home to the future most powerful accelerator-based neutron source, the European Spallation Source in Lund, Sweden, will advance material research for science and innovation. An international hub for world renown scientists, the design prioritizes a sense of community within the campus, creating a collaboration and learning environment of the highest caliber.

作为未来世界上最先进的中子源设置,占地12万平方米的ESS,将供材料科学、化学、生物学和物理学的研究人员所使用。该设施的主要目的是产生中子,供科学家以研究材料的原子与分子结构。ESS通过仪器收集的研究成果,将帮助为社会最紧迫的问题提出解决方案,这其中包括新材料、能源、健康和环境领域。
The future world’s most advanced neutron source, the 120,000 m2 European Spallation Source (ESS) will be used by researchers from material science, chemistry, biology and physics. Its main purpose is to produce neutrons that scientists can use to study the atomic and molecular structure of materials. The insights gathered with instruments at ESS will help propose solutions to society’s most pressing issues including new materials, energy, health and the environment.
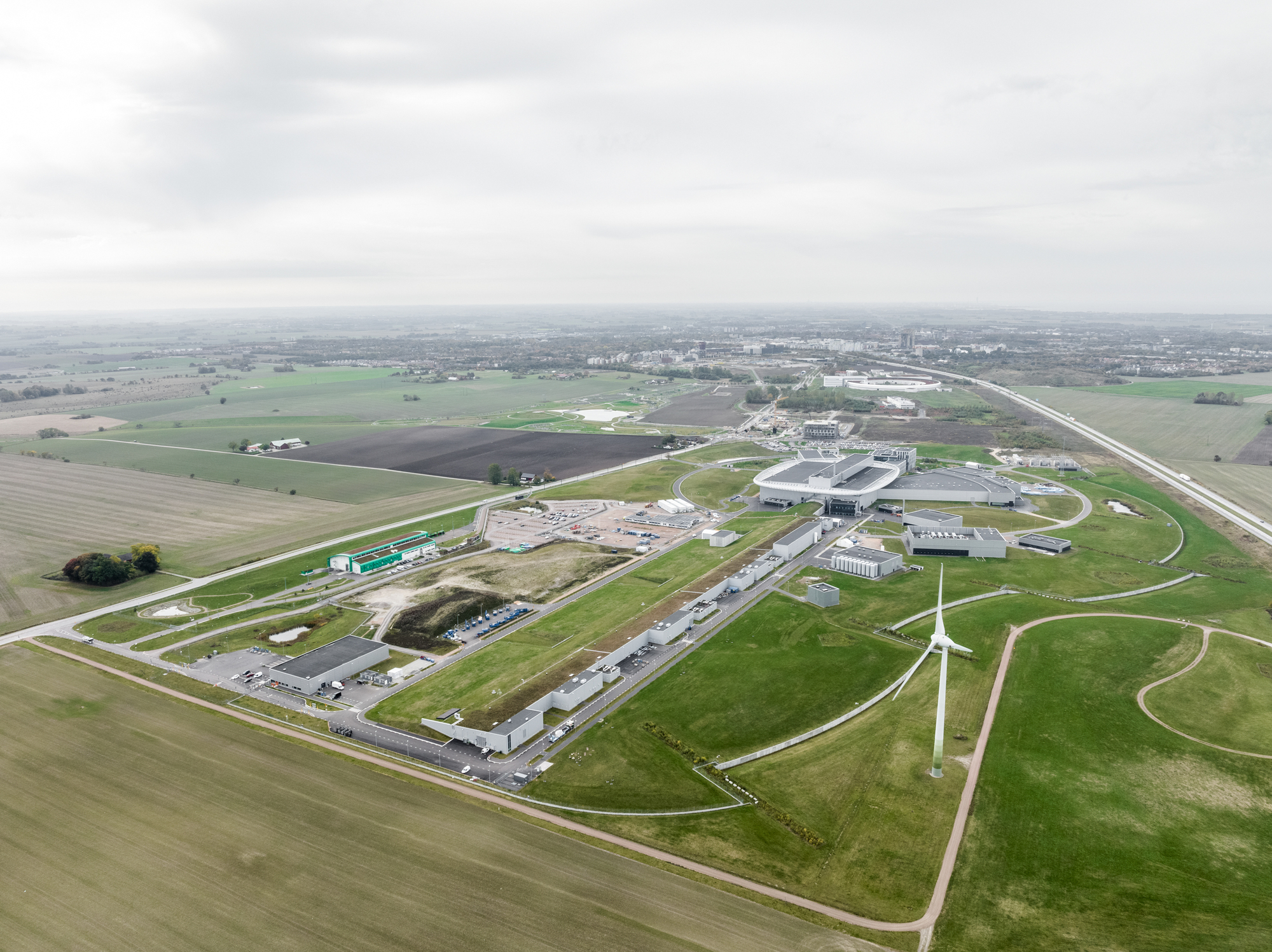
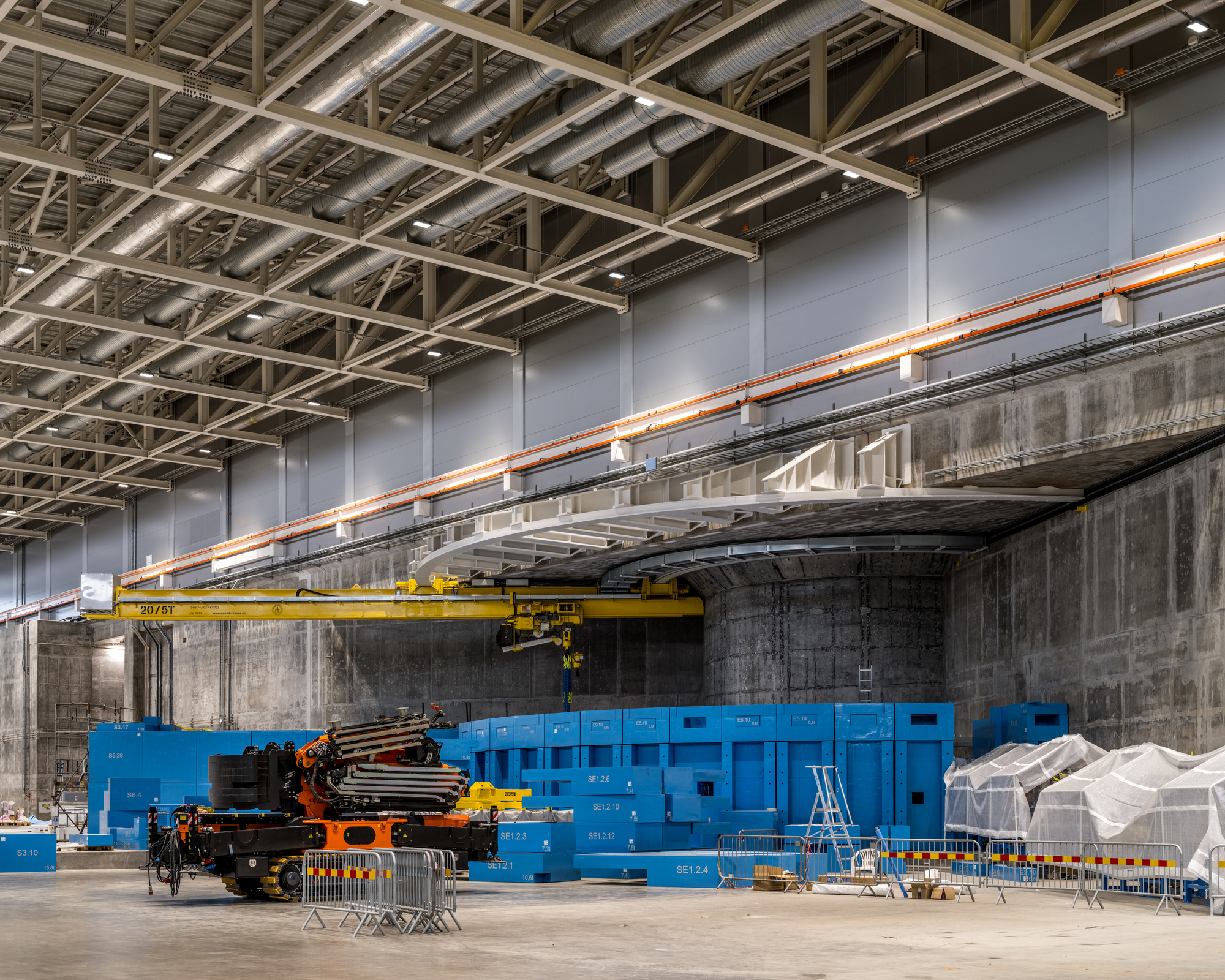
