
设计单位 天友设计集团
建设地点 北京大兴
建成时间 2021年5月(二次改造)
建设规模 400平方米
这个位于北京近郊村庄的项目直面中国农村原住民流失、乡村空心化的问题,旨在借助绿色的改造,提高居住舒适度,实现能源自给,同时引入创意办公等功能,实现功能转换与乡村复兴。
This village project in the suburbs of Beijing focuses on the problem of indigenous resident loss in rural areas of China. The overall goal is to improve residential comfortableness and realize energy self-sufficiency by means of green transformation, to introduce functions such as creative office, and to realize function conversion and rural revival.


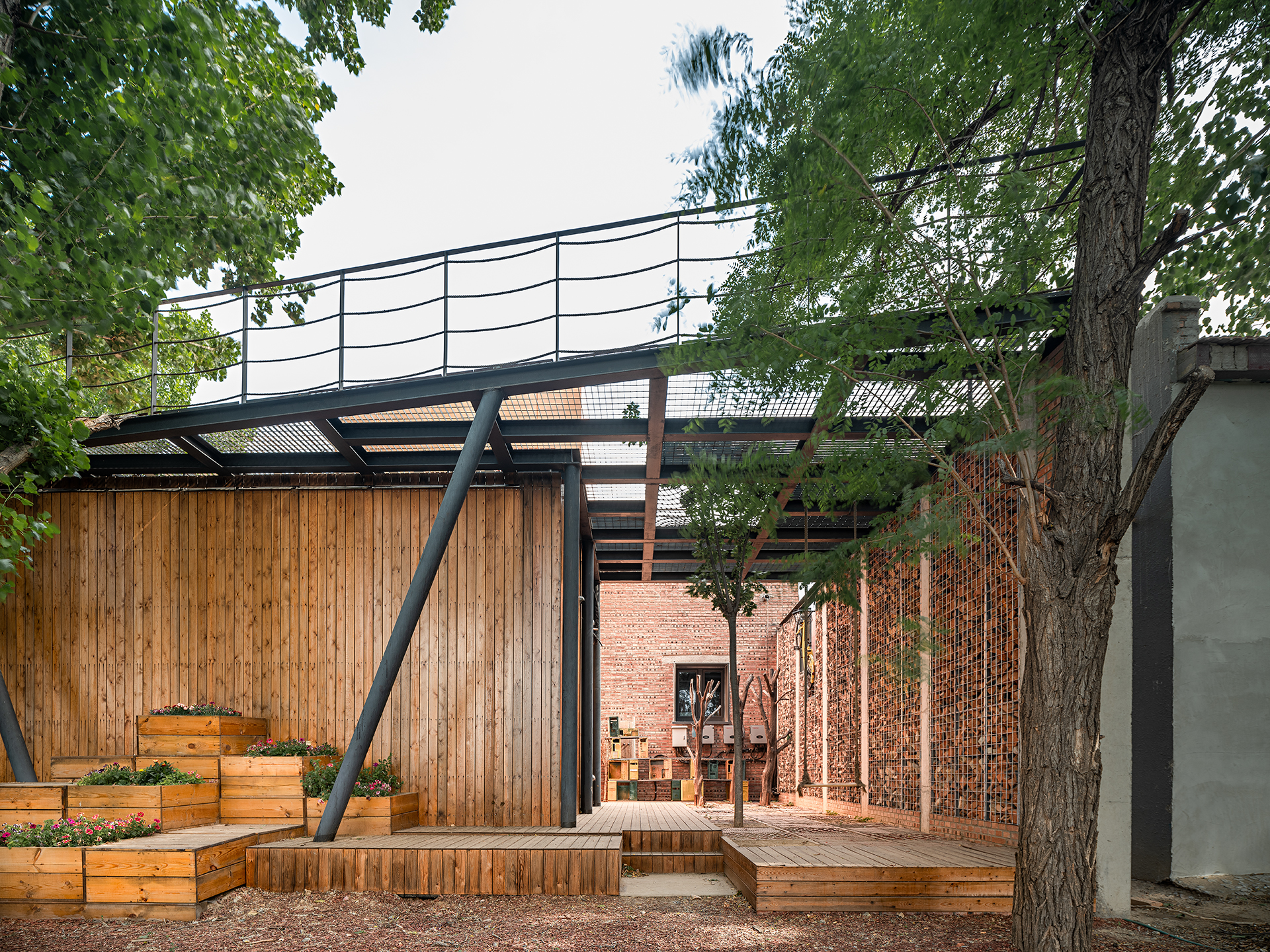
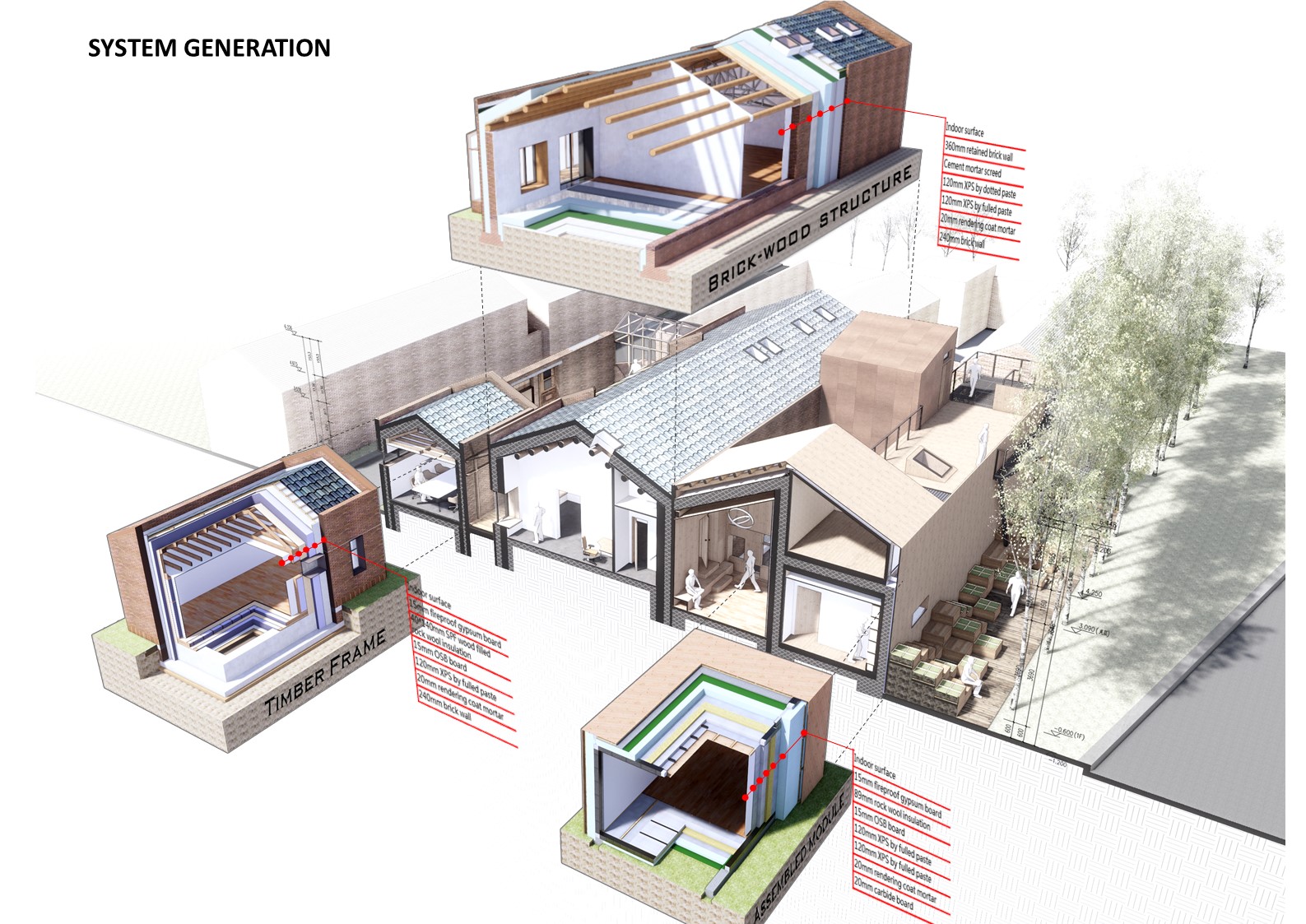
项目主要目标是探索装配式近零能耗农宅改造的技术可能性和建造的实现性。其实现途径是针对性地呼应乡村生态和寒冷气候,运用被动房(passive house)的技术策略来实现最小的能源需求,同时结合多种新型太阳能利用方式,实现近零能耗(nearly Zero Energy Building)。加建居住部分采用了工厂预制模块,在现场组装完成。
The main goal of the project is to explore the technical possibilities and construction realizability of assembled nearly zero energy rural house reconstruction. The approach to this goal is to respond to rural ecology and cold climate in a targeted manner, to use the technical strategy of passive house to achieve minimum energy requirement, and to combine multiple new solar energy utilization methods to achieve nearly zero energy building. Prefabricated modules are used for the added residential part, and are assembled on site.

