设计单位 产业园区研究中心
项目地点 安徽滁州
建成状态 方案阶段
建筑面积 27.22万平方米
撰文 廉毅锐

滁州科技谷项目位于滁州市高铁新区,距离安徽省省会合肥仅130公里,距江苏省省会南京更是仅有50公里。滁州凭借其地理优势,能够同时串联、共享、补充两个省会城市的发展资源。因此,业主要求设计具有创新示范性,能够通过设计促进园区甚至城区的联动发展。
Chuzhou Science and Technology Valley Project is located in Chuzhou New High-speed Railway District, which is only 130 kilometres away from Hefei, the capital of Anhui Province, and about 50 kilometers away from Nanjing, the capital of Jiangsu Province. Chuzhou could interlink, share and supplement the resources with the two provincial capitals at the same time by virtue of its geographical advantages. Therefore, the owner hopes that this project could be innovative and exemplary, while promoting the development of the park and even the urban area.

01
产业园区的发展迭代
Development Iteration of Industrial Park
回溯产业园区的发展过程,其早期为生产密集型的工业园,功能单一、远离城市、边界封闭;随后逐渐引入研究车间和实验室等功能,产业园区的人员结构也开始更加多元;再后来,出现了更加包容的复合型园区,更多的创新型企业开始聚集,园区更加注重空间氛围,并且开始向城市靠拢。
Back to the development process of industrial park, in the early days, they were always production-intensive factories with single function, closed boundary,and far away from the city. Subsequently, as the introduce of research workshops and laboratories into these parks, the personnel structure became much more diversified. Later, more inclusive complex parks appeared, along with the gathering of an increasing number of innovative enterprises. These parks paid more attention to the spatial atmosphere and began to move closer to the city.
近十年,多数园区已经身处城市环境,即国内俗称“科技园”的都市产业园区。园区逐渐将重心放在技术的改良式小型研发,从产业楼宇聚集走向以地产属性和贸易内容为导向的复合都市产业园。然而,这些园区却依然存在着物理或者心理的边界,始终没有向城市开放。
In the last decade, most parks have been located in urban environments, commonly known as "technology parks" in China. These parks have gradually focused on small-scale R&D with improved technology, moving away from an agglomeration of industrial buildings towards a composite with real estate properties and trade content. However, these parks still have physical or psychological boundaries and have never opened up to the city.

在先前四代产业园区的基础上,我们希望找到属于城市之中的“第五代园区”,来和上一代“都市产业园”进行进一步分离。城市已经无法提供一个纯粹的新的工业用地来承载亩产GDP和存量较低的产业,必须大胆地向科学要产值——即从“制造业”到“创造业”的质变。
Building on the four previous generations of industrial parks, we want to find a 'fifth generation park' belong to the city to further separate them from the previous ones. The city can no longer provide a purely new industrial site to host GDP per acre and industries with low stocks, we should turn to science for output ambitiously- a qualitative change from 'manufacturing' to 'creation'.
而“创造业”的形成,意味着必须要提供一个科学与制造之间的平台,给予配套城市崭新产业属性和前景的新生产业用地,要更好地服务于科学、实验、小试、中试以及一小部分装备组装。“创造业”这个词汇或许令人陌生,但唯因其陌生,才预示着崭新的产业属性和发展前景。
The formation of "creative industry" means that a platform must be provided between science and manufacturing, giving the supporting city new industry land with new industrial properties and prospects, so that to better serve science, experiments, small trials, pilot tests and a small part of equipment assembly. The term "creative industry" may be unfamiliar, but it is the reason why it signals new industrial properties and prospects for development.

02
空间解放的新产业构成组织
New industrial organisation for space liberation
这次崭新的空间形态不仅仅是一种城市形态,也关乎于一个新的园区产业类型组织方式。
The new spatial form is not only urban from, but also about a new type of park organization.

上一代的都市产业园,为了强调产城融合,设计时很容易坠入片面追求增高商业配套面积的途径。而在园区内部,生产性服务业是与小型分散的新兴科技园相适应的、面积少但是效率高的室内商业服务区域,以及类似室外广场的、服务休闲与街巷化的开放场所。
The previous generation of industrial parks, with their emphasis on city-industry integration, were designed in a way that easily led to a one-sided pursuit of increased commercial space. Inside the park, the productive services sector is a small but efficient indoor commercial service area that fits in with the small and dispersed emerging technology park, or an outdoor plaza-like open space for leisure and services.
这种商业裙房与生产性服务业混淆的设置模式,面积不少但效率不高,仍然不能提供给城市内的园区以最佳的服务氛围;生产性服务业需要的大面积的实验室、中试等部分就被挤压,失去了平面展开的机会;同时,商业与产业服务业争抢园区地面,商业和经济逻辑也没有得到合理的市场反馈。产城融合从空间上与内容上只得到了单纯的数量提升,同时却造成地面层与城市边界的封闭,再开放的口号,也都仅限于多开几个园区入口和取消围墙而已。这也恰是约束新一代科技园继续走地产化旧路的措施。
The confusion between commercial podiums and productive services always need large space with low efficiency, and still does not provide the best service atmosphere for the inner-city park. Also, the large area for laboratories and pilot tests needed by the productive services is squeezed, and the opportunity for expansion is missing. At the same time, commercial and industrial services compete for the ground level of the park, and their economic logic does not receive reasonable market feedback. The integration of production and city has only got a simple quantity improvement in space and content, but has resulted in the closure of the ground floor to the city. The slogan of openness is limited to the opening of a few more entrances to the park and the removal of walls. This is precisely the measure that restrains the new generation of technology parks from continuing the old path of real estate.
用商业、生产性服务业与研究、制造本身相混合,形成一个有智能、有制造的中小型复杂社区,即“创造性制造业综合体园区”,正是我们在寻找的中国城市中的“第五代园区”。
Mixing business and productive services with research and manufacturing to form a small to medium-sized complex community with intelligence and manufacturing - a 'creative manufacturing complex park' - is what we are looking for as the 'fifth generation park’ in Chinese cities.

由此,对于环境的创新,是“第五代园区”设计的另一个特点。
Thus, innovation in the environment is another feature of the "5th Generation Park".
我们将园区商业服务放置在地面一层,并结合以最适合商业的“街巷”格局,增加商业延展面与价值。利用好城市优势的生活服务品质,是提供给产业用地以科学和技术的创造性加持。
We place the park's commercial services on the ground floor and combined them with a "street" pattern that is much more suitable for business, increasing the commercial extension and value. Taking advantage of the city’s quality living service is the creative addition of science and technology to the industrial land.