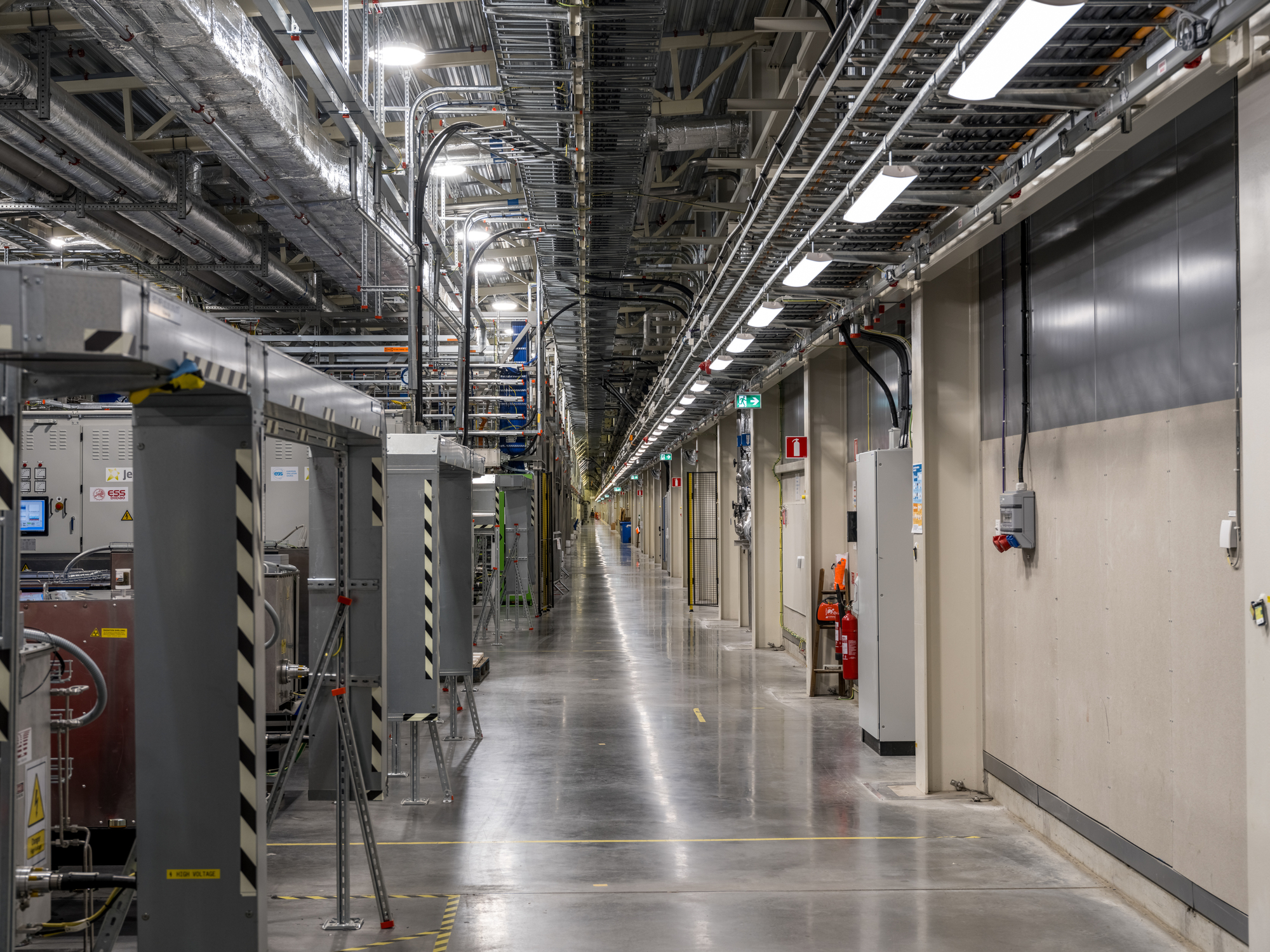
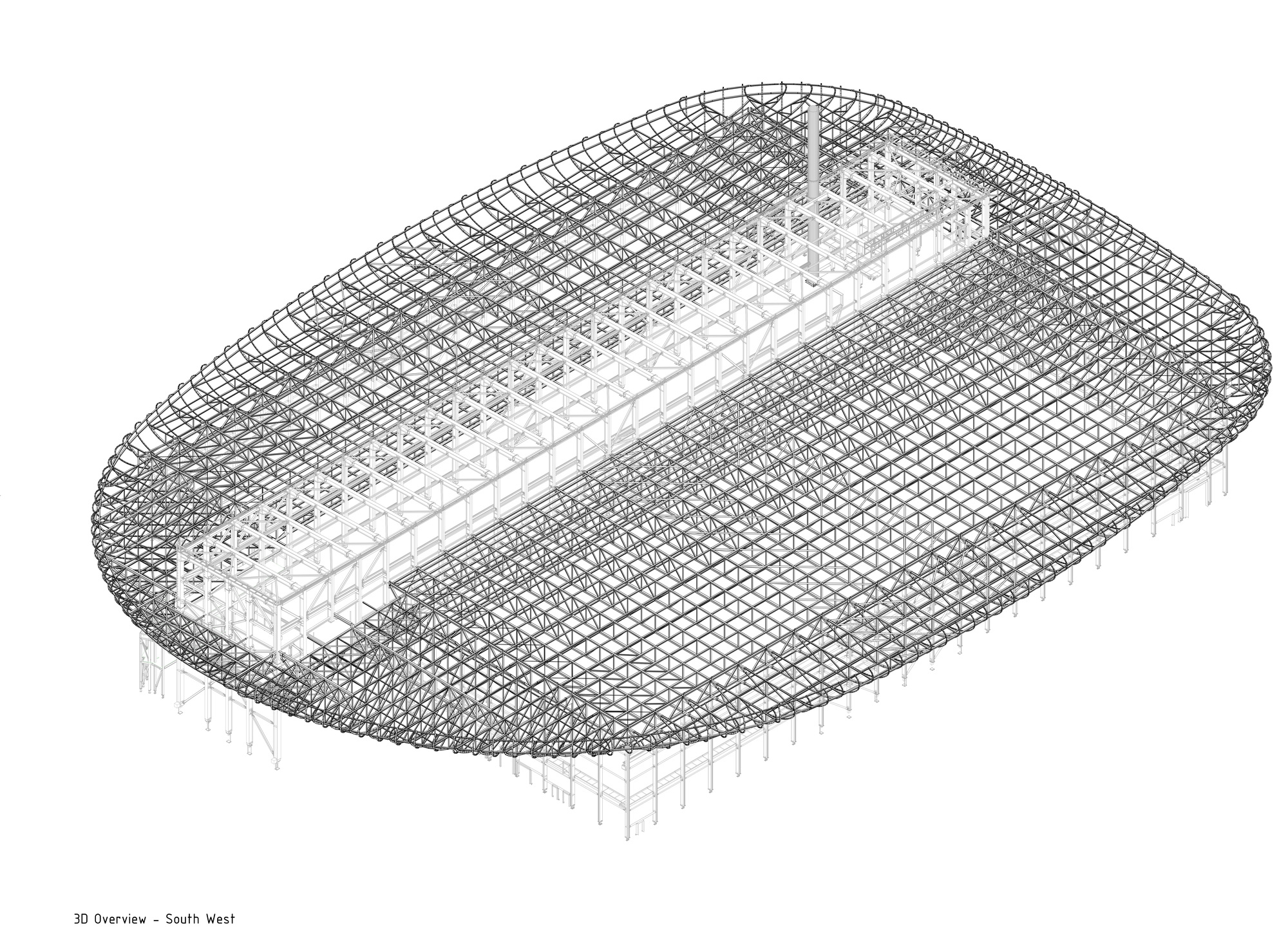
这座获得英国建筑性能评估体系(BREEAM)杰出认证的研究园区,其关键部件是一台600米长的质子加速器,它通过一种名为“散裂”的过程产生中子,并向目标发射高能质子束。当质子撞击目标时,会导致原子破裂,产生中子雨,并将中子射向用于研究材料特性的仪器。
Generating neutrons through a process called spallation, the critical component of the BREEAM Outstanding-certified research campus is a 600m long proton accelerator which fires a high-energy proton beam at a target. When the protons hit the target, they cause the atoms to break apart, producing a shower of neutrons which are directed towards the instruments that allow scientists to study the properties of materials.



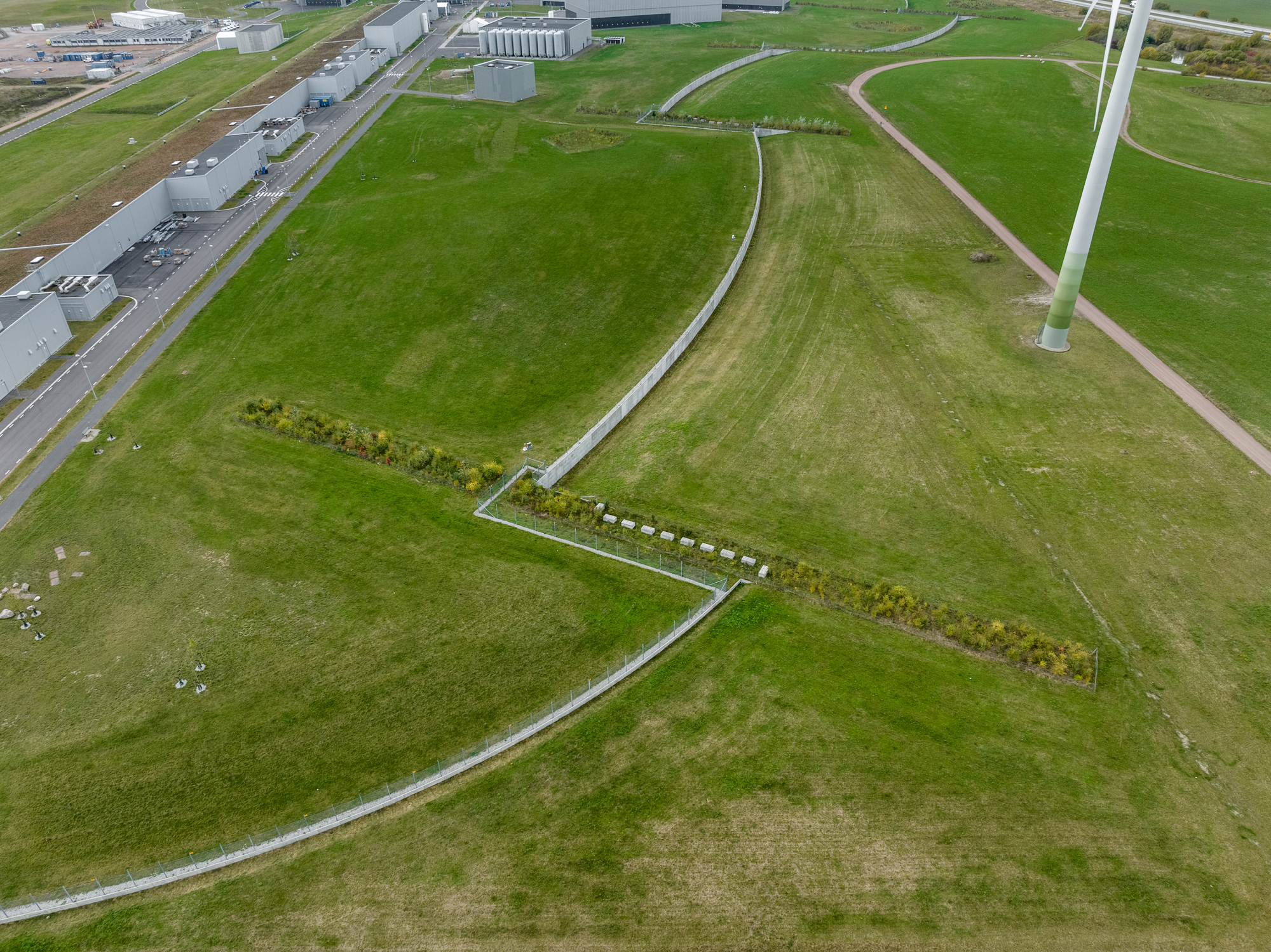
加速器本身位于地下,坐落在一条隧道中,与地貌融为一体。一座被称为“调速管长廊”的建筑掩映在土堤之下,坐落在加速器上方——只在一侧可见,另一侧建筑与瑞典的自然景观融为一体,看起来像是一片草地。
The accelerator itself is below ground, housed in a tunnel which sits within the landscape. Disguised beneath a berm of soil, a building known as the ‘klystron gallery’ sits above the accelerator - only visible as a wall on one side, on the other the building blends into the Swedish landscape, appearing to be a meadow.