PROCESS
超低能耗与模块装配式相结合的乡村近零能耗建筑
设计对适应单层院落布局的近零能耗建筑空间体系进行了改进。院落将建筑分为形体简单的三部分,并用被动式太阳房和楼梯间风塔连接气密性单元,实现增强冬季热辐射和引导过渡季自然通风的作用。
The building has improved the nearly zero energy building space system that is suitable for the single-story courtyard layout. The courtyard divides the building into three parts of simple shapes, and air-tightness units are connected with passive house and stairwell wind tower to enhance heat radiation in winter and guide the natural ventilation in transitional seasons.


建筑实验了一种低成本的装配式居住模块。采用轻钢体系与OSB板复合的模式,内填外贴两种保温材料,以稳定系统的传热系数和气密性。从结构到内装修的标准居住模块在工厂就已完成,三个模块在现场组合,成为一套功能完善的居住单元。坡屋面用天窗实现天然采光,同时利用光伏瓦提供电能。
The building is an experiment of low-cost assembled residential modules. The composite model is consisting of light steel system and OSB board, and two kinds of thermal insulation materials are filled inside and applied outside to ensure the system’s heat transfer coefficient and air tightness. The standard residential modules from the structure to the interior decoration are completed in the factory, and three modules are combined to a residential unit of complete functions on site. The sloping roof uses skylights to achieve natural lighting and uses photovoltaic tiles to provide electric energy.
运行阶段实现近零能耗,可最大限度减少空调、采暖、照明的能耗及碳排放。生产建造阶段调用乡土材料及当地的施工人员,以此减少运输施工的碳排放。通过上述减碳策略,每年可减少碳排放7.6吨。
The nearly zero energy consumption during the operation phase can minimize the energy consumption and carbon emission arising from air conditioning, heating and lighting. During the production and construction phase, rustic materials and local constructor are used to reduce carbon emission arising from transportation and construction. Through these carbon reduction strategies, the annual carbon emission can be reduced by 7.6 tons.
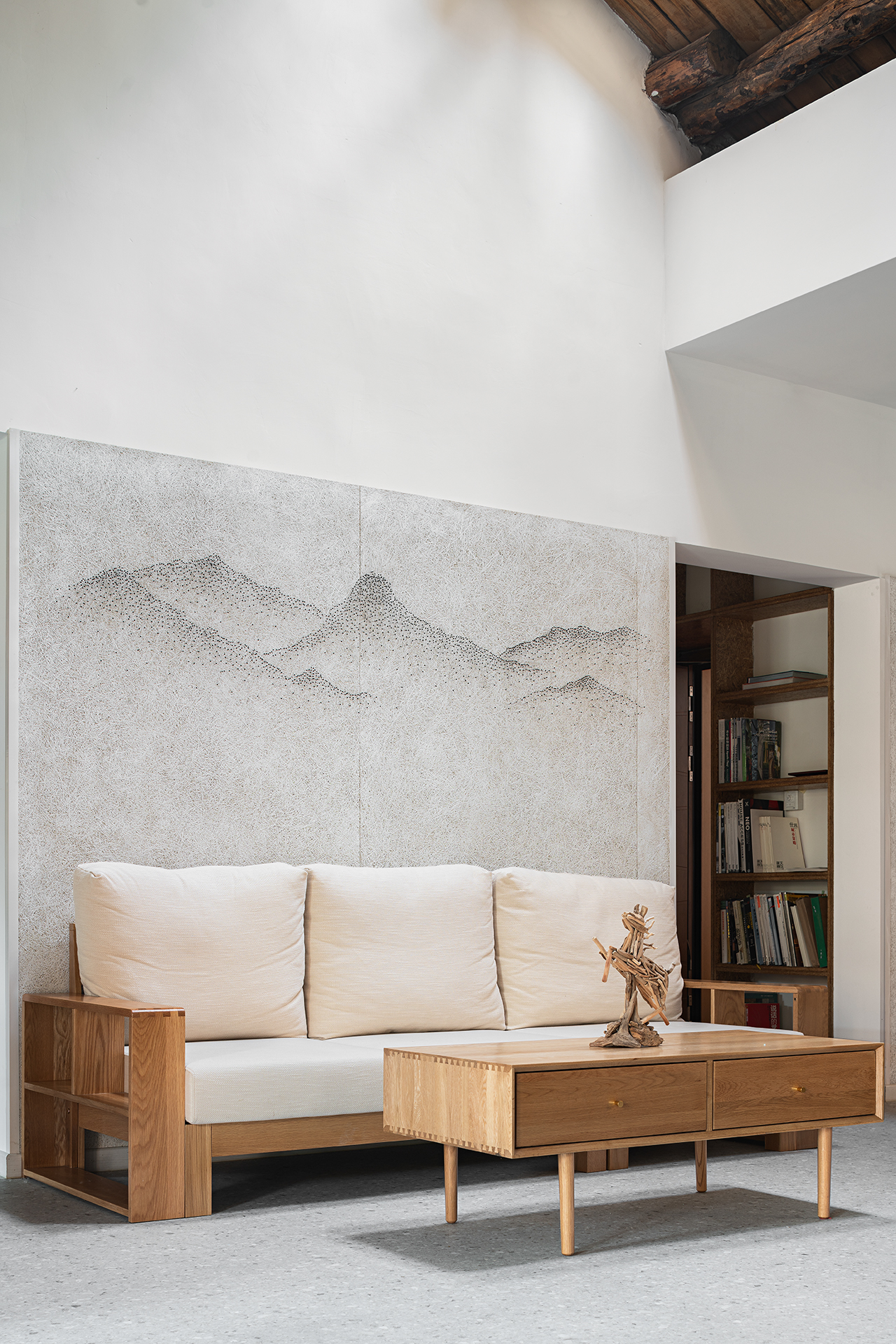



庭院和建筑立面集成了先进的绿色技术,书屋收集了近百本可持续建筑的图书,展厅集中展示了近零农宅的节能和建造技术,使之成为近零能耗农宅模式的展示与示范。
The courtyard and building facade integrate advanced green technology, the book room gathers nearly a hundred books on sustainable buildings, and the exhibition hall shows the energy-saving and construction technologies of nearly zero energy rural house, making it a showcase and demonstration of the nearly zero energy rural house model.