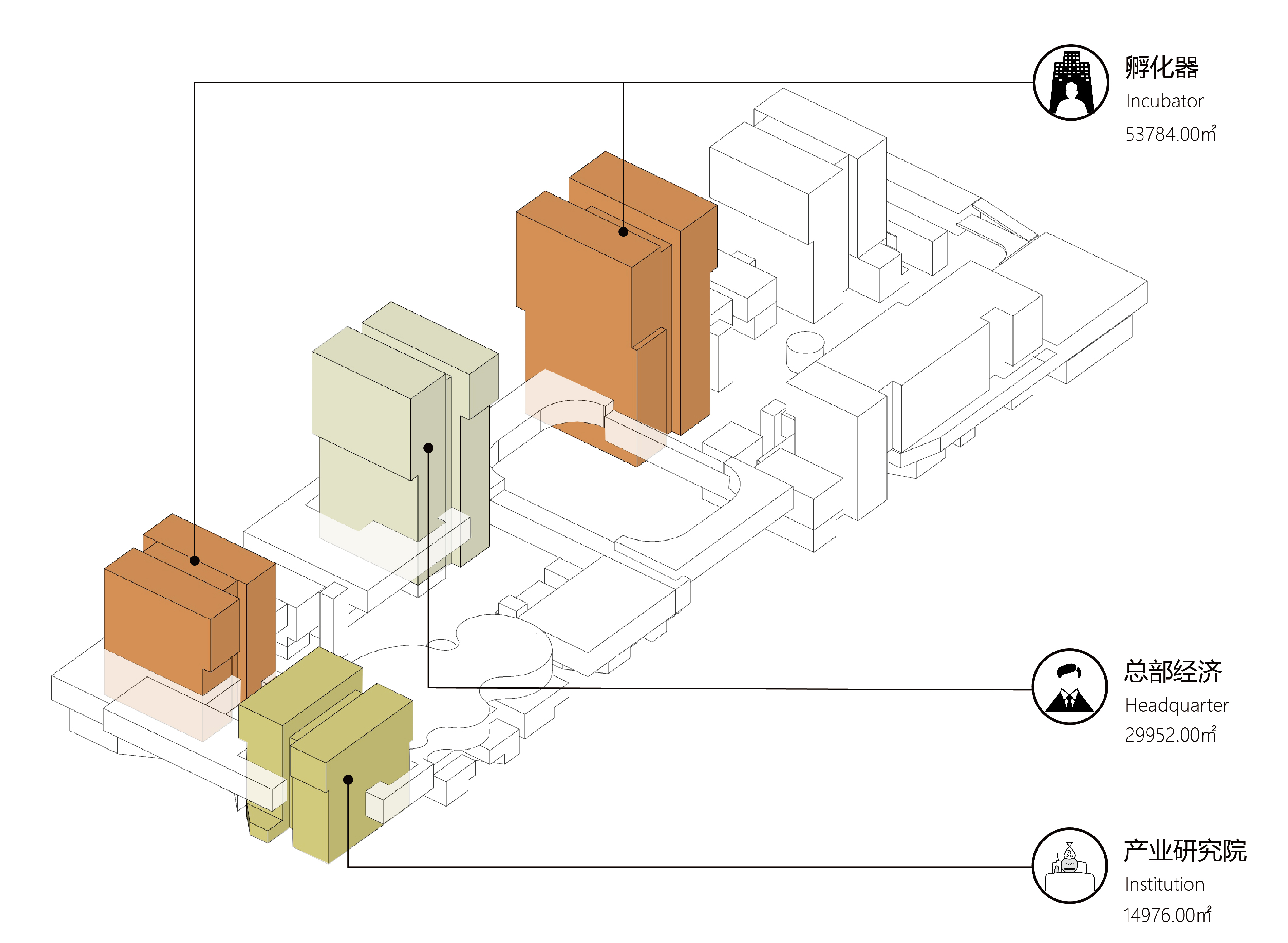
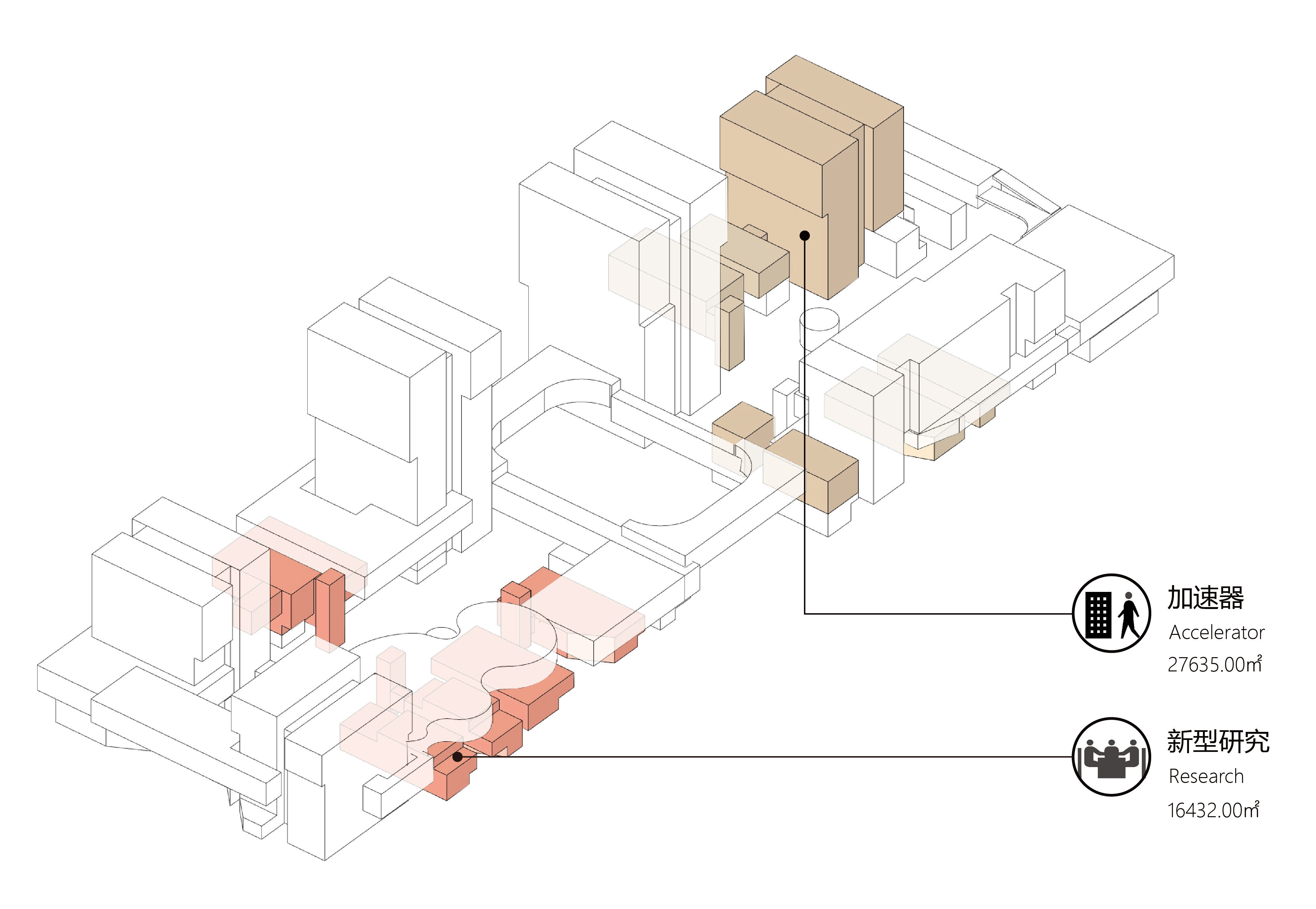
我们将生活服务业空间放置在首层,但生产性服务业架空于地面,二层大开间的空间也不再用作商业,而是作为科学园区的生产性服务业——共享实验室、共享小试和中试车间,以补偿国内诸多已有一些研发成果的中小型公司缺乏单独设置的实验室设备和中试车间的研究短板。这个环节所对应的空间,也是区别产业园区是围绕产业或是围绕地产与贸易的试金石之一。走过需要科技地产化的时代,而接下来的时间,是要欢迎制造业的回归。
We place the living service on the ground floor, but production service is elevated on the second floor with large open space for shared laboratory, sharing pilot plant, compensating for many small and medium-sized companies that already have some R&D achievements but lack of separate laboratory facilities and pilot plants. The space corresponding to this link is one of the touchstones that distinguishes industrial parks from those based on industry or real estate and trade. After the era of science and technology estate, the next is to welcome the return of manufacturing.
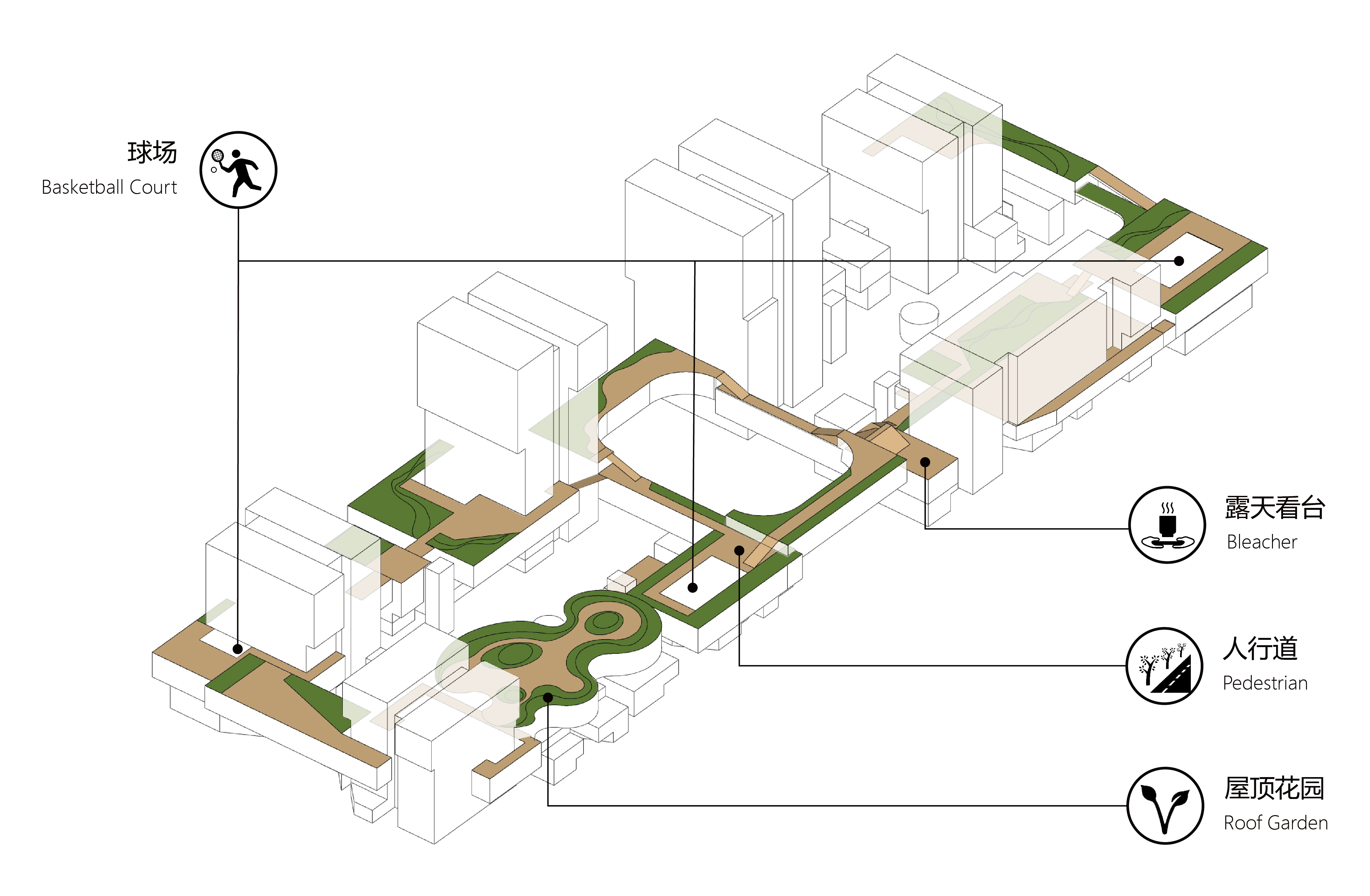
此外,我们在四层裙房屋顶增设产业空中花园,增加园区步行道路和绿廊的空中层级。
In addition, we have added an industrial sky garden on the roof of the four-storey podium to increase the sky level of the park's pedestrian paths and green corridors.