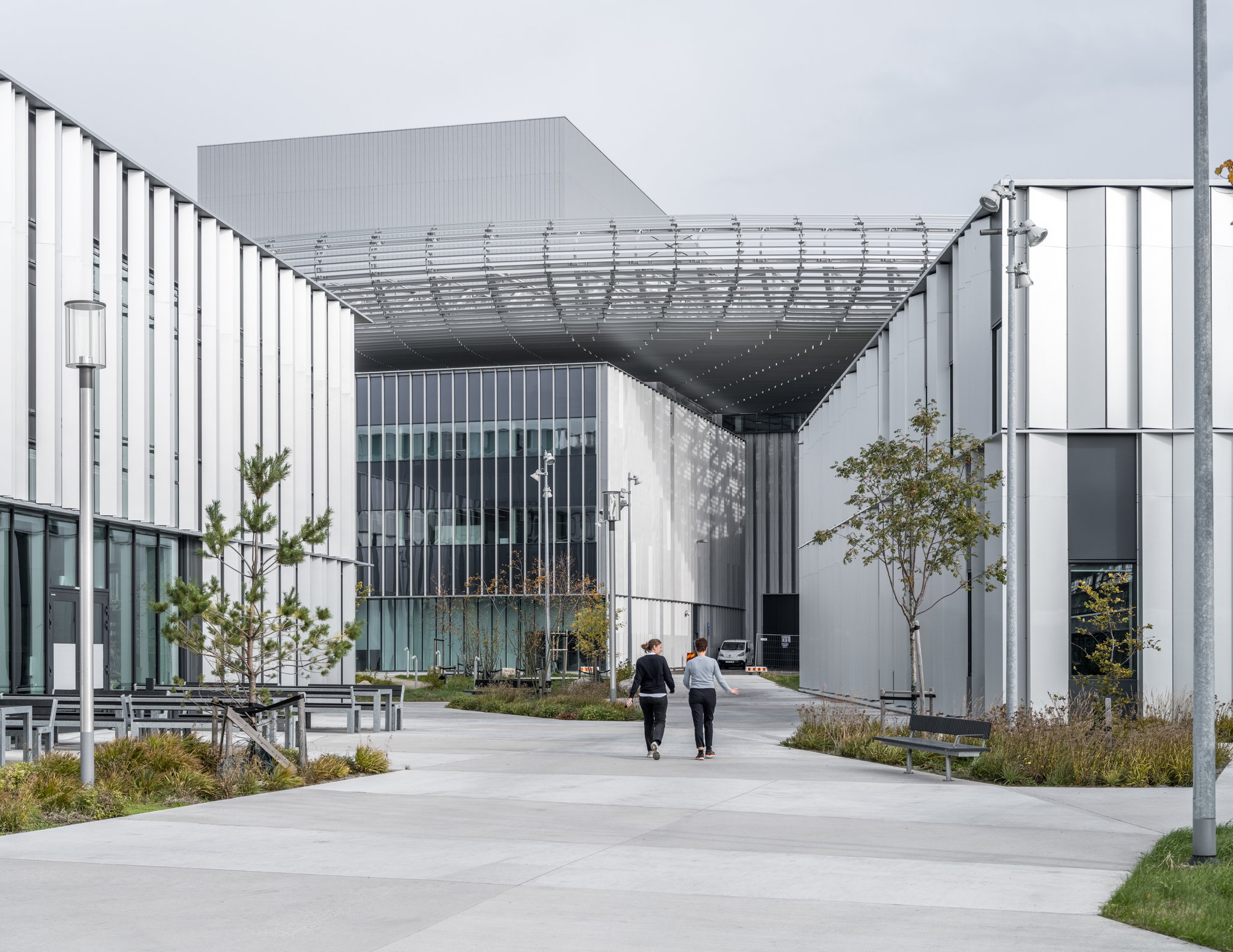
ESS研究设施隐喻了一个分裂过程:“中子”穿过直线加速器,与“钨芯”碰撞,将“电子”散射到自然景观中。整个建筑群通过布局复制了这一过程,形成了一个灵活的、面向未来的总体规划—— 一个景观化的质子加速器、一个圆形靶站屋顶和错落有致的设施建筑,巧妙而精致地布置在景观中。
The ESS research facility becomes a metaphor for the spallation process: a neutron sped through a linear accelerator – colliding with a tungsten core – scattering electrons into the landscape. The complex as a whole replicates this process through its layout generating a flexible, future proof master plan – a landscaped proton accelerator, a circular target roof and scattered facility buildings intricately and delicately placed in the landscape.
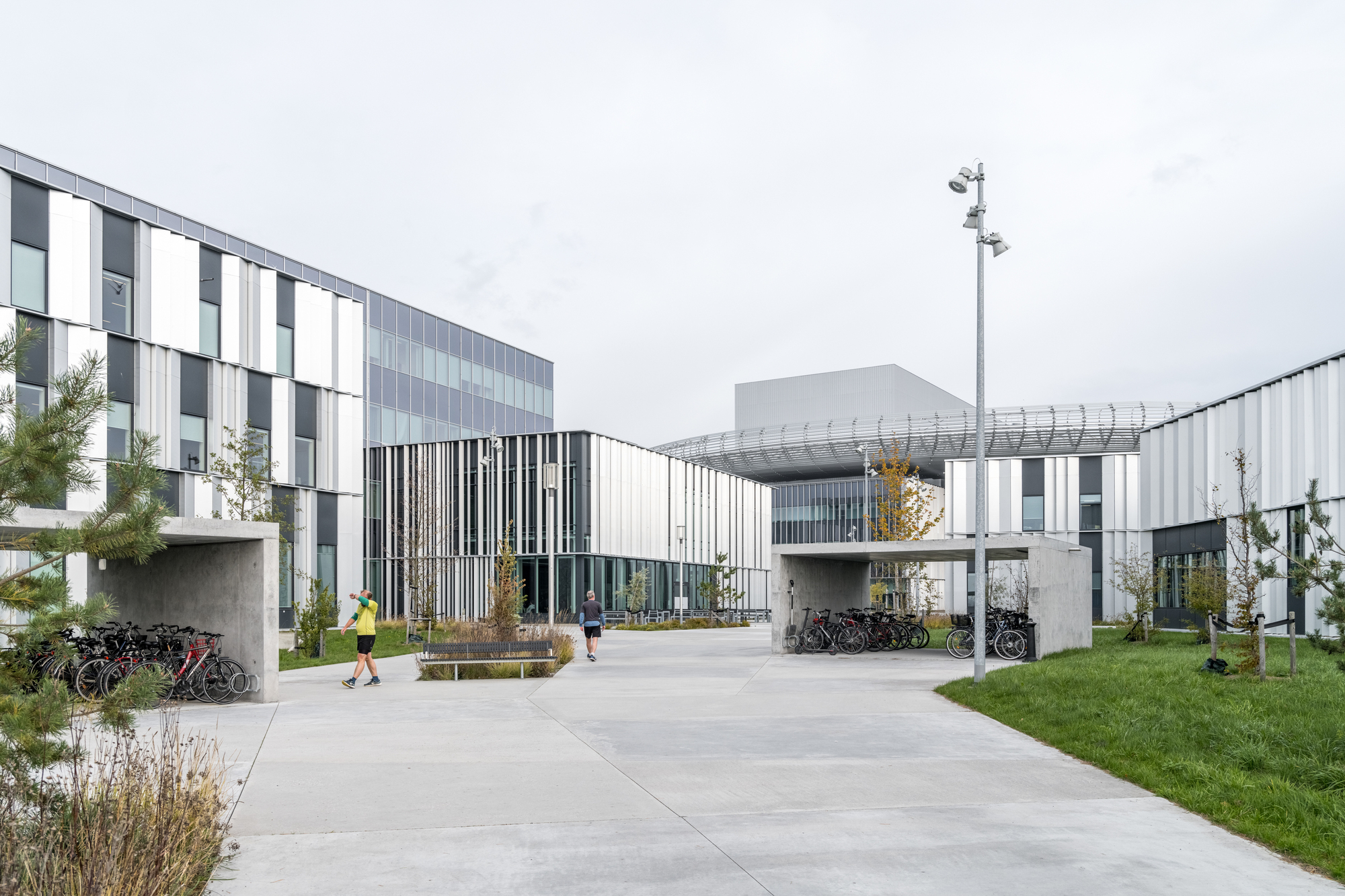


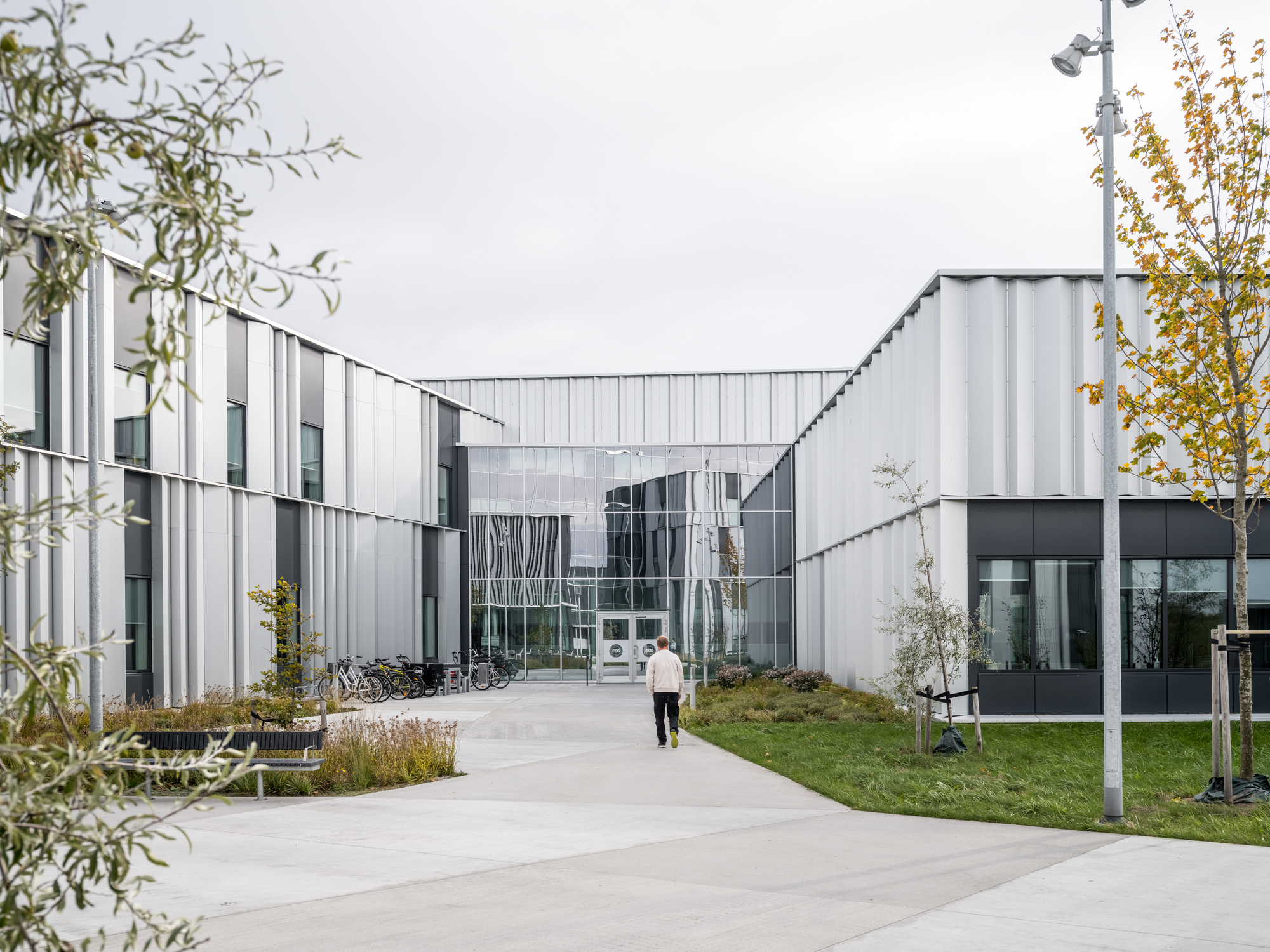
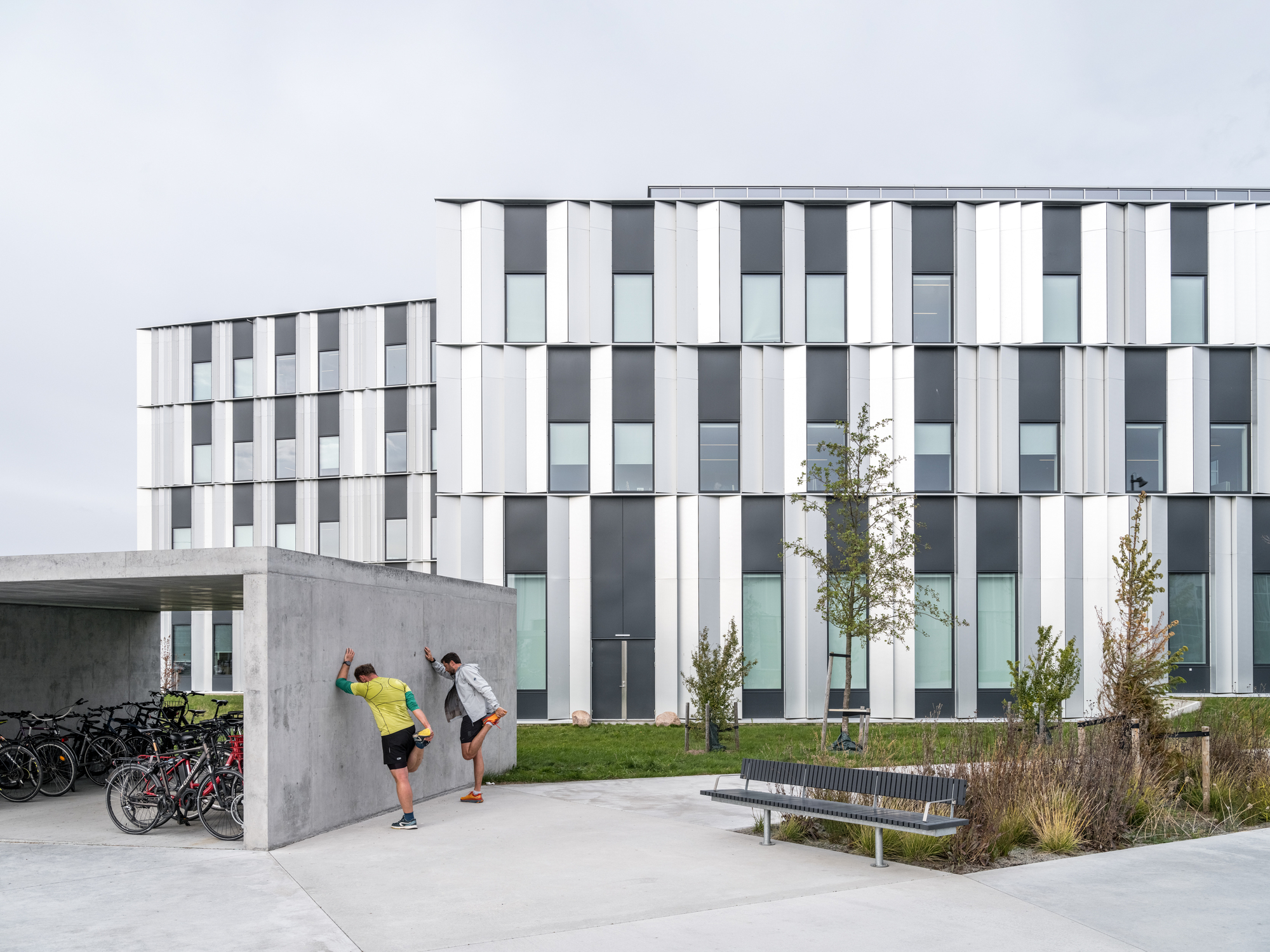
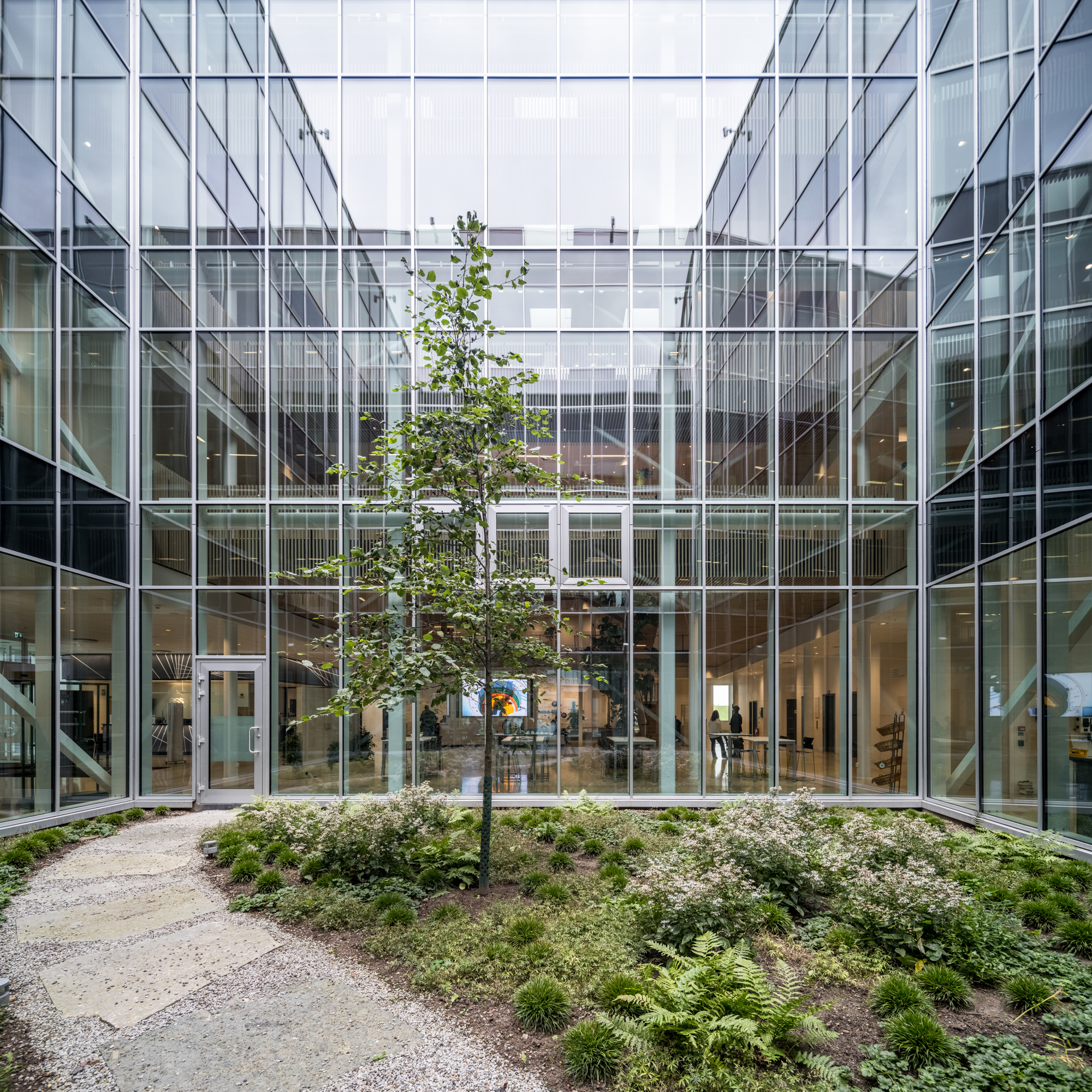
作为园区发展的关键性因素,Henning Larsen、Cobe与SLA共同为这个国际科学家社区构思了一个“村落”;内部亦有丰富的空间,包括步道、慢跑路径及雨水池,允许来自全球科研机构的访学人员在室内外进行非正式的交流。以自然为基础的“无栅栏”式景观,特别设计有下沉式的“ha-ha”矮墙和多样化的植被,既保持了设施的安全性,又不会阻挡人的视野,同时在设施周围还营造出了更为宁静、迷人的氛围。
Integral to the success of the campus, Henning Larsen, Cobe and SLA envisioned a village for an international community of scientists; a multitude of spaces allow visiting researchers from global science institutions to meet each other informally both indoors and outdoors, including pathways for walking and jogging and rainwater ponds. A nature-based ‘fenceless’ landscape with specially designed sunken ‘ha-ha’ fences and diverse vegetation keeps the facility secure without blocking the view whilst also creating a more serene and inviting atmosphere surrounding the facility.