PLANET
减少生态影响,实现净零能耗的碳中和建筑
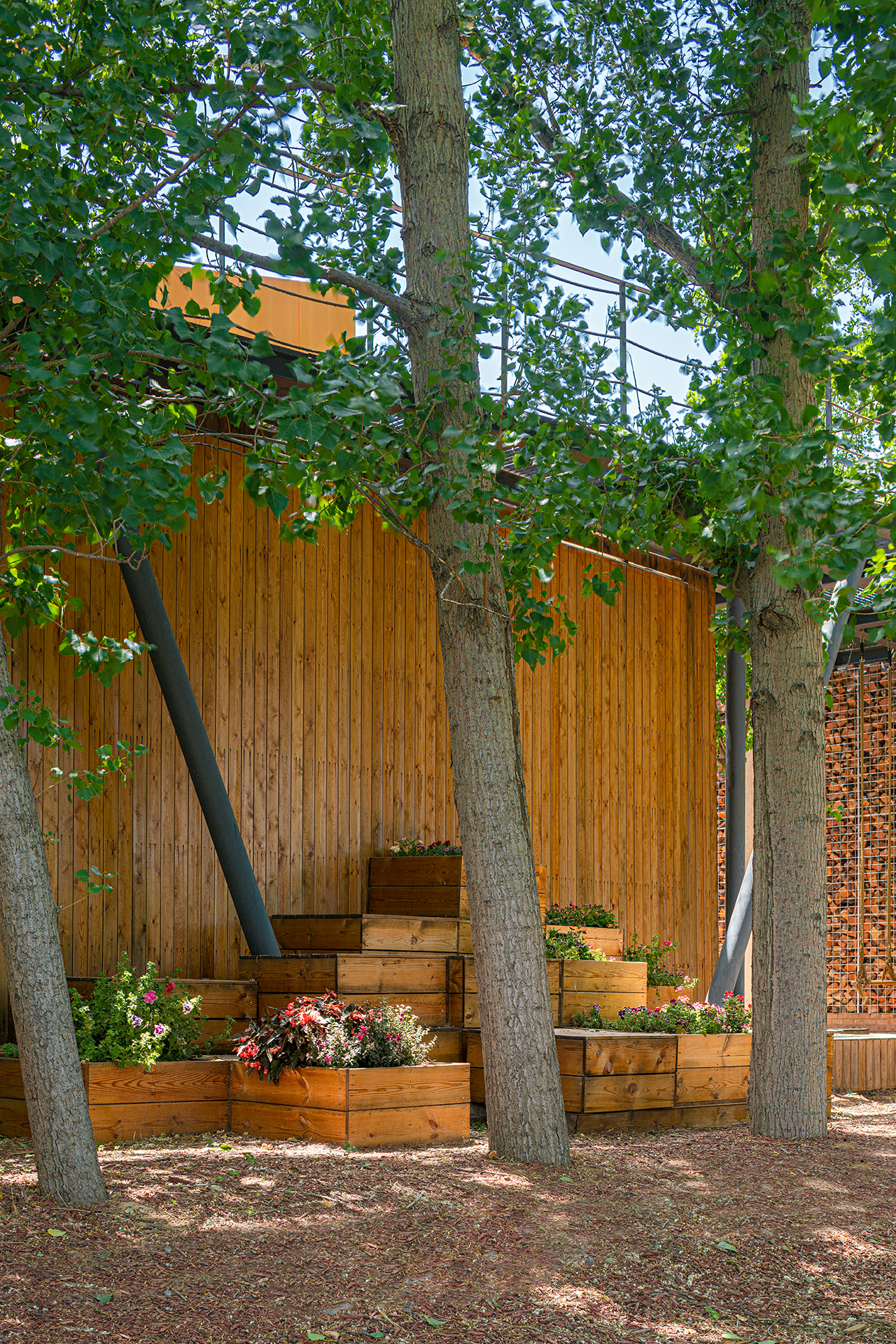
建筑延续了文脉中的庭院式布局,并设计为不同的绿色主题庭院。
The building keeps the courtyard layout in the local culture and is designed as different green themed courtyards.
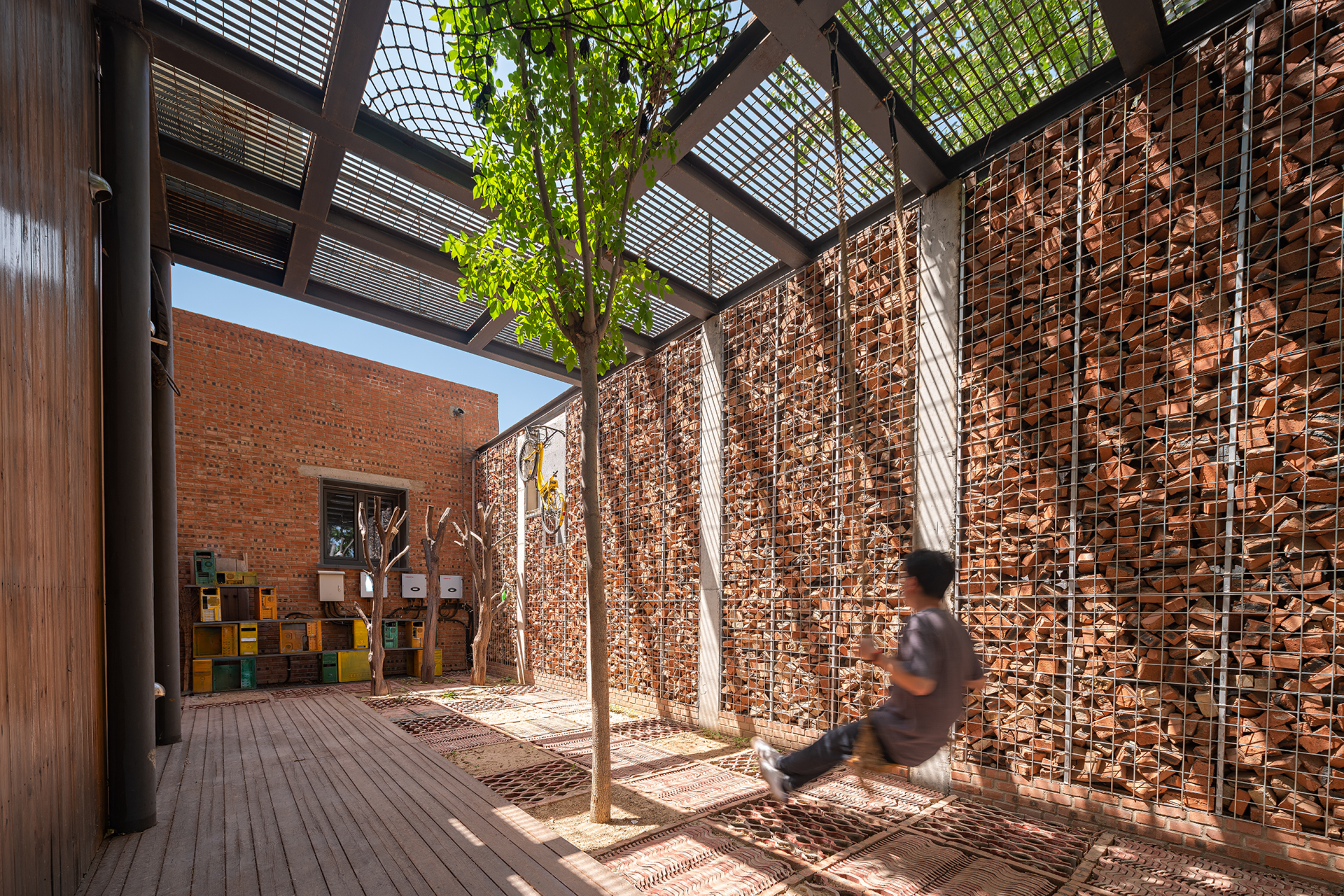
设计保持乡村生态和用地东侧北侧高大的杨树,结合杨树和村口绿地设计了阶梯状的树林菜园,并结合三个庭院的生态功能定义为不同的主题庭院——水庭院、太阳能庭院和废弃物装饰的零碳花园。南侧庭院中设置一个温室,种植由水培垂直农业组成的鱼菜共生系统。
The rural ecology and the tall poplars on the north and east sides of the plot are kept, and a ladder shaped vegetable garden is designed in combination with the existing poplars and the green space at the village entrance. Based on the ecological functions, the three courtyards are defined as different themed courtyards, respectively water courtyard, solar courtyard and zero carbon garden decorated with waste. A greenhouse is set in the south courtyard, where a fish and vegetable symbiosis system composed of vertical hydroponic plants is arranged.