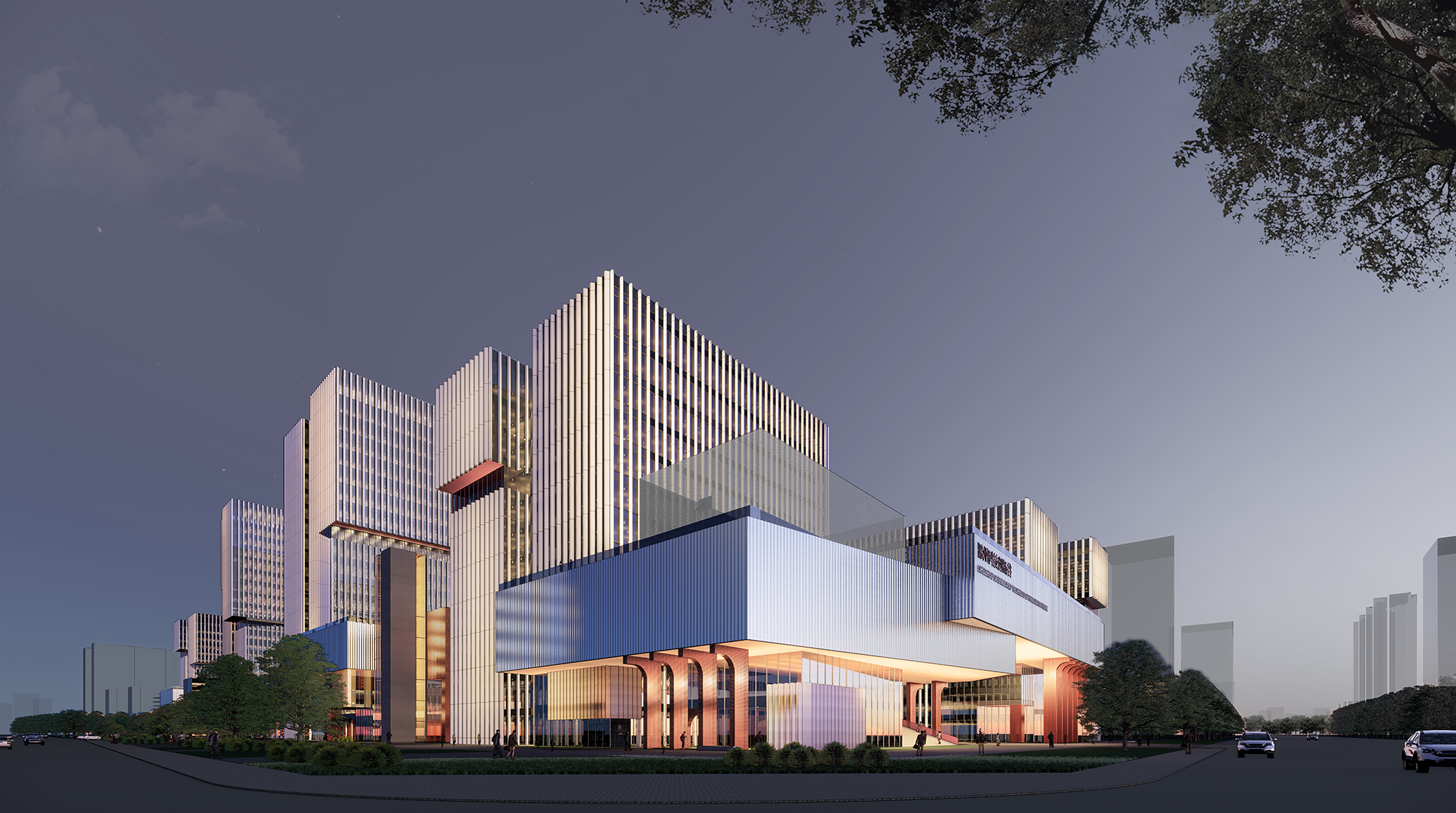
结合项目的区位以及条件,我们为滁州科技谷项目提出了“厂区、园区+街区+社区”的定位,使之成为一个集工作、研学、生产、生活、休闲于一体的具有鲜明当代特征的综合体园区。
Considering the location and conditions of the project, we put forward the positioning of ' factory, park + block + community ' for the Chuzhou Science and Technology Valley, making it a park-complex with distinct contemporary characteristics including work, research, production, living and leisure.
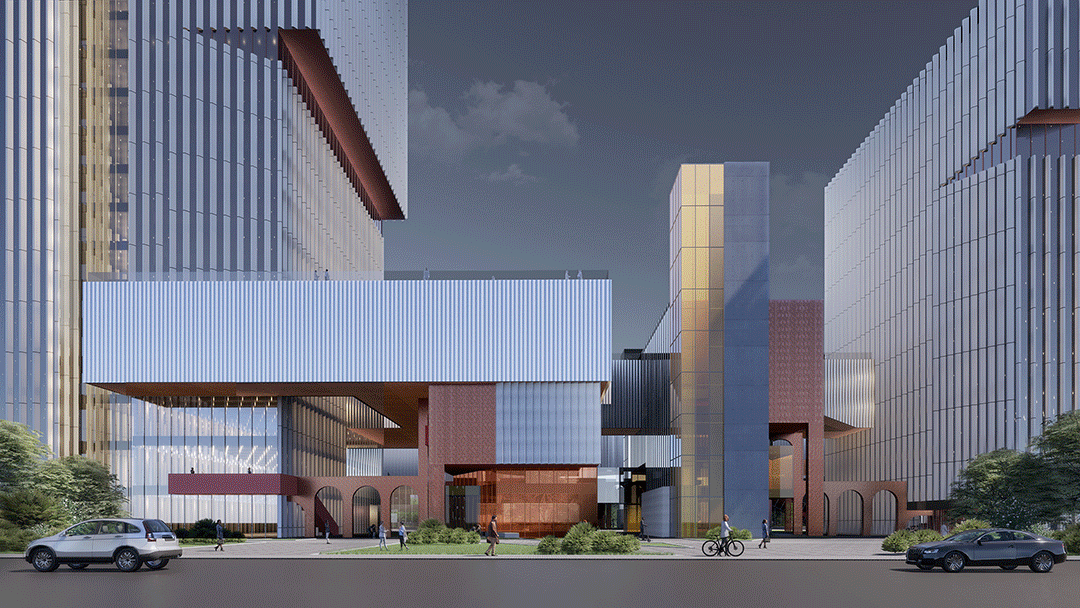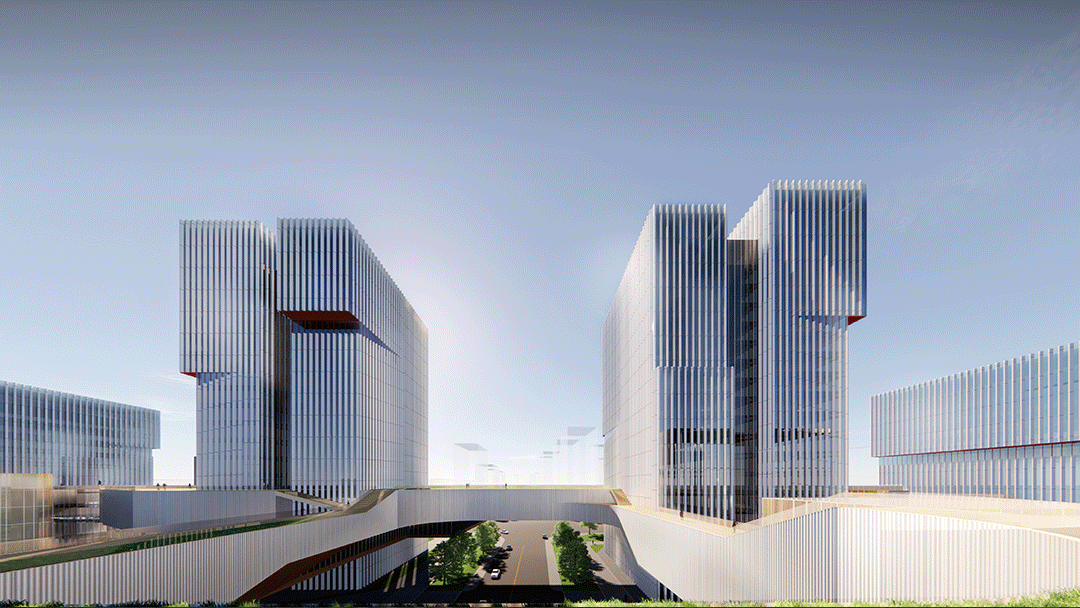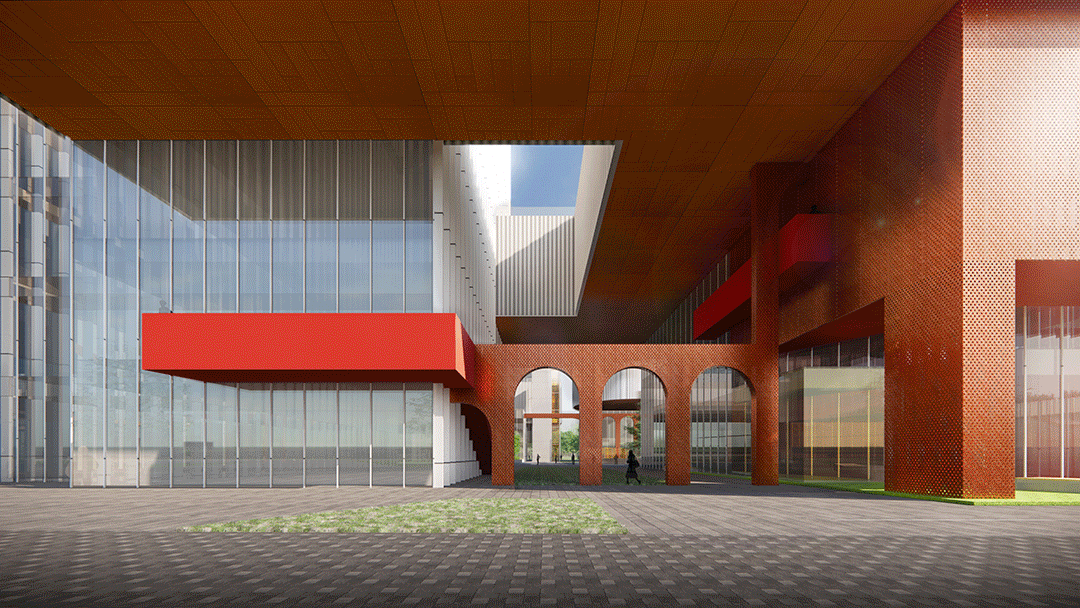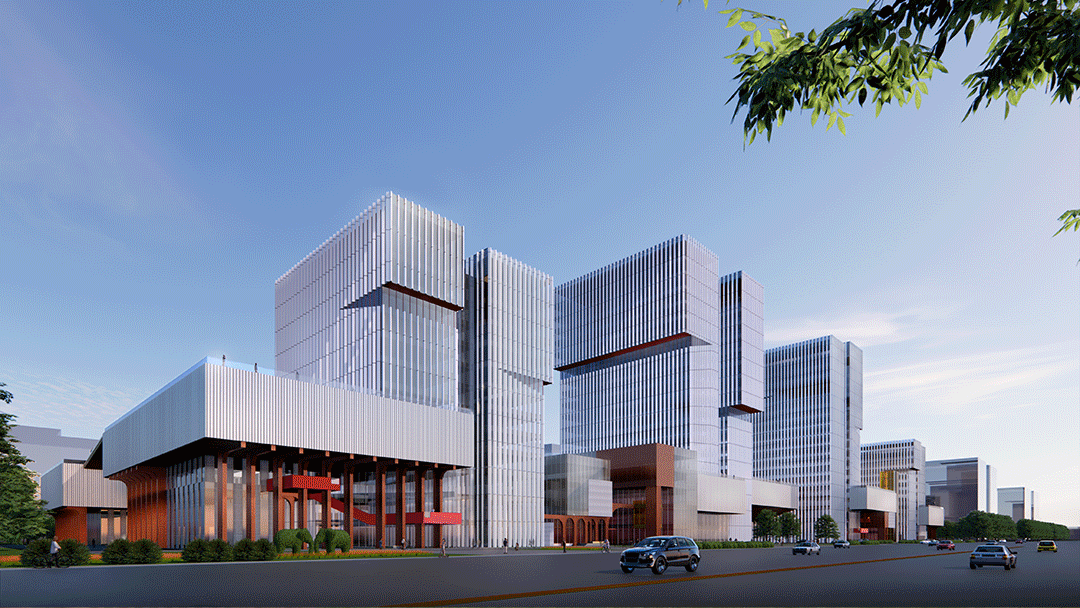
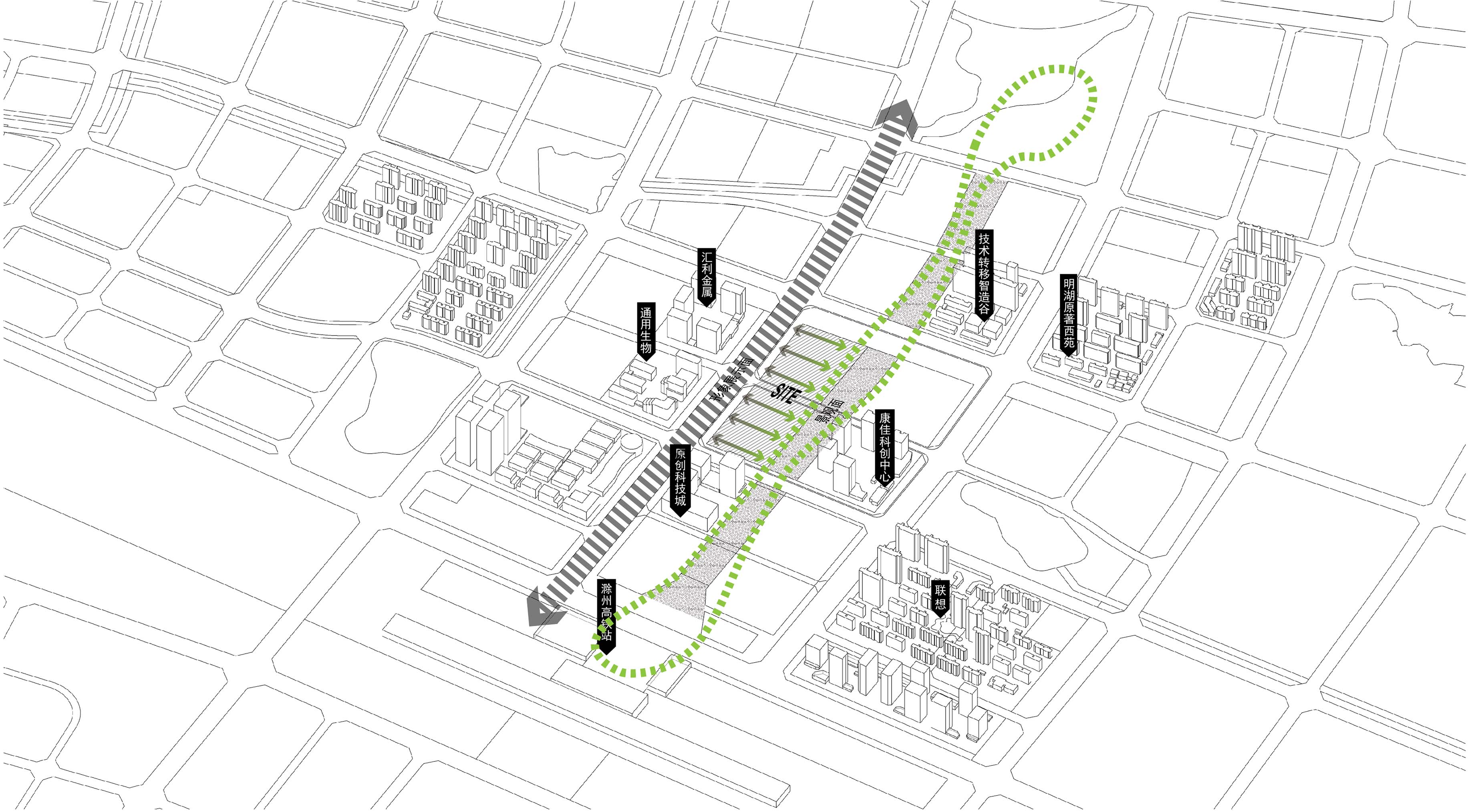
地块南北长,东西短。场地西侧,紧邻连接高铁站与滁州市主城区的繁忙通道——中都大道,被作为项目的主要形象展示面;东侧是高铁新城中心景观轴,被作为项目的景观休闲面。方案通过建立中都大道与中心景观带之间的联系,缝合场地两侧的城市界面,将人流和景观引入场地的同时,也将场地向城市开放,激活场地内活力,提升园区空间品质和价值。
The plot is long from north to south and short from east to west. As the main image display of this project, the west side of the plot is close to Zhongdu Avenue, which is a busy channel connecting the high-speed rail station and the main urban area of Chuzhou City. The east side that represents the leisrure image of the park connects the landscape axis of the high-speed rail new town. This project sutures the urban interface on both sides of the site by establishing a connection between Zhongdu Avenue and the central landscape belt, which could not only introduce people and landscape into the park, but also allow it open to the city, so as to activate the vitality of the project, and enhance the quality and value of the park.