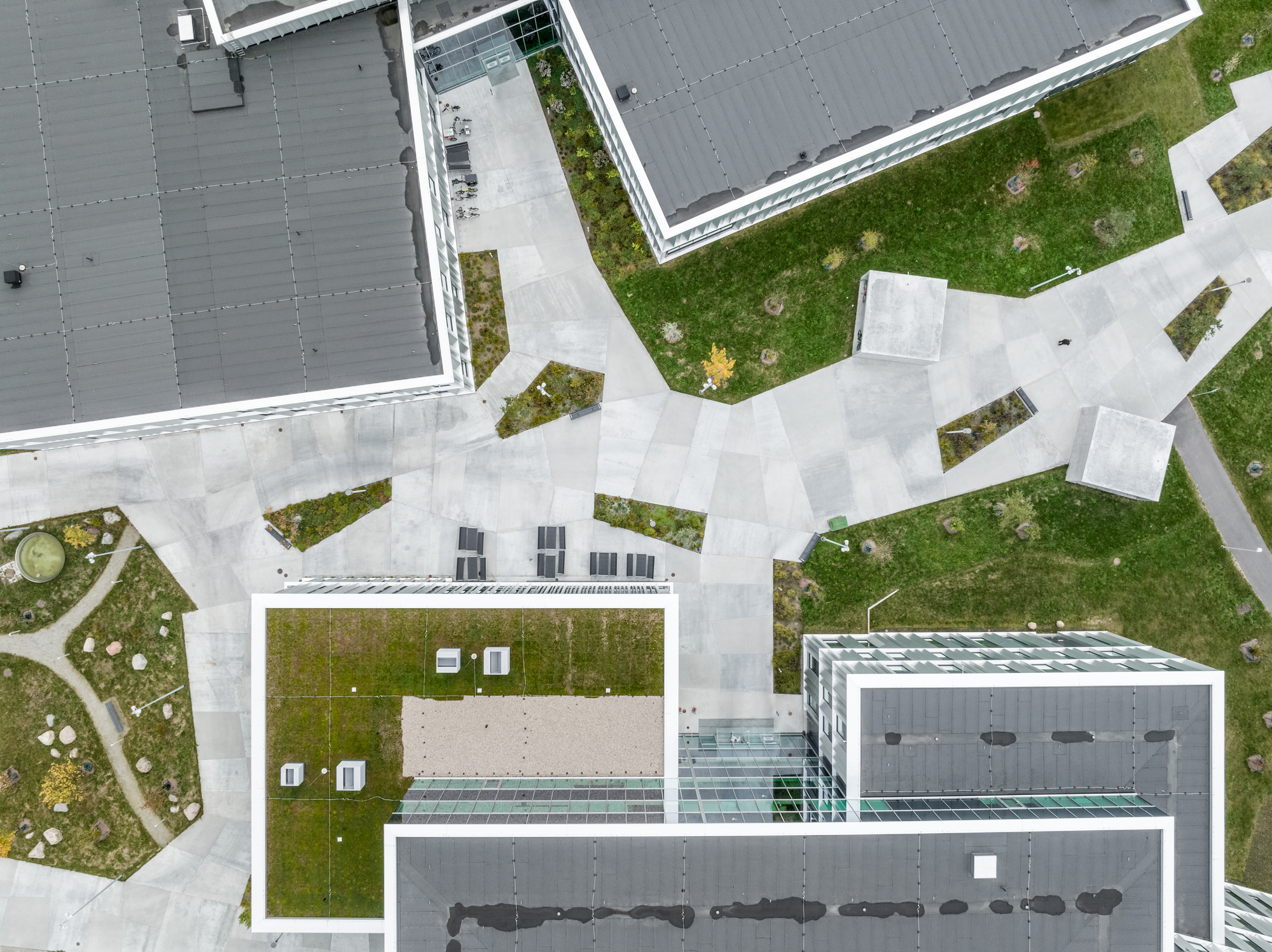




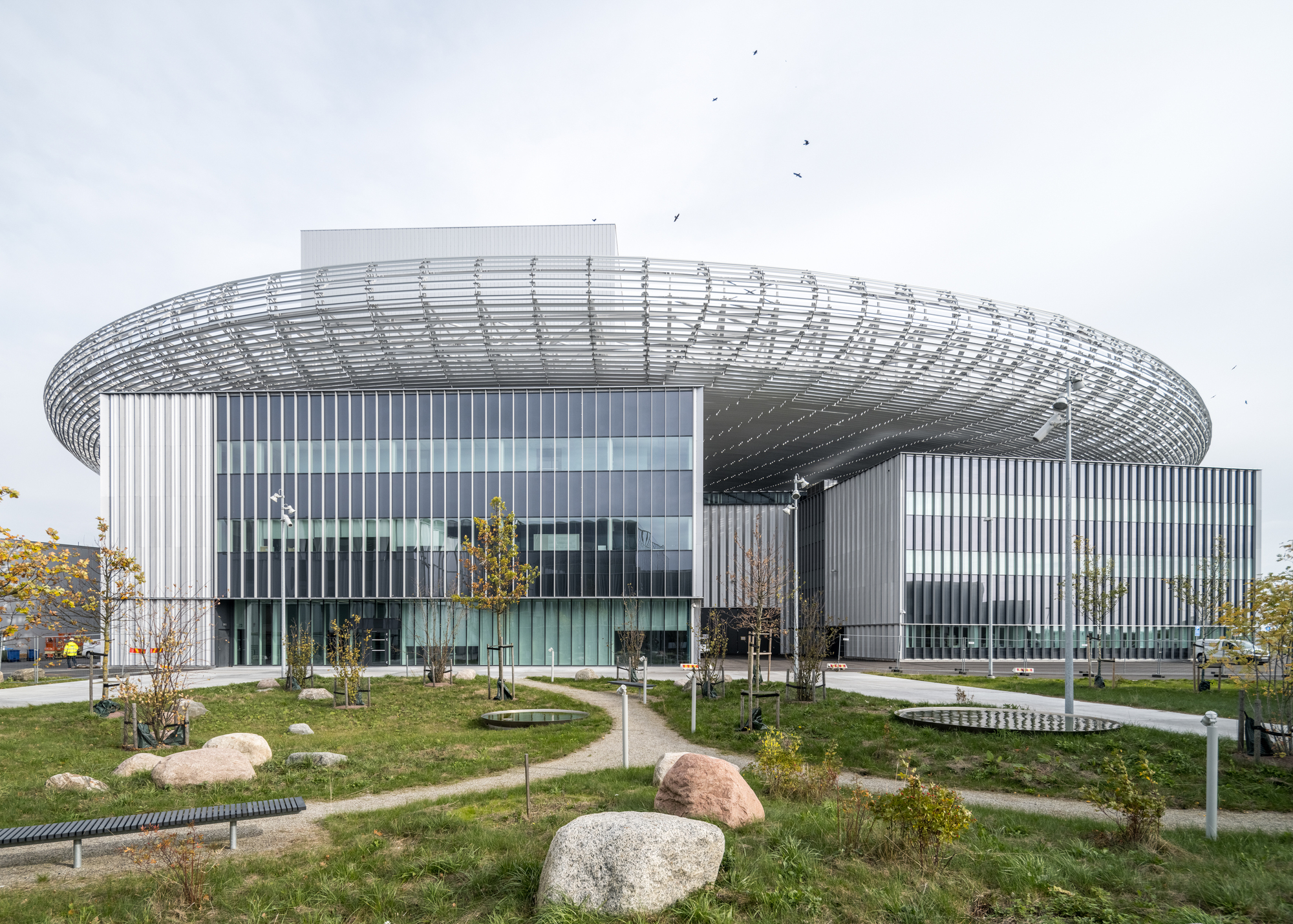
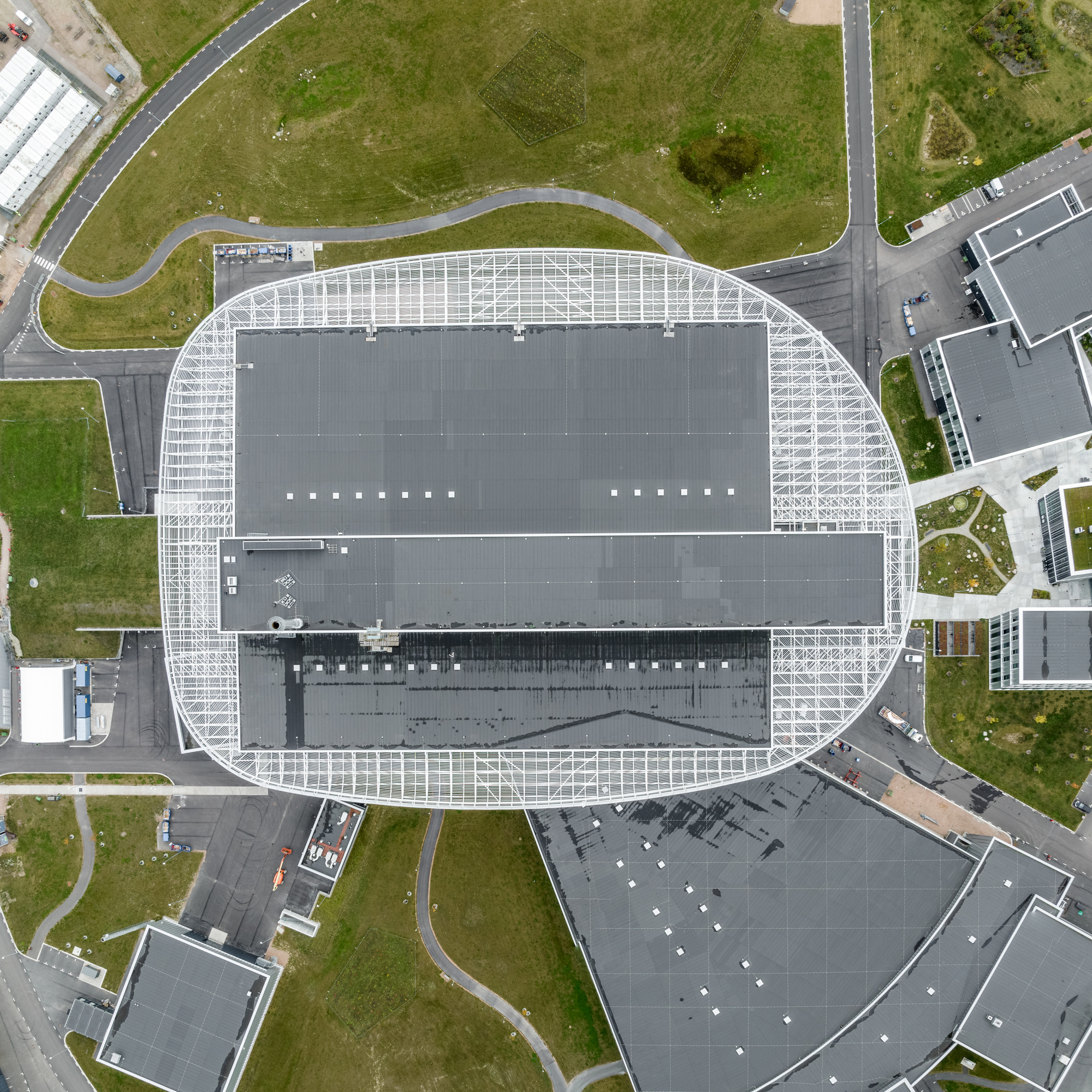
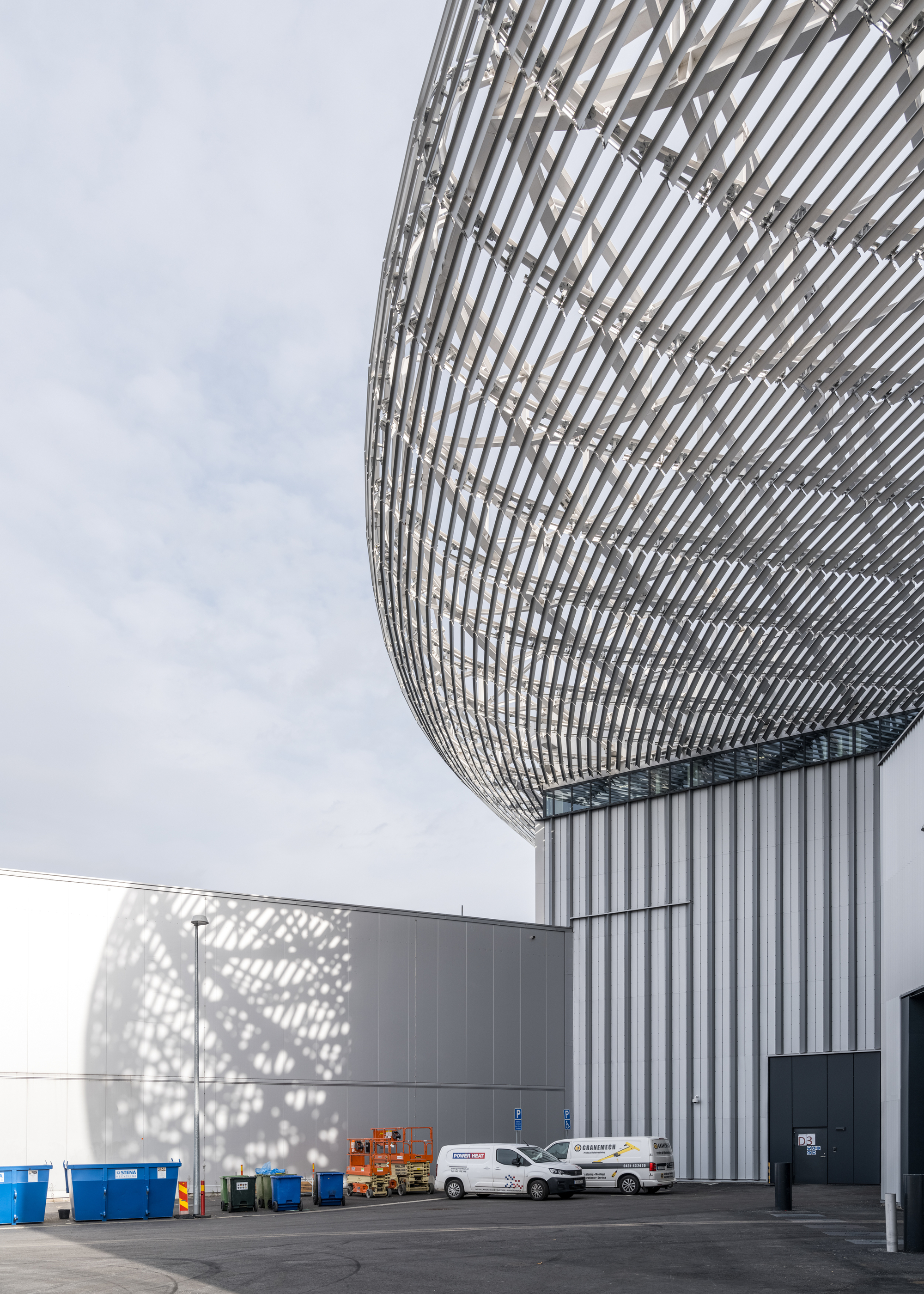
靶站大厅上方的圆形屋顶是整个ESS园区中心的定位点,它是散裂过程中最重要的元素之一 ——钨轮的所在地。受车轮的启发,屋顶的大型圆形结构仿佛飘浮在大厅的上方——轻质的结构确保了屋顶在承载其巨大体量的同时,还能让光线进入大厅,并抵御瑞典多雪的气候。
A central point of orientation for the entire ESS campus is the circular roof above the target hall, home to one of the most important elements in the spallation process, the tungsten wheel. Taking inspiration from the wheel, the roof’s large, rounded structure appears to float above the hall – a lightweight construction ensures the roof carries its significant volume whilst also letting light into the hall and withstanding Sweden’s snowy climate.
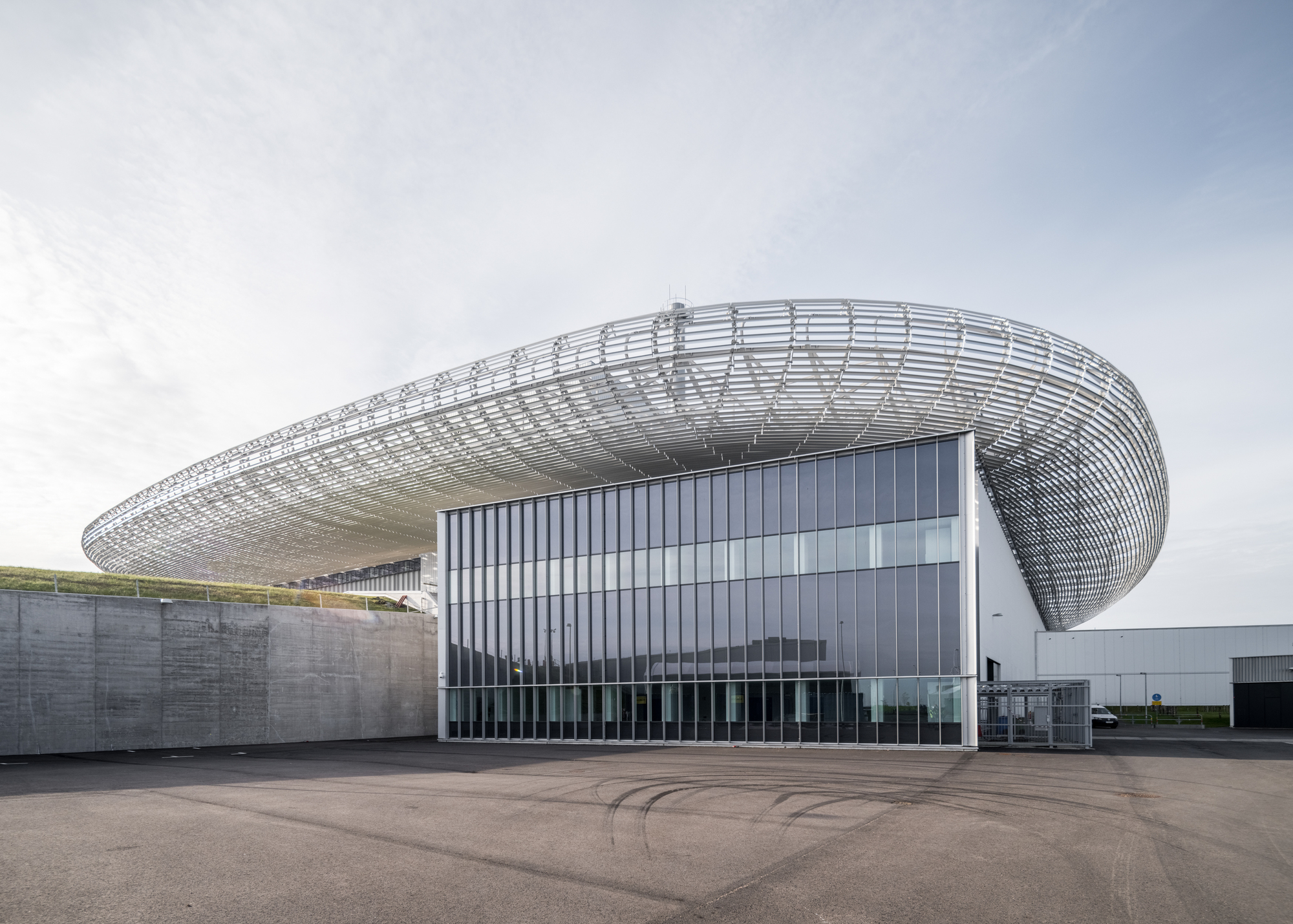
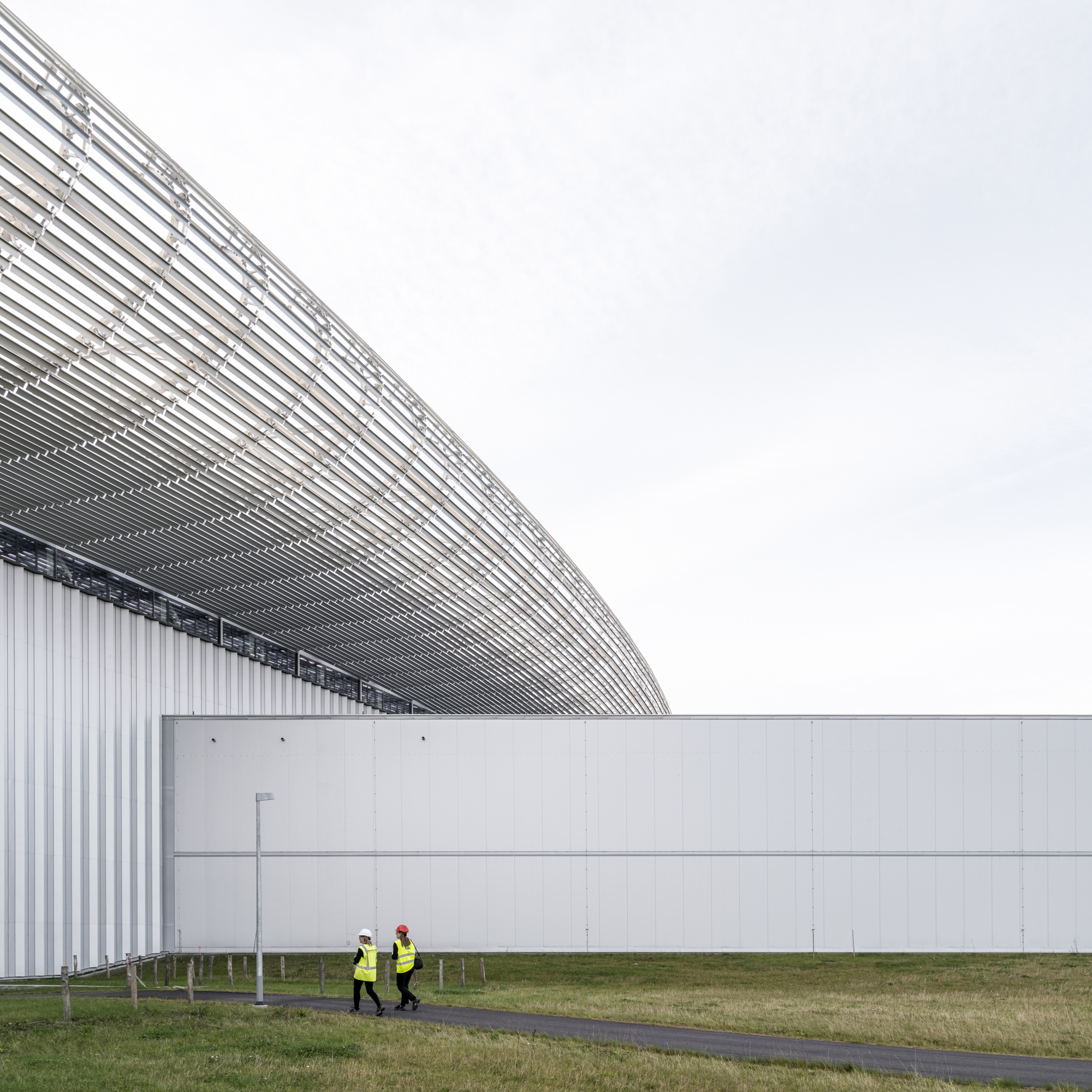



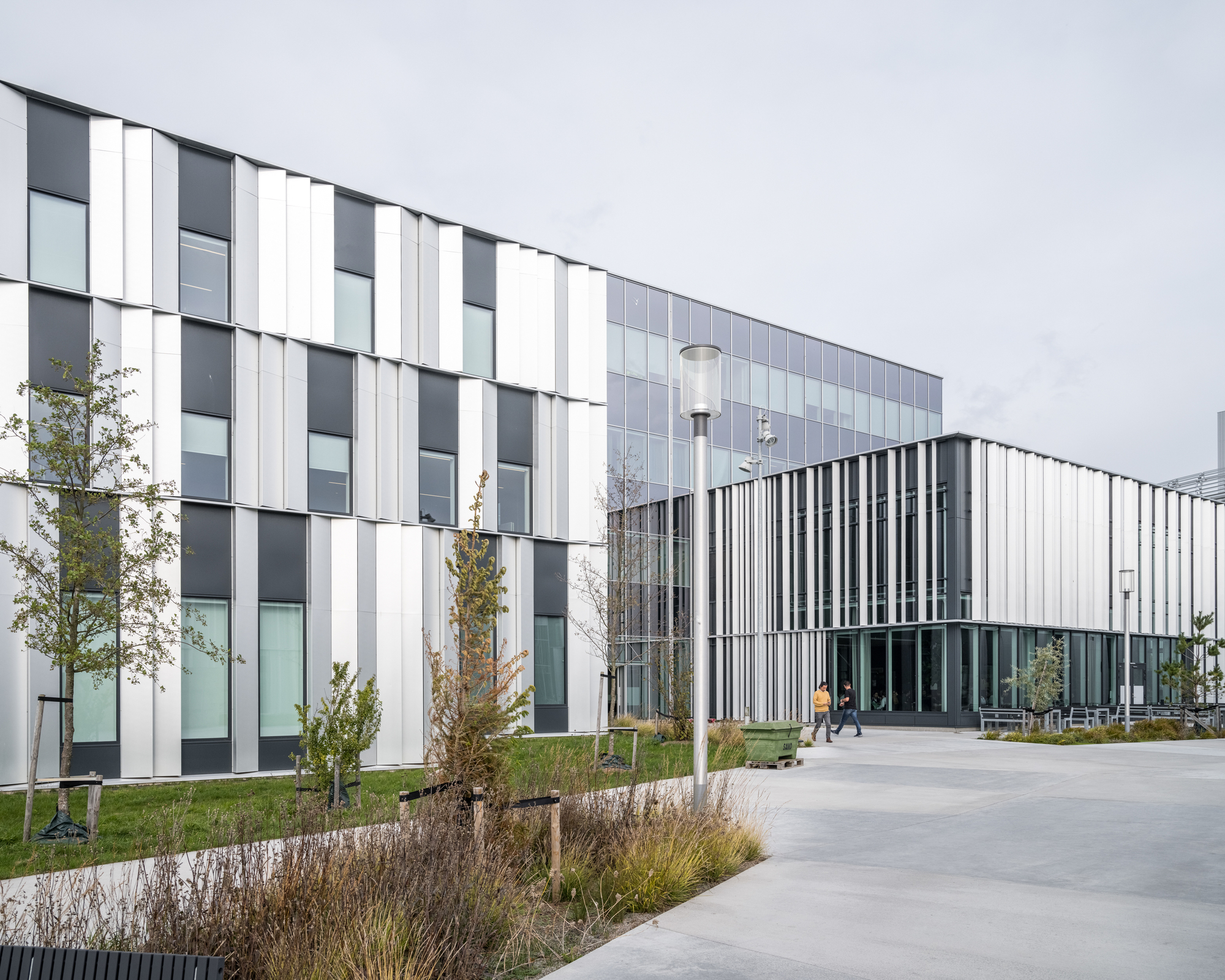
为了使整个园区保持一致的设计语言,所有建筑都被设计成置于景观之中的独立大地艺术品。ESS的每栋建筑在大小和功能上都各不相同,其位置也与散裂的过程息息相关。虽然布置上有着策略性的考量,但园区整体上并不局限于规整的网格布局当中。