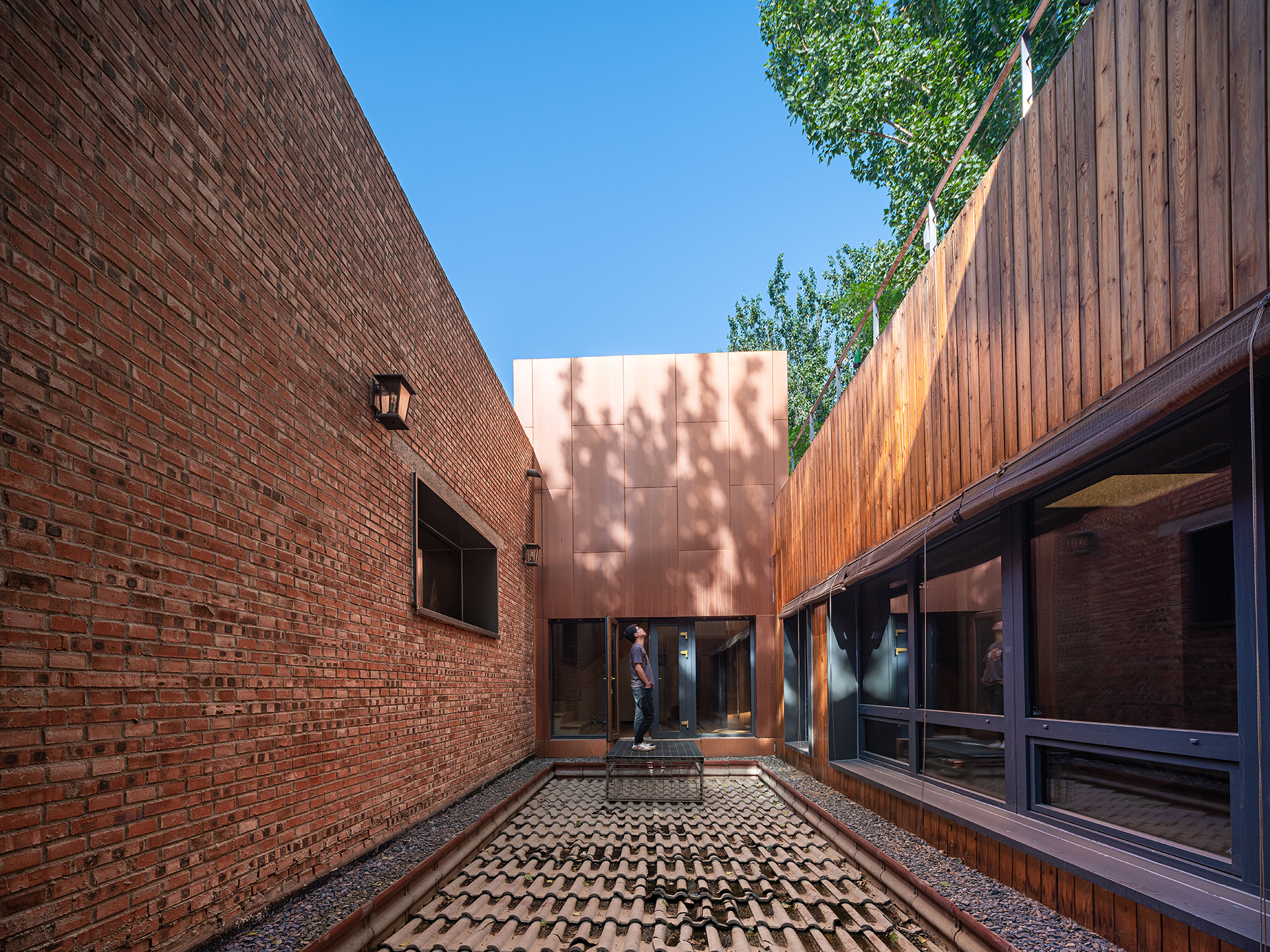

能源系统通过主被动节能技术的集成应用实现能源平衡。被动式节能从太阳辐射的利用出发,采用超级保温围护结构、气密性单元及无热桥设计,将冬季采暖需求控制在15瓦以下,单位面积总能耗为14.6kWh/m2.a。
The energy system realizes energy balance through the integrated application of active and passive energy-saving technologies. In terms of passive energy saving, it starts with the utilization of solar radiation, and uses super thermal insulation envelope, air-tightness units and a thermal-bridge-free design to control the heating demand in winter to below 15W, so that the total energy consumption per unit area is 14.6 kWh/m2.a.

主动式产能以太阳能光伏瓦和彩色薄膜光伏相结合的方式为建筑提供电能,太阳能热水系统为居住部分的厨房卫生间提供热水。建筑每年总能耗为5938.46千瓦时,年产能7130.70千瓦时,从而实现净零能耗。
In terms of active energy production, it combines photovoltaic tile and colored photovoltaic film to provide power for the building, and uses solar hot water system to provide hot water for the kitchen and bathroom of the residential part. The total annual energy consumption of the building is 5938.46 kWh, and the annual energy production capacity is 7130.70 kWh, so that net zero energy consumption is achieved.