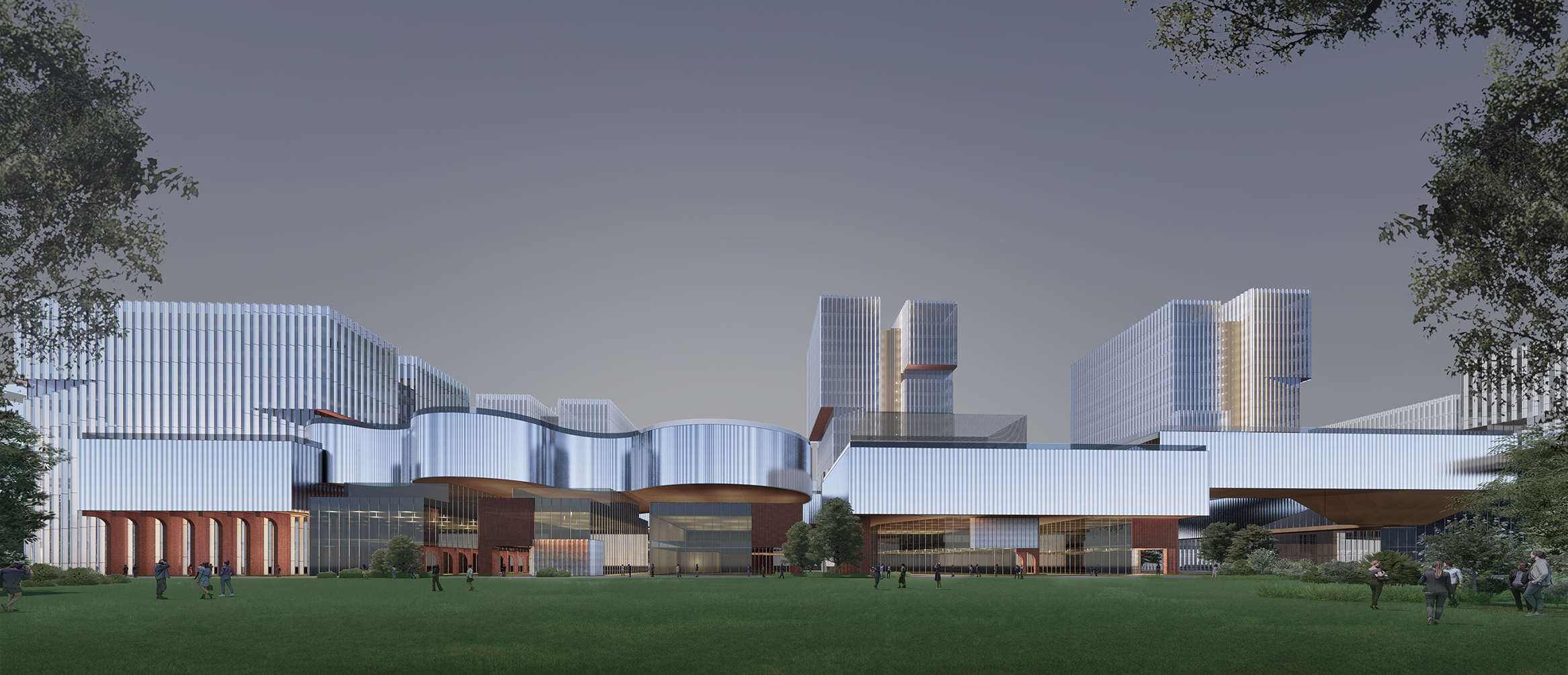
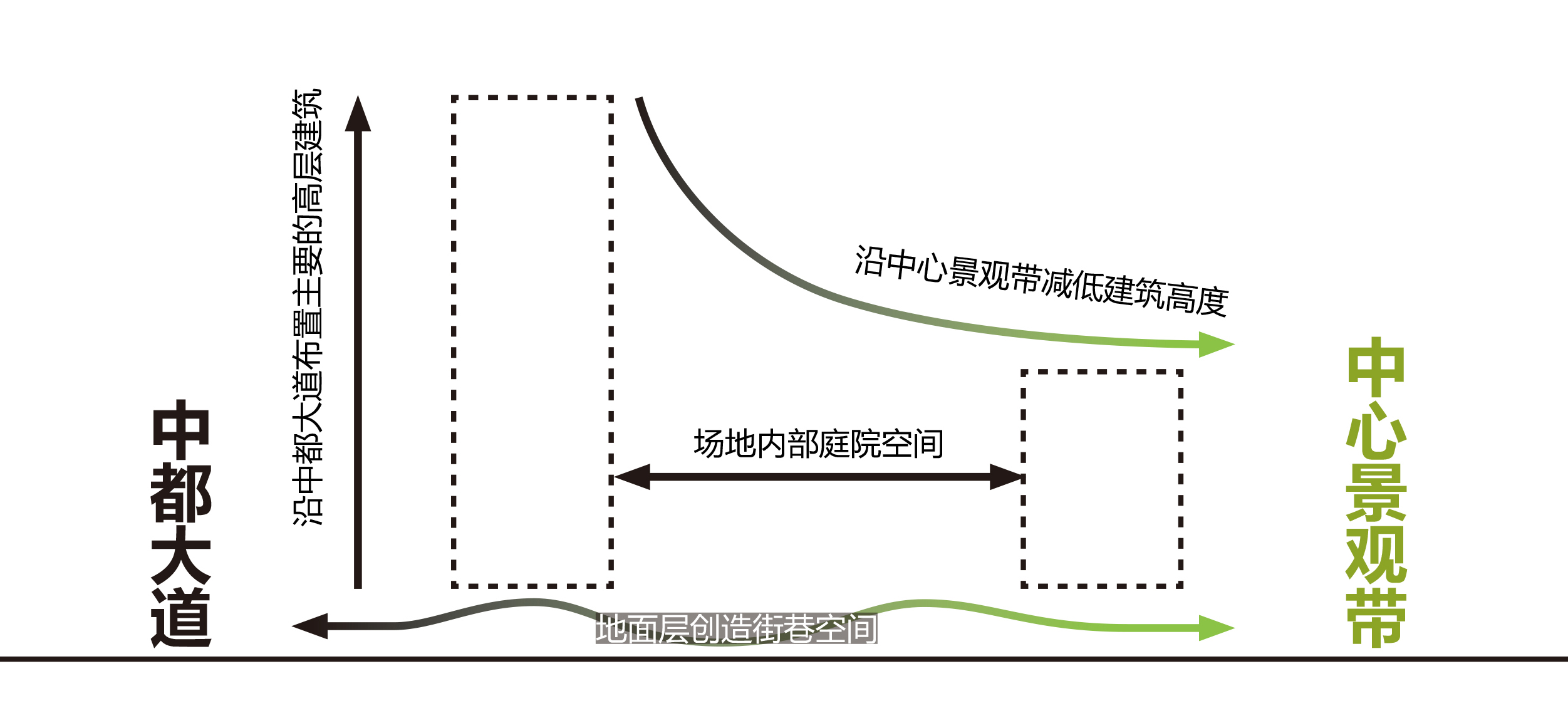
场地东西两侧的不同属性决定了建筑在东西两侧的不同高度:面向西侧布置较高的建筑体量,以形成更好的形象昭示性;面对中心景观带一侧则布置较低的建筑体量,最大限度创造场地和景观的关联;场地内部则创造出庭院空间。
The different properties of the east and west sides of the site determine the different heights of buildings on each side: higher building masses are placed on the west to create a better image; lower building masses facing the central landscape area to maximise the connection between the site and the landscape; and courtyard spaces are created within the block.