To maintain a coherent design expression for the entire campus, the intention is that all buildings are monolithic land-art-objects placed in the landscape. Each building at ESS varies in size and function, positioned in correlation with the spallation process; strategically, yet without a strict grid.
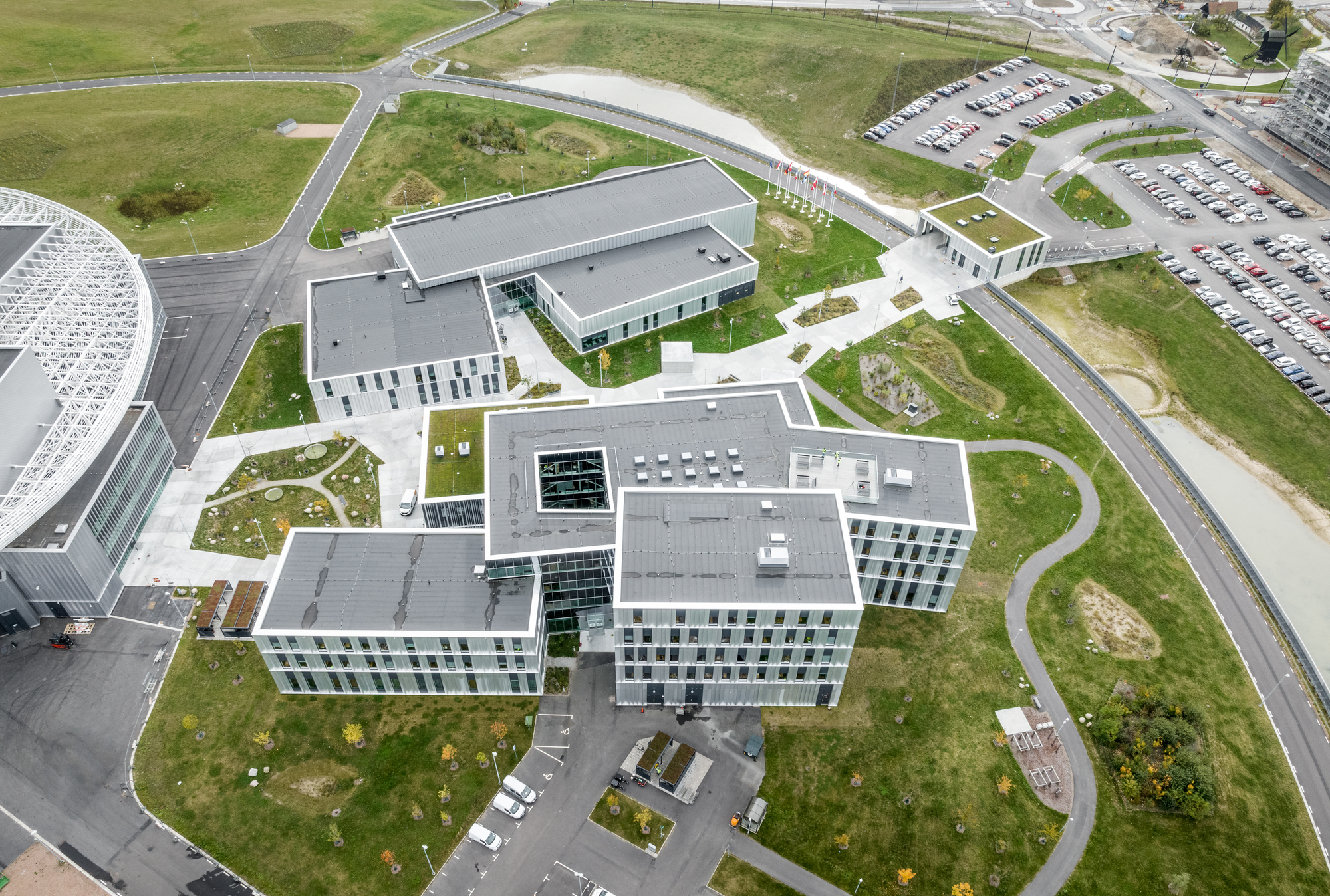
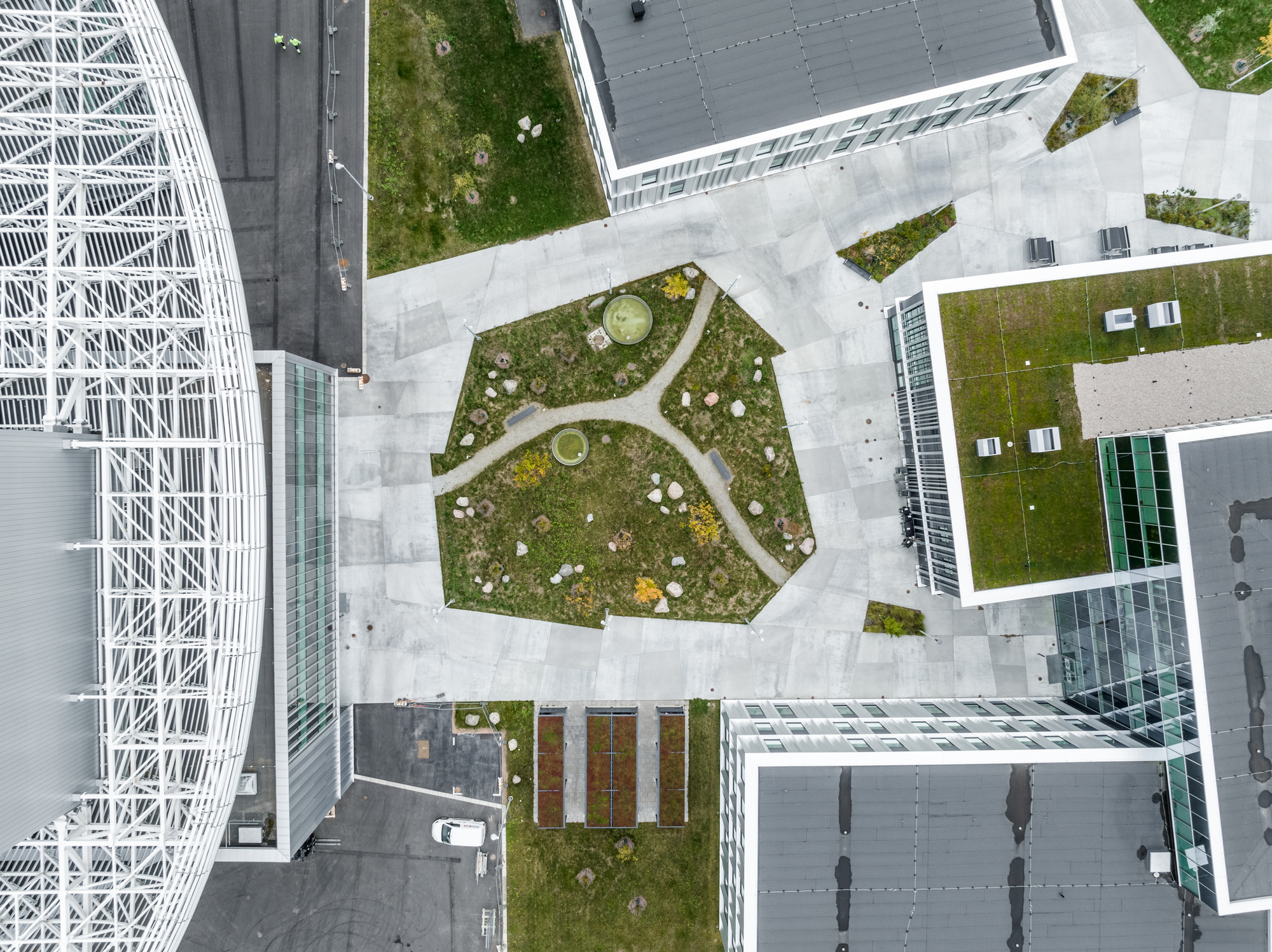


园区中有的建筑保持着独立的体量,有的又是成组出现,因为设计必须要具有灵活性,以便在未来能增加新的建筑。建筑的外观也反映出了自身的用途,其外立面的类型和尺度也遵循了从工业风格到更精致的风格的渐变。这些建筑包括迎宾和办公空间、礼堂和实验室、加速器大楼、靶站和大厅。具有工业建筑风格的外立面设计也体现着内部空间容纳着的流动粒子,而更精致的、有遮挡的外立面下则包含了人们聚集、交流知识和研究的空间。
Some volumes are solitary, and others are clustered, as it is imperative that the design also has the flexibility to accommodate new buildings in the future. The exterior reflects the purpose of each building, the type and scale of the facades is based on a graduation scale from industrial to more refined. The buildings comprise of welcome and office spaces, auditoriums and laboratories, the accelerator building, target room and halls. Industrial facades indicate an interior housing the travelling particles, whereas more refined and shadow facades contain spaces for people to gather, exchange knowledge, and research.