PLACE
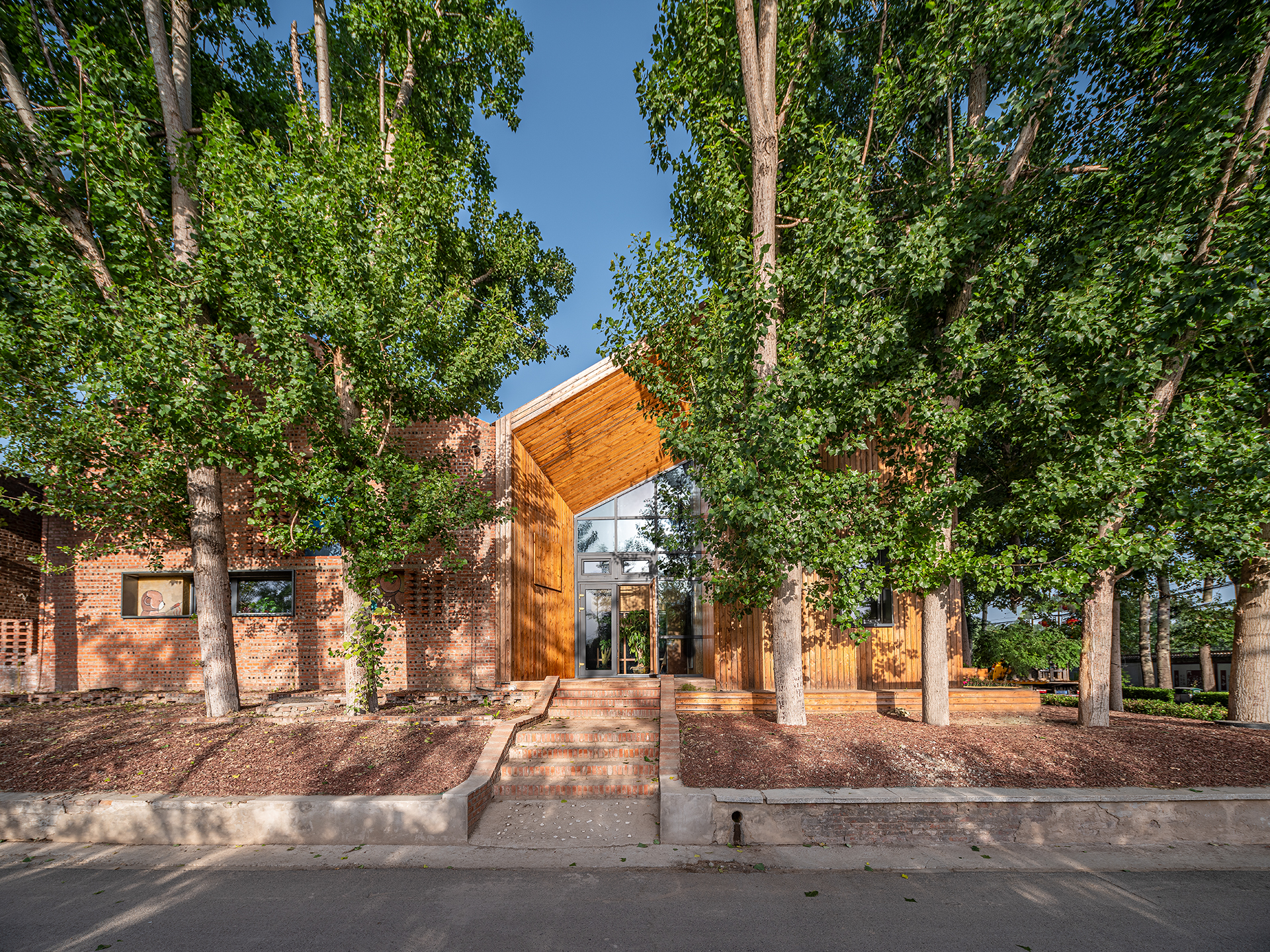
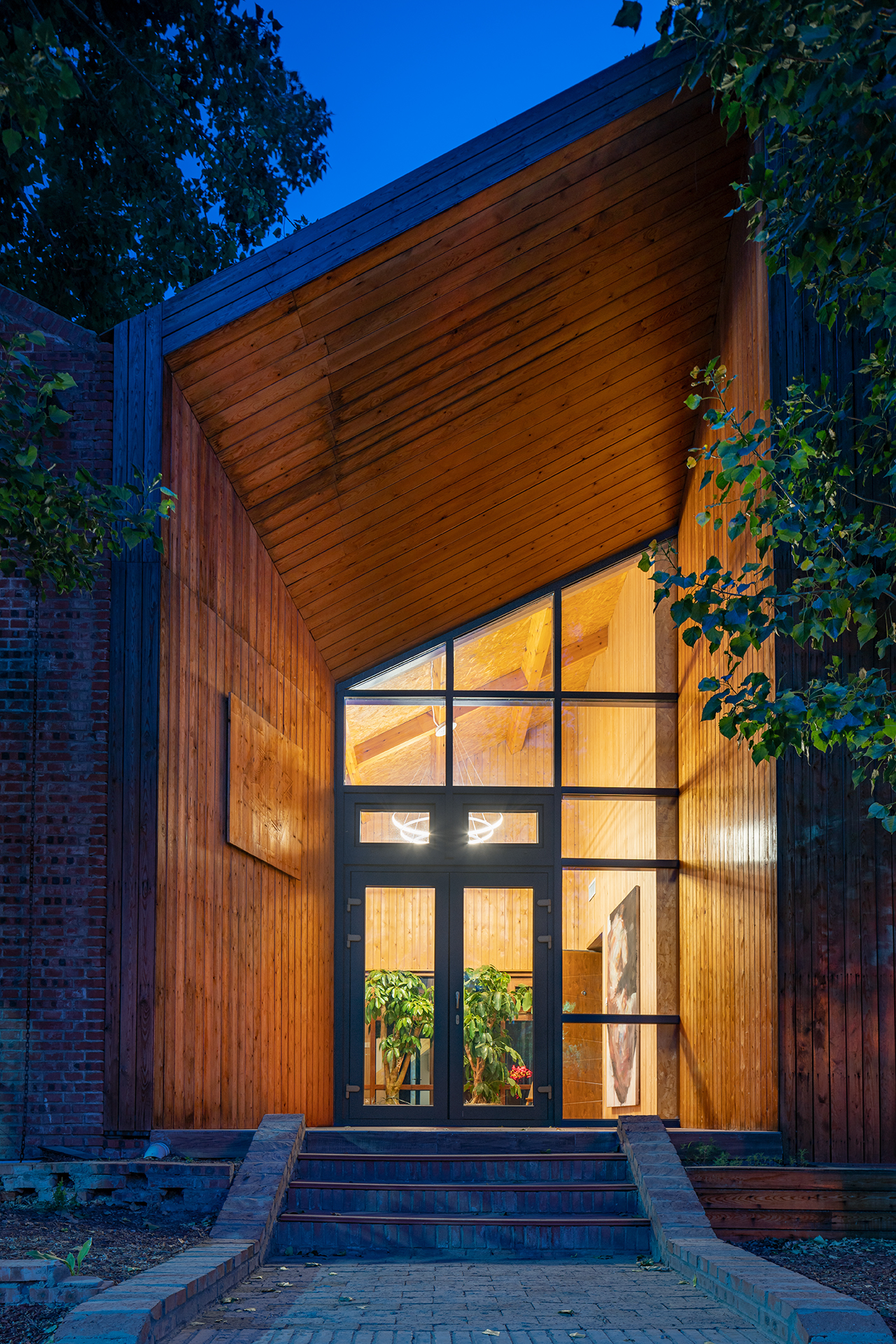
融入红砖乡土文脉与地域风貌的乡村建筑
建筑采用地域材料与砖木结构体系,尝试了砖混、轻木、模块装配不同的围护体系被动房构造,并结合红砖外墙形成夹心保温系统及光伏瓦的坡屋面系统,使立面表现出传统乡村建筑风貌。
The building uses regional materials and a brick-wood structure system, and tries passive house structures with different enclosure systems such as brick-wood system, timber-frame system and assembled module system. In addition, red brick exterior wall is used to form a sandwich thermal insulation system, and a sloping roof system with photovoltaic tiles is arranged, so that the facade shows the traditional rural architectural style.