在整体体量策略基础上,场地内的功能和空间策略则进一步强调了“厂区、园区+街区+社区”的构想。
Based on the overall massing strategy, the functional and spatial strategy further emphasises the concept of "factory, park + neighbourhood + community".
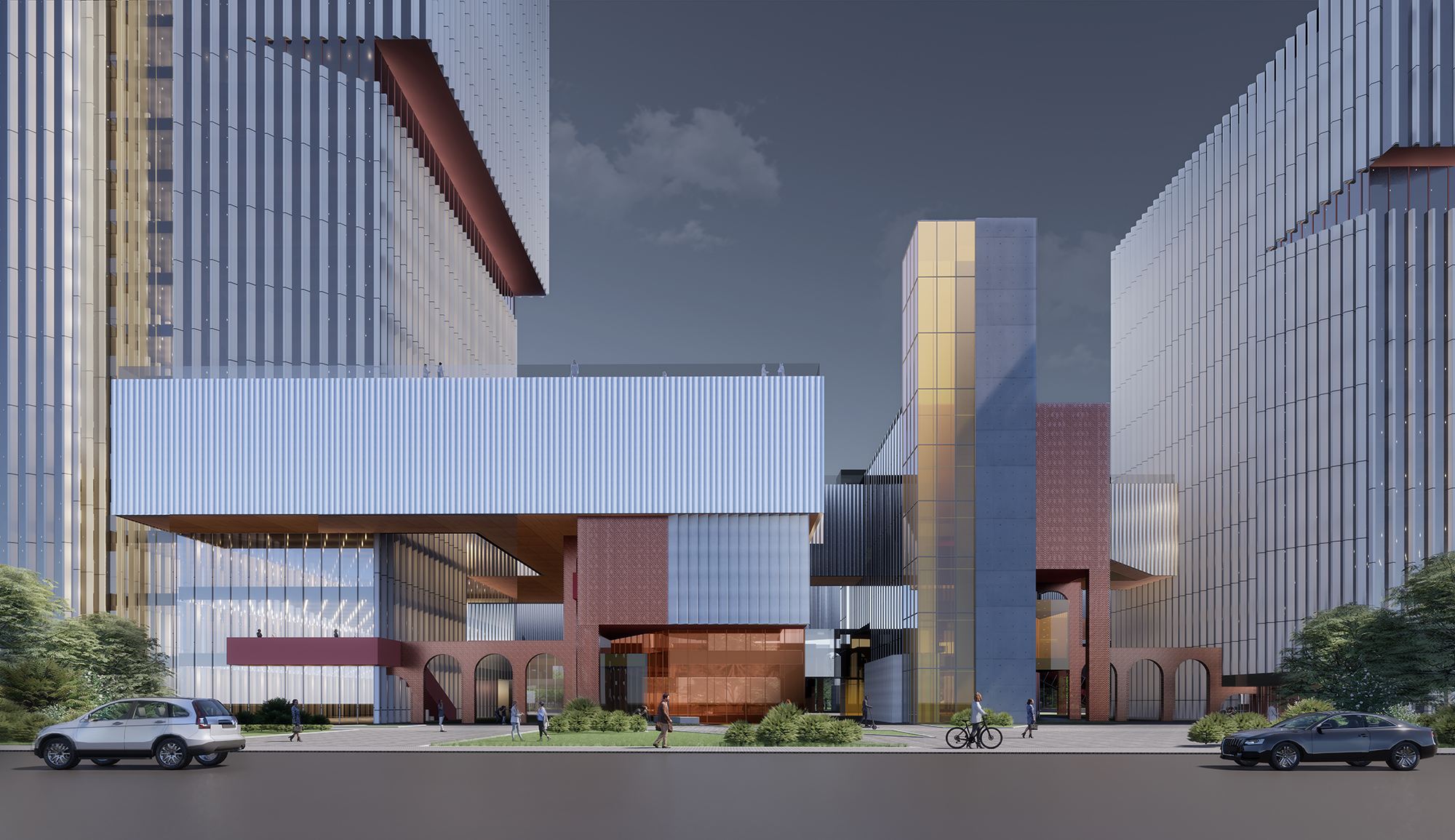
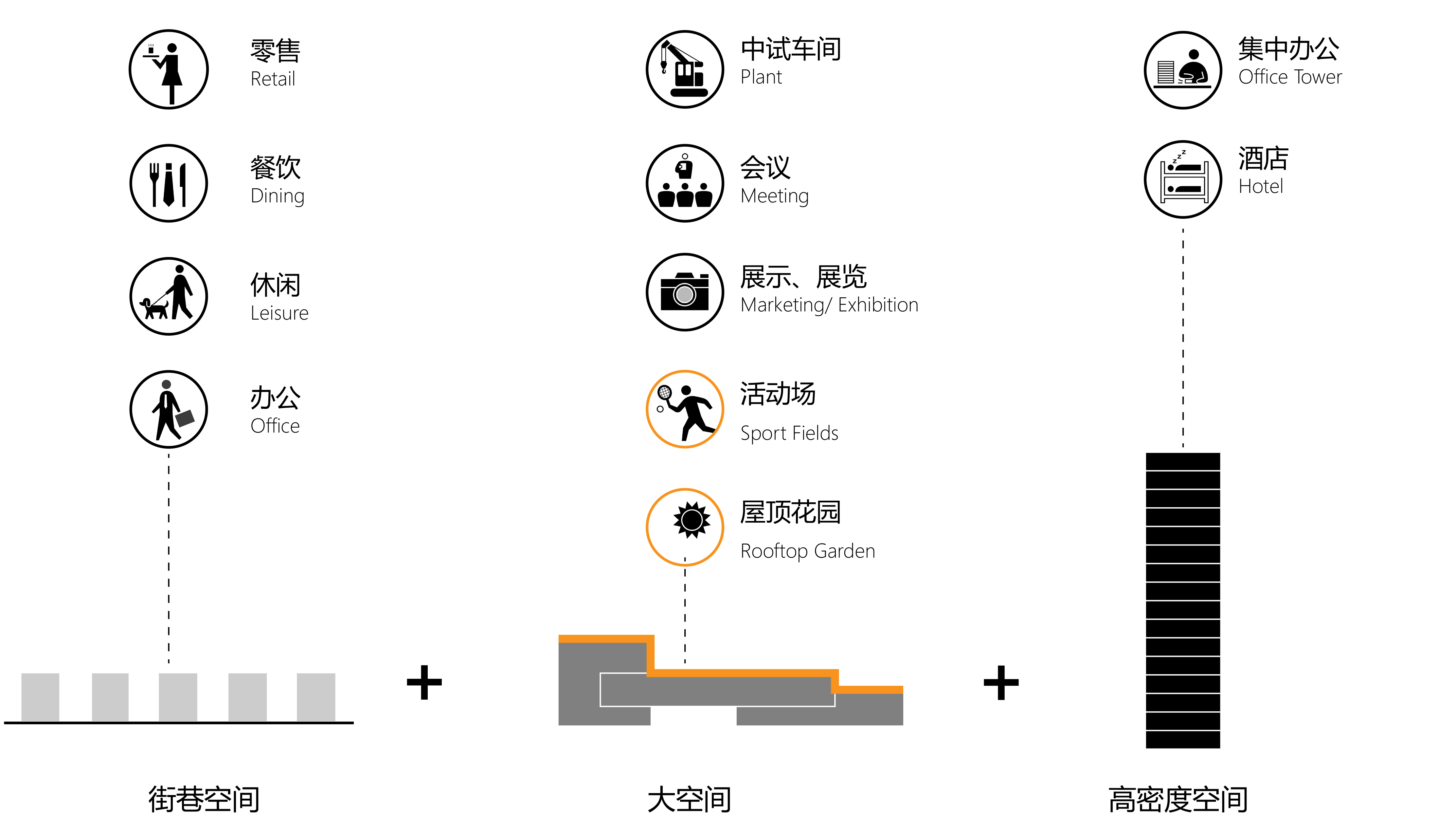