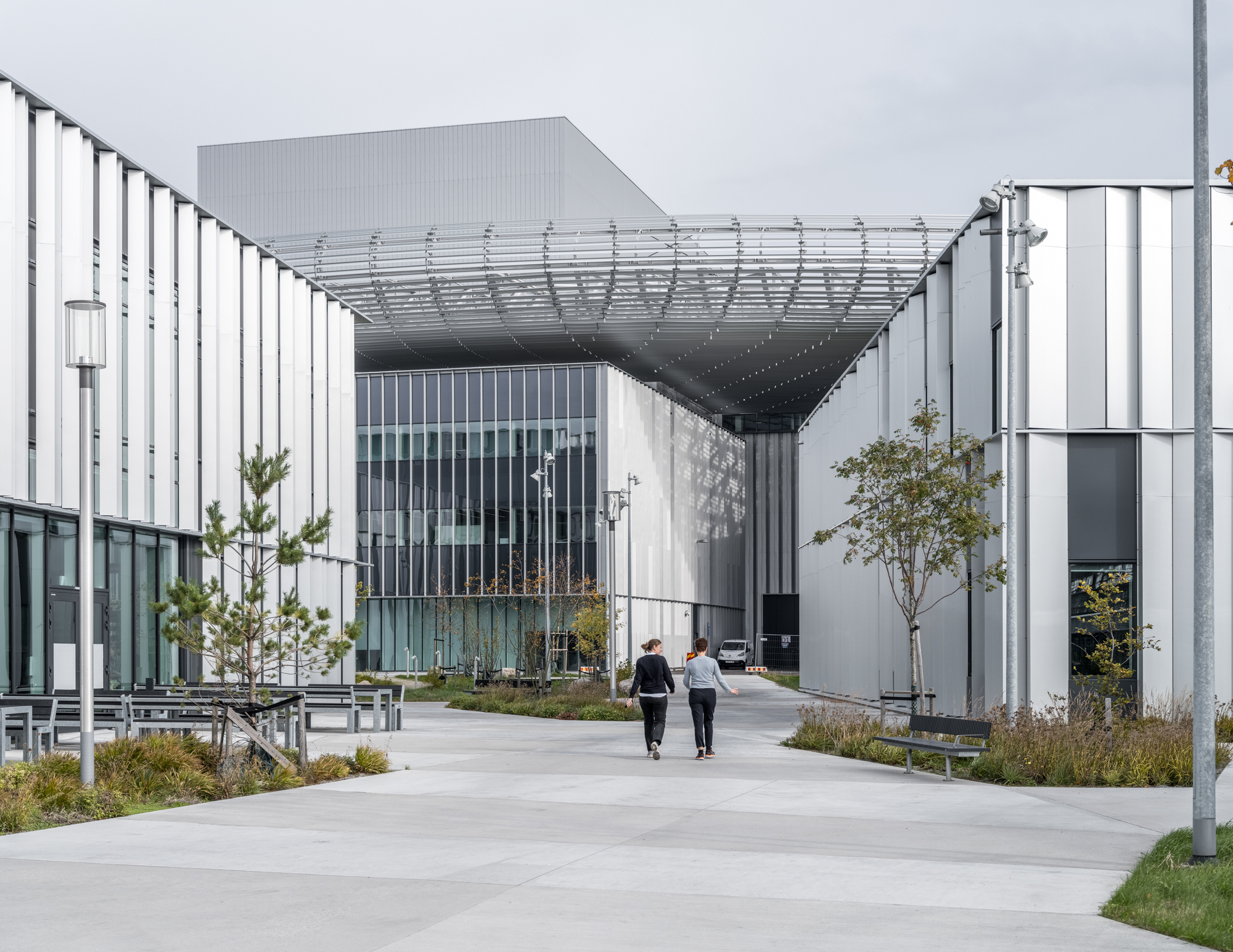


设施的主体部分包括了实验室和会议厅。加速器位于开发项目的中心,是空间与视觉上的焦点所在,促进着园区的活动与形态组织。研究园区内的工作和协作空间旨在最大限度地提高信息交流的效率,营造具有国际水准的学习环境。
The facility contains laboratories, and meeting halls in its main volume. The accelerator sits at the center of the development and becomes a physical and visual focal point that drives the activity and organization of the campus. The working and collaboration spaces in the research campus are designed to maximize efficiency of information exchange, a learning environment of international caliber.



ESS预计将为科学领域的研究人员提供新的机会,在材料和生命科学、能源、环境技术、文化遗产和基础物理学等发挥效益。目前,ESS项目仍在建设中,首批实验预计将于2025或2026年开始,设施将于2027年全面投入运行。
ESS is expected to enable new opportunities for researchers across the spectrum of scientific discovery, including materials and life sciences, energy, environmental technology, cultural heritage and fundamental physics. The European Spallation Source is currently under construction and the first experiments are expected to start in 2025/2026. The facility will be fully operational by 2027.


完整项目信息
Location: Lund, Sweden
Client: ESS – European Spallation Source
Architects: Henning Larsen and Cobe
Landscape Architect: SLA
Collaborators: Buro Happold, NNE Pharmaplan, Piacon AB, Bent Lauritzen, Head of Division, Center for Nuclear Technologies, Radiation Physics
Site: approx. 70 hectares
Gross floor area: 100,000 m2
Number of users: ESS anticipates that up to 3,000 researchers from around the world will come to ESS each year to carry out experiments. At the same time ESS will provide an attractive workplace for more than 500 employees.
Certifications: BREEAM Outstanding
Project cost
Budget: 1 843 M€ (including instruments)
Financing split between member states: The two host countries Denmark and Sweden: 47.5%. Non-host members: 52.5%
Furthermore, the project has gotten in-kind contributions of 550 M€.
版权声明:本文由Henning Larsen授权发布。欢迎转发,禁止以有方编辑版本转载。
投稿邮箱:media@archiposition.com
上一篇:在建方案︱墨西哥LAGUNA纺织厂改造项目 / PRODUCTORA
下一篇:Herzog & de Meuron新作:框架与环路,瑞士创新园主园区