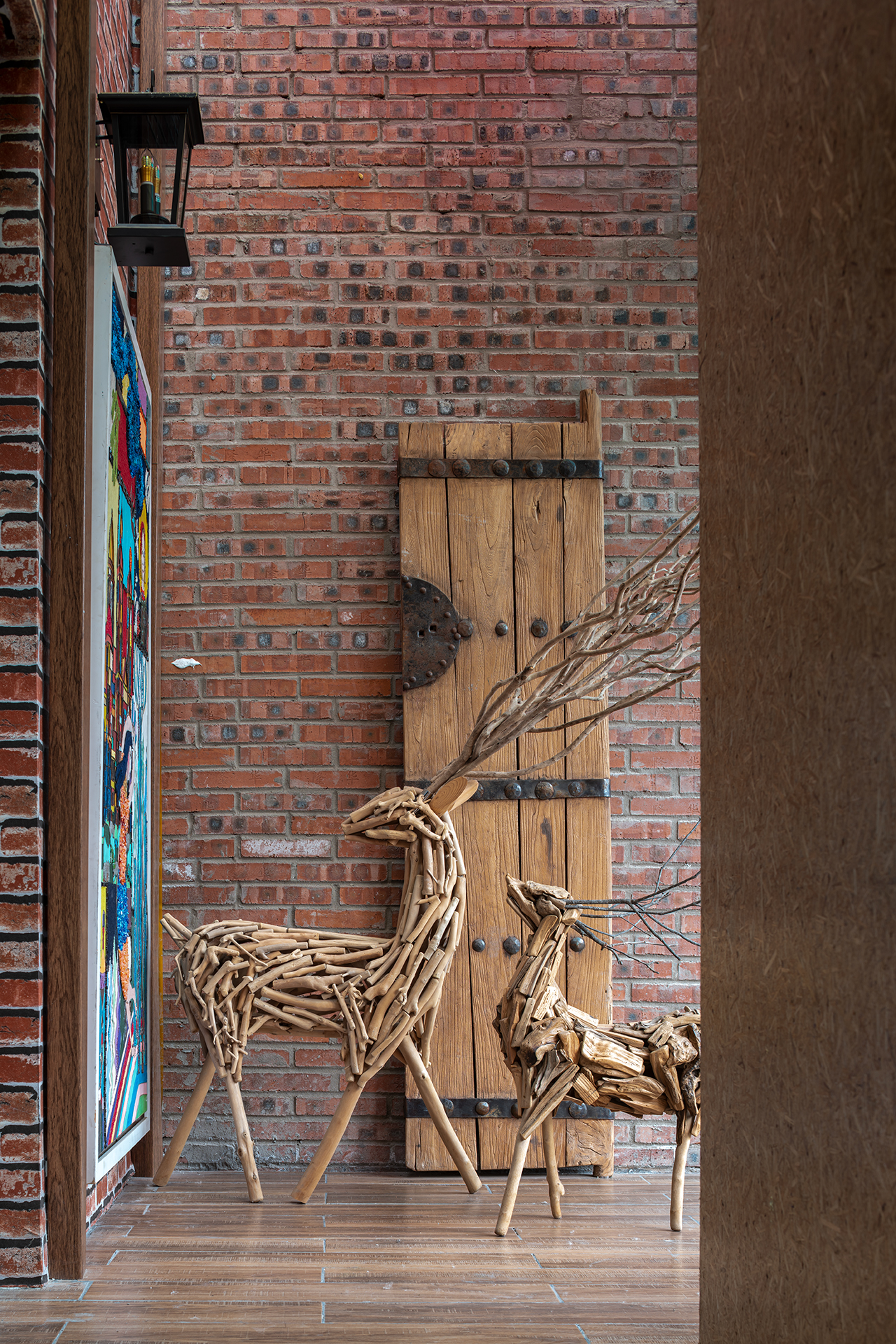
建筑使用拆除下来的废旧木窗、旧砖旧瓦等废弃材料,在零碳花园等景观中将其设计为艺术化的装置。建筑还利用了既有旧建筑,加建的部分采用了可循环利用的模块装配式,以及可循环材料的轻木结构,实现最小化及循环化的资源利用。
Abandoned materials such as removed wooden window, used bricks and tiles are designed to artistic devices in the zero carbon garden. The building makes use of the existing old building. The added parts adopt a timber-frame system with recyclable materials and a assembled module system with recyclable use to achieve minimization and recycling of resource utilization.
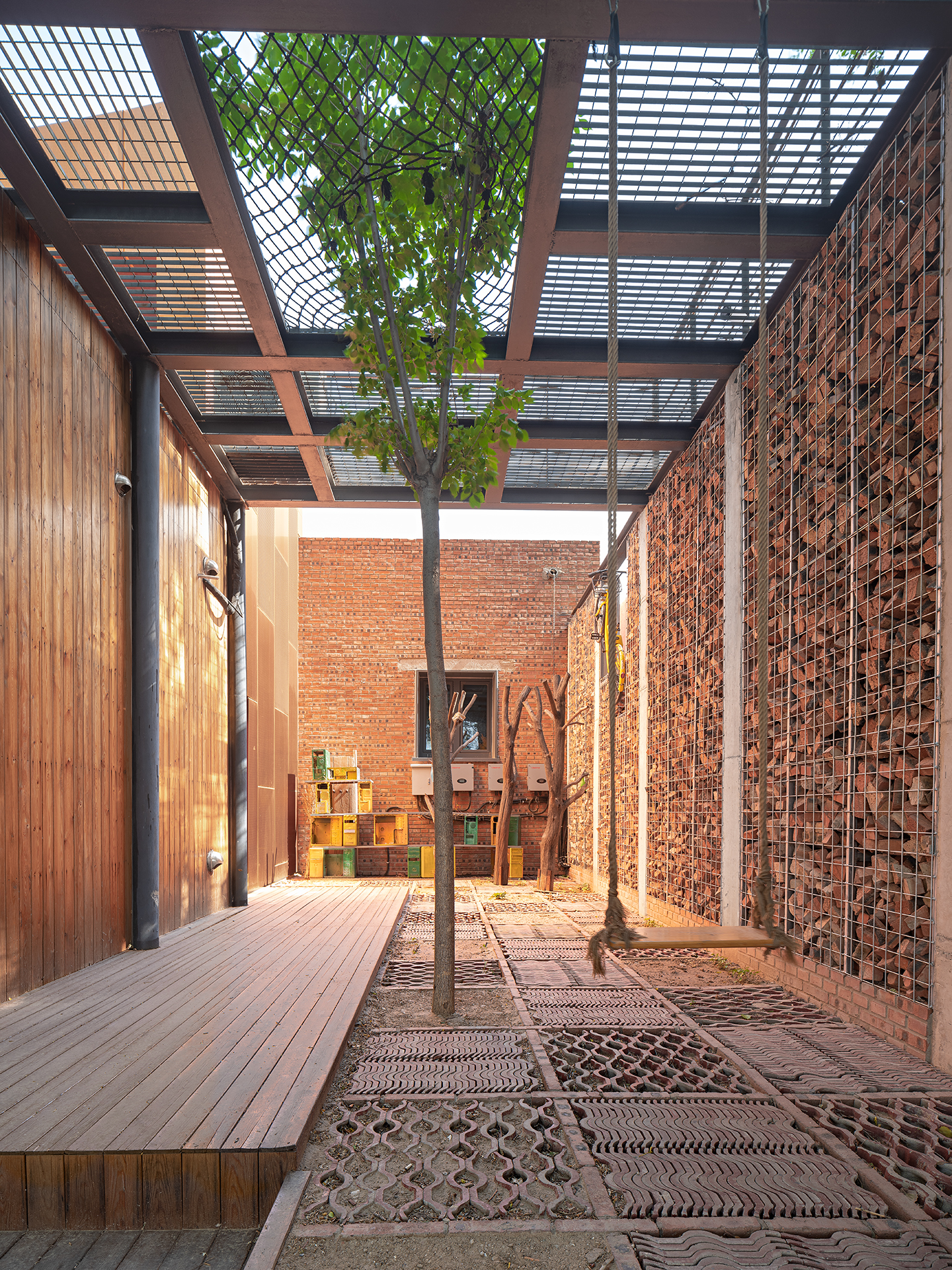