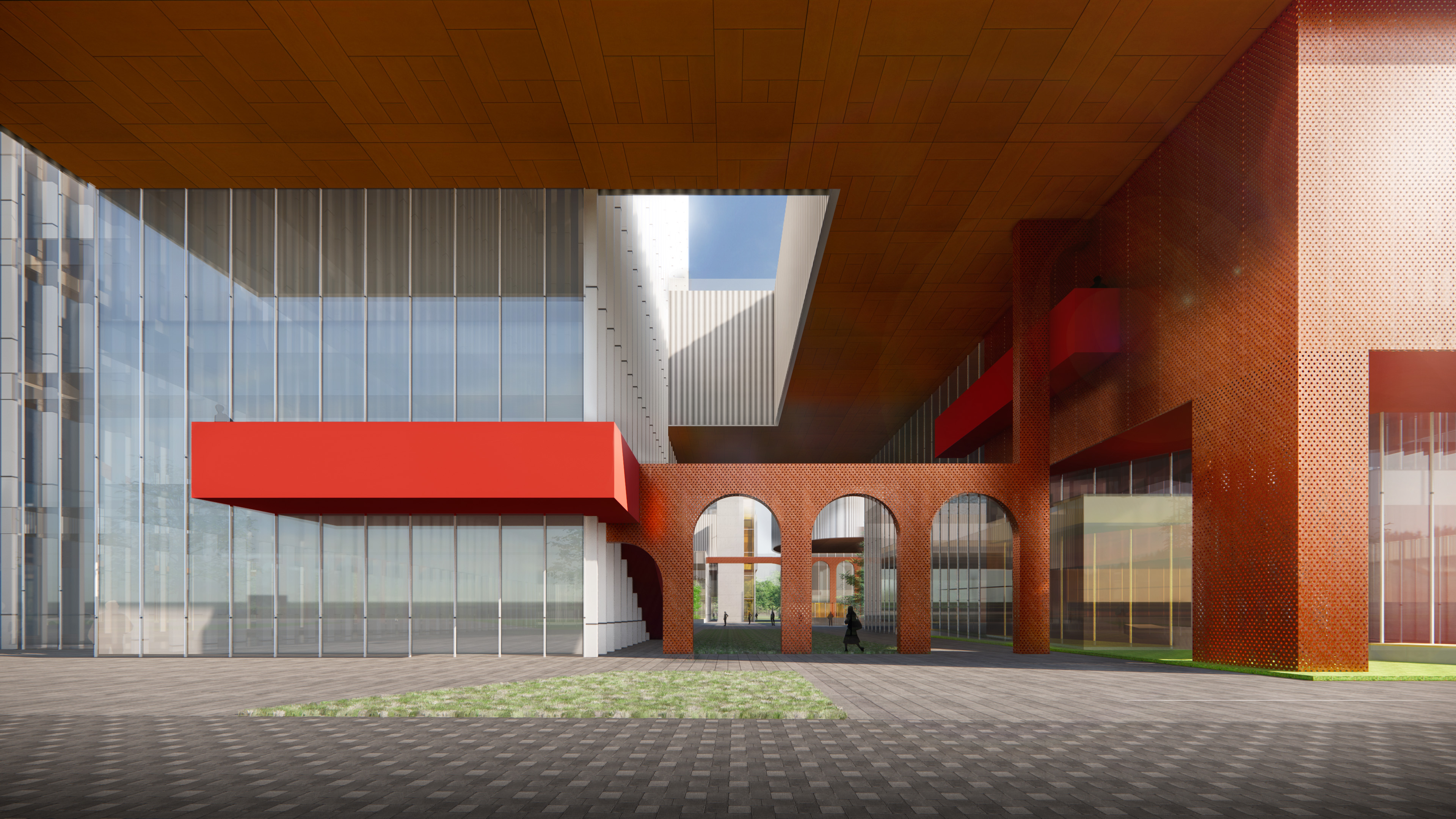
区别于上一代产业园区的疏离感和封闭感,滁州科技谷的底部为较小体量建筑塑造了小尺度开放街巷空间,同时在园区底部主要设置商业功能。因此,园区底部在空间与城市直接相连,提供了亲切的城市尺度,并在业态上同时服务于园区和城市,创造出良好的社区和街区氛围。
Different from the sense of alienation and closure formed by the huge building volume in the traditional industrial park, the ground-floor of Chuzhou Science and Technology Innovation Valley is featured by small-scale open street space shaped by smaller buildings that are mainly for commercial functions. Therefore, the bottom space of the park is directly connected to the city, providing a friendly urban scale, serving the park and the city at the same time, creating an excellent community and neighbourhood atmosphere.