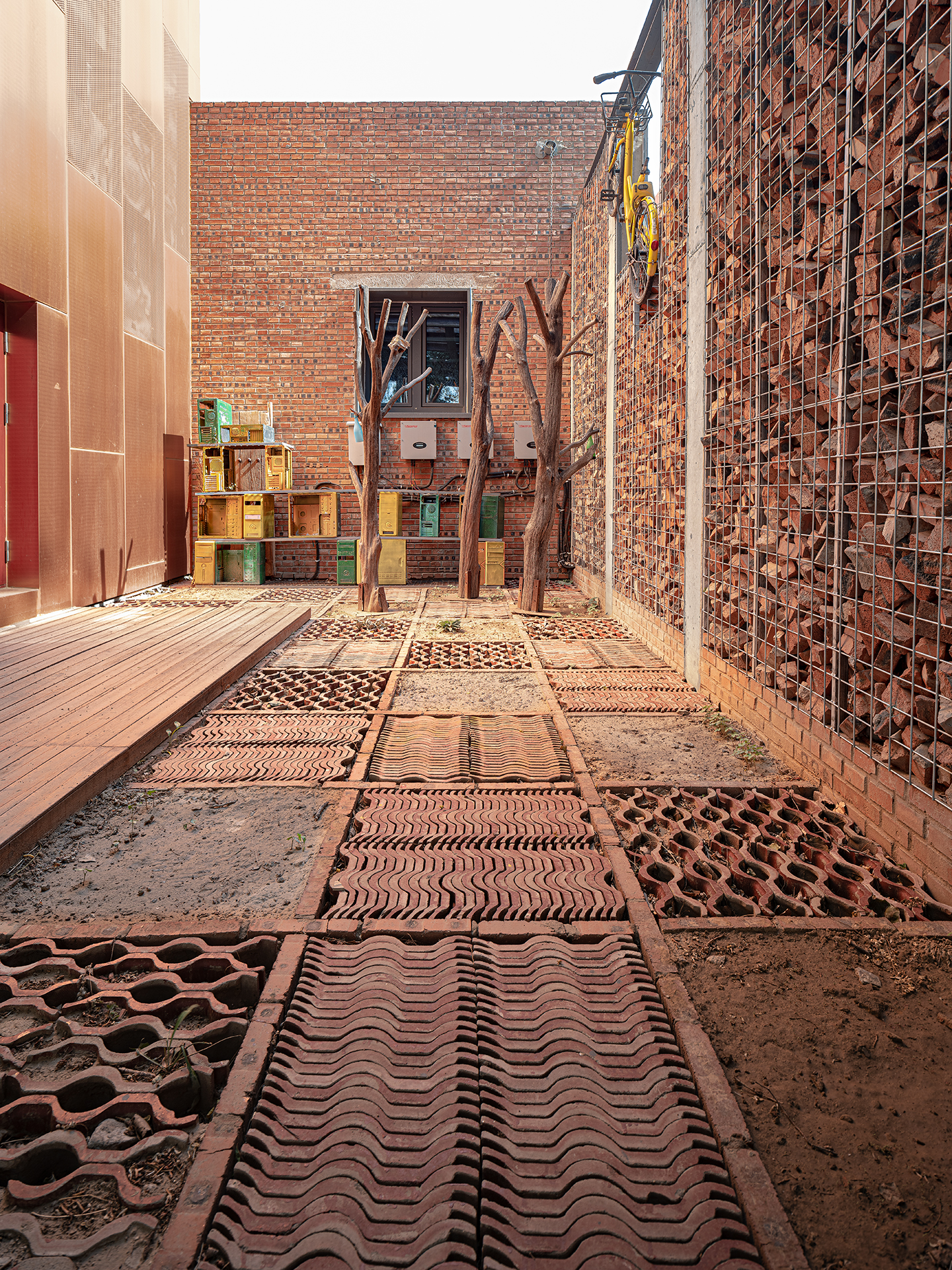


原有建筑周边种满了茂密高大的杨树,北侧的杨树林下贴着建筑设置了覆土的模块菜园,庭院中增加了垂直绿化,温室花房中养殖了鱼菜共生的垂直农业,通过这些策略增加碳汇。
From the perspective of carbon sink, the surrounding area of the original building is full of lush and tall poplars, and modular vegetable boxes filled with soil is set under the poplars and close to the building on the north side. Besides, vertical greening is added to the courtyard, and vertical agriculture with aquaponics is set in the greenhouse. By means of these strategies, carbon sinks are increased.