园区中段为大空间,空间之间相互穿插渗透,从而能够实现灵活的空间变化,满足中试、会议、展览等功能对空间的不同形态需求。大空间错落的顶部高低相连,同时也成为供办公人群使用的活动场地和屋顶花园。
Large spaces interlocked with each other are located on the middle layer of the park, allowing flexibility and spatial diversity, as well as meeting changing needs including pilot test, conference, exhibition and other functions. At the same time, the tops of these large spaces are connected, providing sharing activity space and roof garden for the staff.


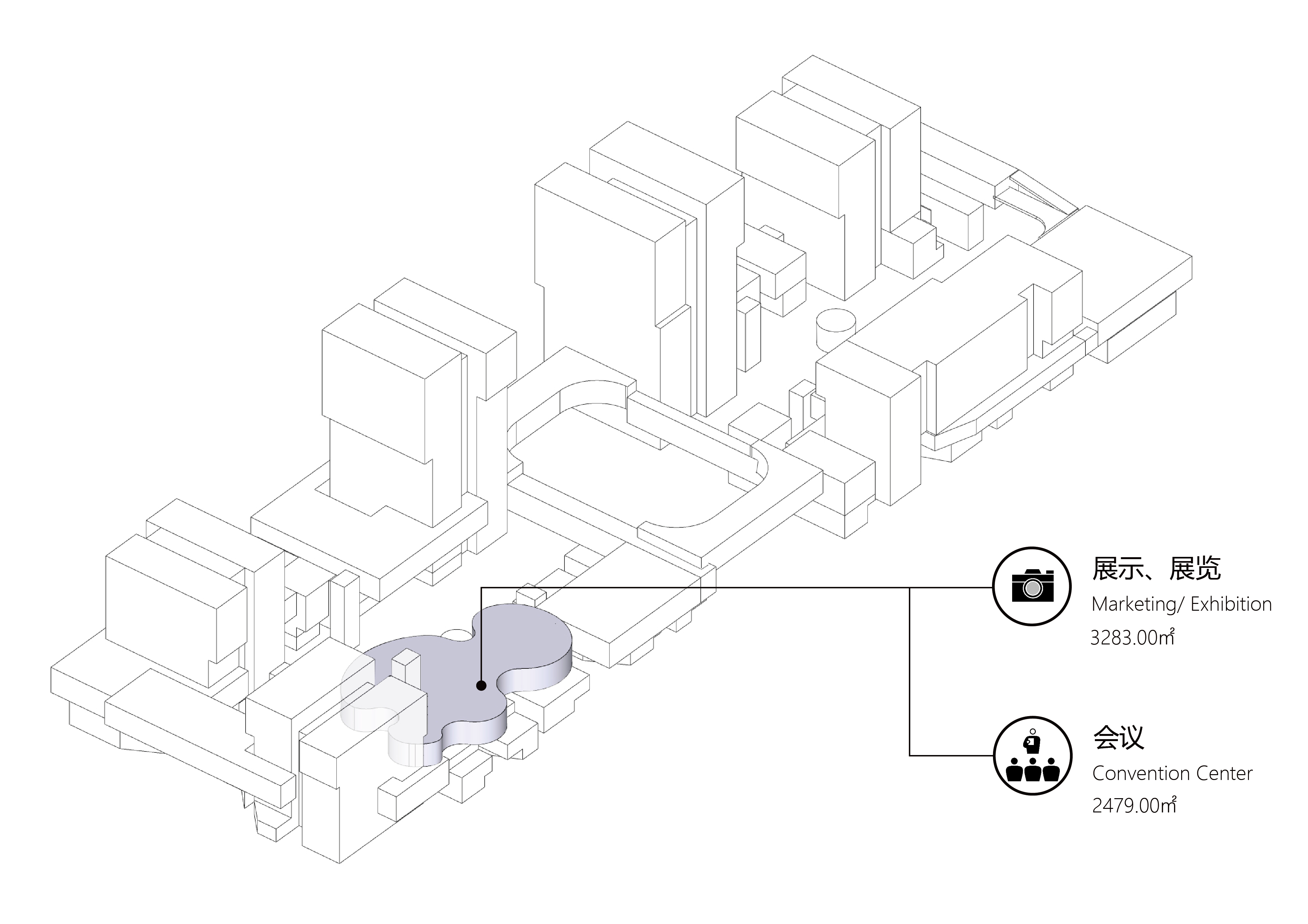

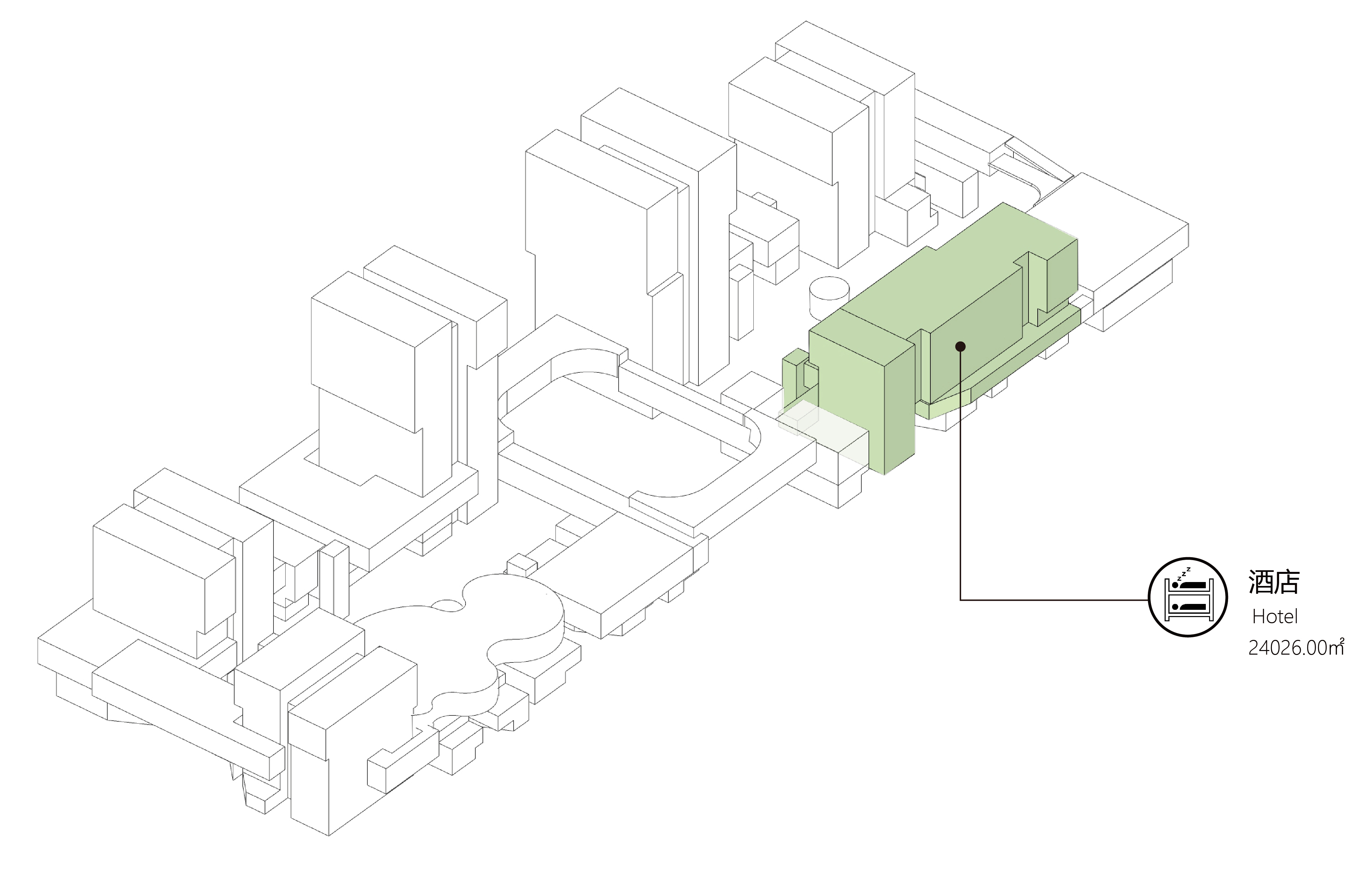
园区上部为高层建筑,不仅为园区提供了大量的高密度集中办公和酒店空间,而且形成了园区的天际线,塑造了项目的城市形象。
The upper layer of the park are high-rise buildings, which not only provides a large number of high-density centralised office and hotel space for the park, but also forms the skyline of the park and reshapes the city image.