设计图纸 ▽
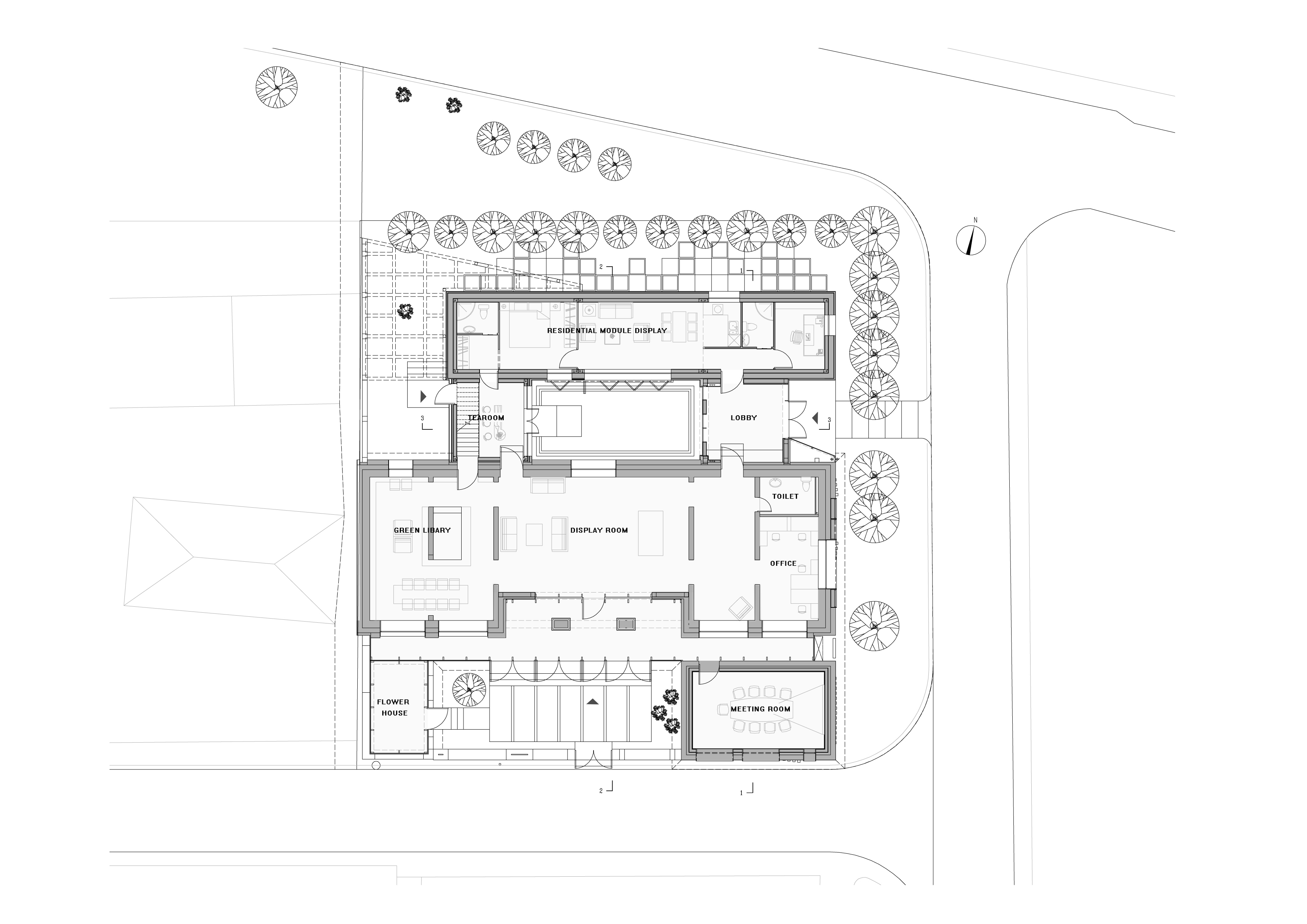
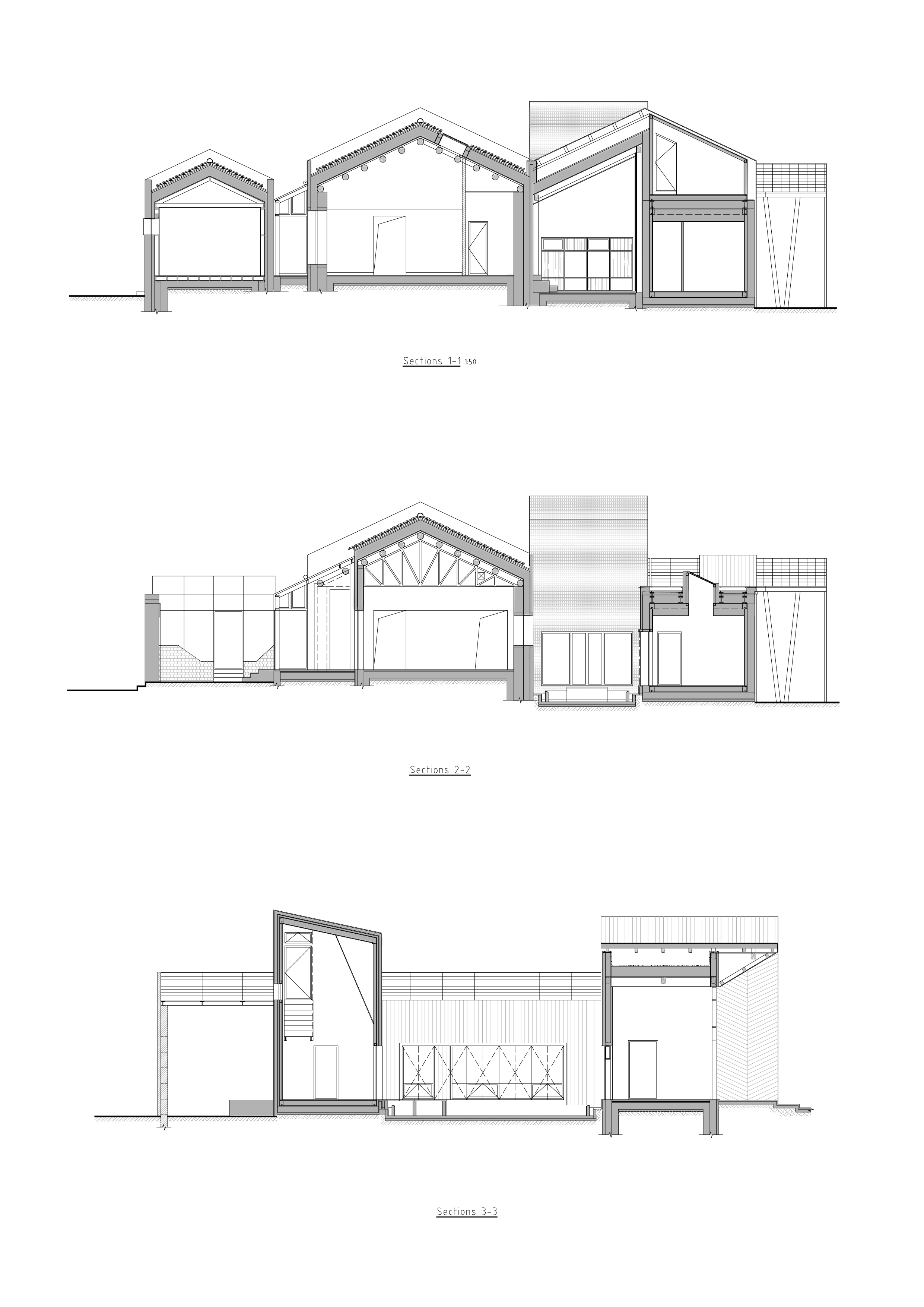
完整项目信息
项目名称:天友·零舍
建设单位:天友设计集团
项目类型:近零能耗乡居改造
建设规模:400平方米
建设地点:北京大兴区
项目策划:天友设计集团、天津大学建筑学院
服务模式:EPC全流程管理模式,天友实现从“设计—施工—运营”全流程、一体化服务
建筑师:任军、郭润博、邸扬、姜楠
结构师:于学增
设备师:刘冰、韩帅、刘卫
项目管理:张宝军、陆晓涛、郝林冲、肖荣彦
施工单位:北方国兴
施工管理:中建六局
摄影:心造文化
版权声明:本文由天友设计集团授权发布。欢迎转发,禁止以有方编辑版本转载。
投稿邮箱:media@archiposition.com
上一篇:重庆消费品研究院办公室:“中介空间”室内化 / 植田建筑工作室
下一篇:夏末秋初,住进山里