04
高密度空间
产业与社区空间的有机融合
High Density Space
Organic Integration of Industry and Community
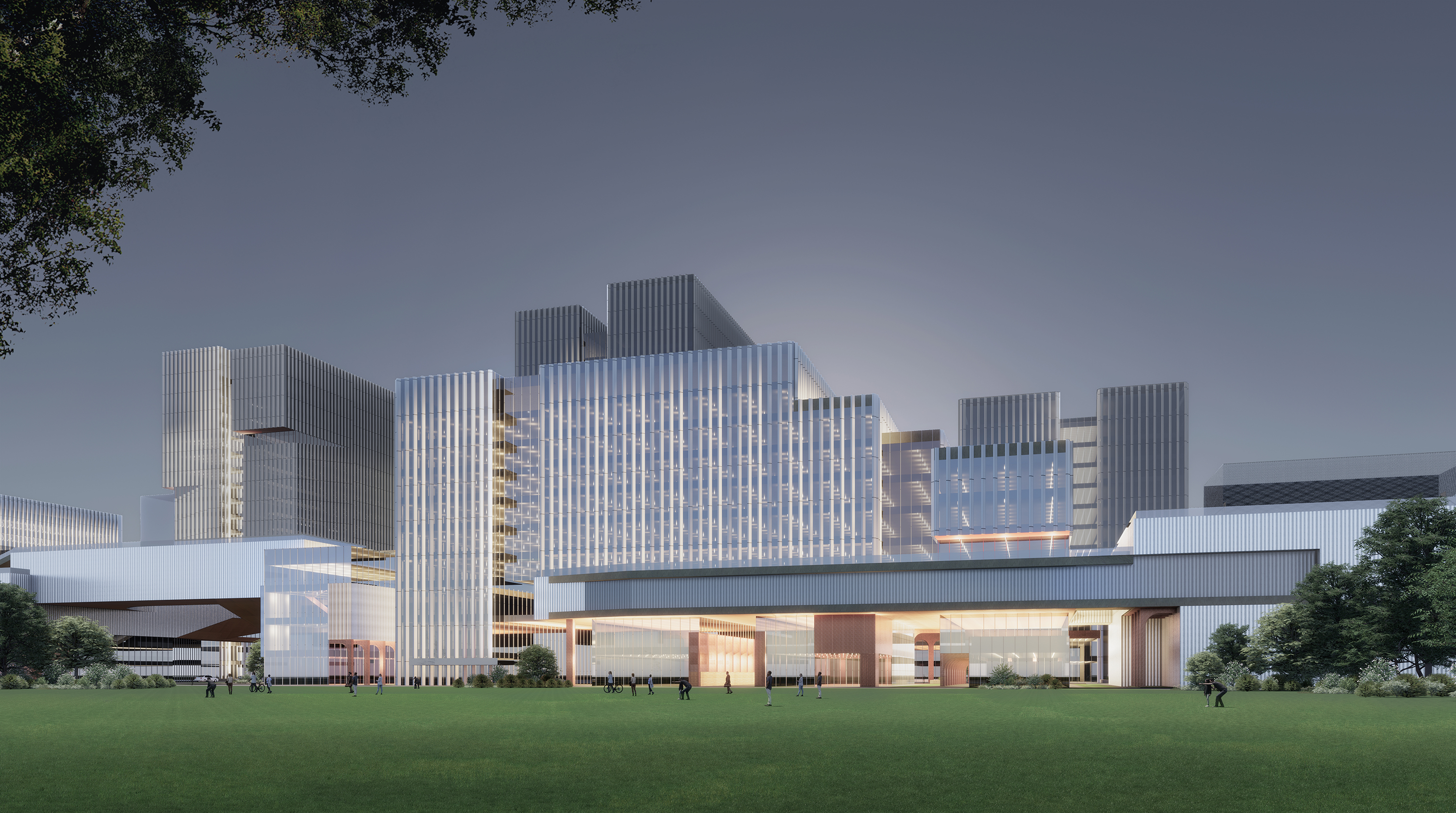
“厂区、园区+街区+社区”三类空间的竖向叠加,解放了传统园区的边界感,引入的街区将园区编织进城市系统,园区本身丰富的功能、业态,也使其成为一个激发创新的城市社区,从而实现了垂直复合新型园区的构想。
The vertical superposition of the three types of space liberates the sense of boundary of the traditional park. The introduced blocks weave the park into the urban system. The rich functions and business format of the park make itself an urban community that stimulates innovation, forming a new vertical park-composite.

至此,滁州科技谷构成了一个在小面积土地之上高密度垂直复合的空中园区和街区。底部的街巷式架空处理,将西侧的城市街道与东侧的城市绿化景观带以最便捷的方式进行链接,经过中间的园区院落也在地面上形成了一个良好的步行交流系统。科技产业的园区与城市界面悄然地渗透开放融合。园区的规划与城市的规划系统,用同样的道路、边界、开放空间等规划语言交织在了一起。
All in all, Chuzhou Technology Valley generates a density vertical composite sky park and block standing on a small plot. The lane-type overhead spatial strategy at the bottom connects the urban streets on the west side with the green landscape belt on the east side conveniently, forming a healthy walking system on the ground going through the middle park courtyard. With an open interface, this industry park penetrates into the city gradually. Also, through a similar planning strategy for road, border, and open space, the masterplan of the project interweave with the surrounding urban planning system.

园区的空间类型,即是小街区密路网的,又是大地块整体性的;既是院落的,又是高层建筑群的。在功能上,既是生活服务的,又是生产服务的;既是共享科学研究的,又是企业聚集的。多个状态被穿插叠加在了一起,在保障企业内容同时,突出引入了科学实验、中试研发、轻型制造的弹性使用可能,将制造与创造结合,并拉回到城市内部。
The morphology of the park is both a dense road network of small blocks, and an integration of large plots, is both an assemble of courtyards and a gathering of high-rise buildings. In function, it facilitates living ,production, sharing science research, and enterprise aggregation. Multiple volumes are interspersed and superimposed together. While ensuring the content of the enterprise, it highlights the possibility of flexible uses of scientific experiments, pilot research, and light manufacturing. Hence, the combination of manufacturing and creation is pulled back into the city.
这将给一个城市带来新的企业聚集方式和新的科研人才,他们在享受城市内部良好的配套同时,也将给城市带来新的活力、工作和生产成果。
This will bring a new way of gathering enterprises to the city and attract new scientific talents, who could enjoy the good supporting facilities, while generating new vitality, job opportunity and production value to the city.

完整项目信息
项目名称:滁州科技谷
项目地点:安徽省滁州市高铁新区
设计单位:产业园区研究中心
主创建筑师:廉毅锐
设计团队:李丹、陈又新
建成状态:方案阶段
设计时间:2021年
建筑面积:27.22万平方米
本文为产业园区研究中心推广文章,欢迎转发,禁止以有方编辑版本转载。
上一篇:超级规模城市更新:深圳中洲湾C Future City / Aedas
下一篇:2022月度焦点文章 | 行走中的建筑学年度盘点